A novel TALE nuclease scaffold enables high genome editing activity in combination with low toxicity
- PMID: 21813459
- PMCID: PMC3241638
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkr597
A novel TALE nuclease scaffold enables high genome editing activity in combination with low toxicity
Abstract
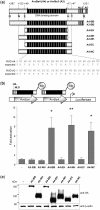
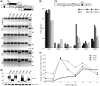
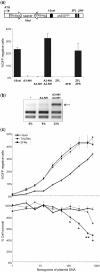
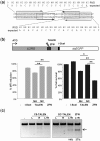
Sequence-specific nucleases represent valuable tools for precision genome engineering. Traditionally, zinc-finger nucleases (ZFNs) and meganucleases have been used to specifically edit complex genomes. Recently, the DNA binding domains of transcription activator-like effectors (TALEs) from the bacterial pathogen Xanthomonas have been harnessed to direct nuclease domains to desired genomic loci. In this study, we tested a panel of truncation variants based on the TALE protein AvrBs4 to identify TALE nucleases (TALENs) with high DNA cleavage activity. The most favorable parameters for efficient DNA cleavage were determined in vitro and in cellular reporter assays. TALENs were designed to disrupt an EGFP marker gene and the human loci CCR5 and IL2RG. Gene editing was achieved in up to 45% of transfected cells. A side-by-side comparison with ZFNs showed similar gene disruption activities by TALENs but significantly reduced nuclease-associated cytotoxicities. Moreover, the CCR5-specific TALEN revealed only minimal off-target activity at the CCR2 locus as compared to the corresponding ZFN, suggesting that the TALEN platform enables the design of nucleases with single-nucleotide specificity. The combination of high nuclease activity with reduced cytotoxicity and the simple design process marks TALENs as a key technology platform for targeted modifications of complex genomes.
Figures
Similar articles
-
TALENs facilitate targeted genome editing in human cells with high specificity and low cytotoxicity.Nucleic Acids Res. 2014 Jun;42(10):6762-73. doi: 10.1093/nar/gku305. Epub 2014 May 3. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014. PMID: 24792154 Free PMC article.
-
Origins of Programmable Nucleases for Genome Engineering.J Mol Biol. 2016 Feb 27;428(5 Pt B):963-89. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2015.10.014. Epub 2015 Oct 23. J Mol Biol. 2016. PMID: 26506267 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A suicidal zinc finger nuclease expression coupled with a surrogate reporter for efficient genome engineering.Biotechnol Lett. 2015 Feb;37(2):299-305. doi: 10.1007/s10529-014-1690-3. Epub 2014 Oct 4. Biotechnol Lett. 2015. PMID: 25280729
-
TALENs: a widely applicable technology for targeted genome editing.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2013 Jan;14(1):49-55. doi: 10.1038/nrm3486. Epub 2012 Nov 21. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2013. PMID: 23169466 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transcription activator-like effector nucleases (TALENs): a highly efficient and versatile tool for genome editing.Biotechnol Bioeng. 2013 Jul;110(7):1811-21. doi: 10.1002/bit.24890. Epub 2013 Apr 7. Biotechnol Bioeng. 2013. PMID: 23508559 Review.
Cited by
-
A library of TAL effector nucleases spanning the human genome.Nat Biotechnol. 2013 Mar;31(3):251-8. doi: 10.1038/nbt.2517. Epub 2013 Feb 17. Nat Biotechnol. 2013. PMID: 23417094
-
FLASH assembly of TALENs for high-throughput genome editing.Nat Biotechnol. 2012 May;30(5):460-5. doi: 10.1038/nbt.2170. Nat Biotechnol. 2012. PMID: 22484455 Free PMC article.
-
Use of genome-editing tools to treat sickle cell disease.Hum Genet. 2016 Sep;135(9):1011-28. doi: 10.1007/s00439-016-1688-0. Epub 2016 Jun 1. Hum Genet. 2016. PMID: 27250347 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Utilization of TALEN and CRISPR/Cas9 technologies for gene targeting and modification.Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2015 Aug;240(8):1065-70. doi: 10.1177/1535370215584932. Epub 2015 May 7. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2015. PMID: 25956682 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeted In Situ Gene Correction of Dysfunctional APOE Alleles to Produce Atheroprotective Plasma ApoE3 Protein.Cardiol Res Pract. 2012;2012:148796. doi: 10.1155/2012/148796. Epub 2012 May 7. Cardiol Res Pract. 2012. PMID: 22645694 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Urnov FD, Rebar EJ, Holmes MC, Zhang HS, Gregory PD. Genome editing with engineered zinc finger nucleases. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2010;11:636–646. - PubMed
-
- Händel EM, Cathomen T. Zinc-finger nuclease based genome surgery: it's all about specificity. Curr. Gene. Ther. 2011;11:28–37. - PubMed
-
- Shukla VK, Doyon Y, Miller JC, DeKelver RC, Moehle EA, Worden SE, Mitchell JC, Arnold NL, Gopalan S, Meng X, et al. Precise genome modification in the crop species Zea mays using zinc-finger nucleases. Nature. 2009;459:437–441. - PubMed
-
- Bibikova M, Beumer K, Trautman JK, Carroll D. Enhancing gene targeting with designed zinc finger nucleases. Science. 2003;300:764. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

