Nucleoside modifications in RNA limit activation of 2'-5'-oligoadenylate synthetase and increase resistance to cleavage by RNase L
- PMID: 21813458
- PMCID: PMC3241635
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkr586
Nucleoside modifications in RNA limit activation of 2'-5'-oligoadenylate synthetase and increase resistance to cleavage by RNase L
Abstract
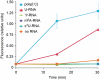
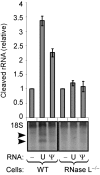
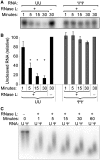
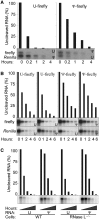
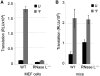
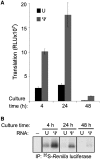
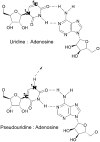
The interferon-induced enzymes 2'-5'-oligoadenylate synthetase (OAS) and RNase L are key components of innate immunity involved in sensory and effector functions following viral infections. Upon binding target RNA, OAS is activated to produce 2'-5'-linked oligoadenylates (2-5A) that activate RNase L, which then cleaves single-stranded self and non-self RNA. Modified nucleosides that are present in cellular transcripts have been shown to suppress activation of several RNA sensors. Here, we demonstrate that in vitro transcribed, unmodified RNA activates OAS, induces RNase L-mediated ribosomal RNA (rRNA) cleavage and is rapidly cleaved by RNase L. In contrast, RNA containing modified nucleosides activates OAS less efficiently and induces limited rRNA cleavage. Nucleoside modifications also make RNA resistant to cleavage by RNase L. Examining translation in RNase L(-/-) cells and mice confirmed that RNase L activity reduces translation of unmodified mRNA, which is not observed with modified mRNA. Additionally, mRNA containing the nucleoside modification pseudouridine is translated longer and has an extended half-life. The observation that modified nucleosides in RNA reduce 2-5A pathway activation joins OAS and RNase L to the list of RNA sensors and effectors whose functions are limited when RNA is modified, confirming the role of nucleoside modifications in suppressing immune recognition of RNA.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Activation of RNase L in Egyptian Rousette Bat-Derived RoNi/7 Cells Is Dependent Primarily on OAS3 and Independent of MAVS Signaling.mBio. 2019 Nov 12;10(6):e02414-19. doi: 10.1128/mBio.02414-19. mBio. 2019. PMID: 31719180 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of RNase L by Murine Coronavirus in Myeloid Cells Is Dependent on Basal Oas Gene Expression and Independent of Virus-Induced Interferon.J Virol. 2016 Jan 6;90(6):3160-72. doi: 10.1128/JVI.03036-15. J Virol. 2016. PMID: 26739051 Free PMC article.
-
Rotavirus Controls Activation of the 2'-5'-Oligoadenylate Synthetase/RNase L Pathway Using at Least Two Distinct Mechanisms.J Virol. 2015 Dec;89(23):12145-53. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01874-15. Epub 2015 Sep 23. J Virol. 2015. PMID: 26401041 Free PMC article.
-
New insights into the role of RNase L in innate immunity.J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2011 Jan;31(1):49-57. doi: 10.1089/jir.2010.0120. Epub 2010 Dec 29. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2011. PMID: 21190483 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Viral phosphodiesterases that antagonize double-stranded RNA signaling to RNase L by degrading 2-5A.J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2014 Jun;34(6):455-63. doi: 10.1089/jir.2014.0007. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2014. PMID: 24905202 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Therapeutic siRNA: state of the art.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2020 Jun 19;5(1):101. doi: 10.1038/s41392-020-0207-x. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2020. PMID: 32561705 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Semi-quantitative detection of pseudouridine modifications and type I/II hypermodifications in human mRNAs using direct long-read sequencing.Nat Commun. 2023 Jan 19;14(1):334. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-35858-w. Nat Commun. 2023. PMID: 36658122 Free PMC article.
-
Nanobiotechnology-Enabled mRNA Stabilization.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Feb 12;15(2):620. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15020620. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 36839942 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The regulation of antiviral innate immunity through non-m6A RNA modifications.Front Immunol. 2023 Oct 17;14:1286820. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1286820. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37915585 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RNA regulation of the antiviral protein 2'-5'-oligoadenylate synthetase.Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2019 Jul;10(4):e1534. doi: 10.1002/wrna.1534. Epub 2019 Apr 15. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2019. PMID: 30989826 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Lane BG. Historical perspective on RNA nucleoside modifications. In: Grosjean H, Benne R, editors. Modification and Editing of RNA. Washington DC: ASM Press; 1998. pp. 1–20.
-
- Charette M, Gray MW. Pseudouridine in RNA: what, where, how, and why. IUBMB Life. 2000;49:341–351. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01CA044059/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R42HL87688/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R42 HL087688-03/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R42 HL087688-02/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32DK07748/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01AI50484/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01NS029331/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA044059/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- T32GM07229/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- T32RR007063/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R42 HL087688-01/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R21DE019059/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

