Genome-wide association study identifies candidate genes for Parkinson's disease in an Ashkenazi Jewish population
- PMID: 21812969
- PMCID: PMC3166909
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2350-12-104
Genome-wide association study identifies candidate genes for Parkinson's disease in an Ashkenazi Jewish population
Abstract
Background: To date, nine Parkinson disease (PD) genome-wide association studies in North American, European and Asian populations have been published. The majority of studies have confirmed the association of the previously identified genetic risk factors, SNCA and MAPT, and two studies have identified three new PD susceptibility loci/genes (PARK16, BST1 and HLA-DRB5). In a recent meta-analysis of datasets from five of the published PD GWAS an additional 6 novel candidate genes (SYT11, ACMSD, STK39, MCCC1/LAMP3, GAK and CCDC62/HIP1R) were identified. Collectively the associations identified in these GWAS account for only a small proportion of the estimated total heritability of PD suggesting that an 'unknown' component of the genetic architecture of PD remains to be identified.
Methods: We applied a GWAS approach to a relatively homogeneous Ashkenazi Jewish (AJ) population from New York to search for both 'rare' and 'common' genetic variants that confer risk of PD by examining any SNPs with allele frequencies exceeding 2%. We have focused on a genetic isolate, the AJ population, as a discovery dataset since this cohort has a higher sharing of genetic background and historically experienced a significant bottleneck. We also conducted a replication study using two publicly available datasets from dbGaP. The joint analysis dataset had a combined sample size of 2,050 cases and 1,836 controls.
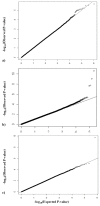
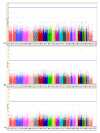
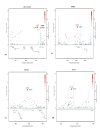
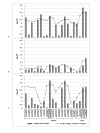
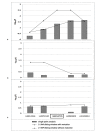
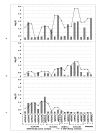
Results: We identified the top 57 SNPs showing the strongest evidence of association in the AJ dataset (p < 9.9 × 10(-5)). Six SNPs located within gene regions had positive signals in at least one other independent dbGaP dataset: LOC100505836 (Chr3p24), LOC153328/SLC25A48 (Chr5q31.1), UNC13B (9p13.3), SLCO3A1(15q26.1), WNT3(17q21.3) and NSF (17q21.3). We also replicated published associations for the gene regions SNCA (Chr4q21; rs3775442, p = 0.037), PARK16 (Chr1q32.1; rs823114 (NUCKS1), p = 6.12 × 10(-4)), BST1 (Chr4p15; rs12502586, p = 0.027), STK39 (Chr2q24.3; rs3754775, p = 0.005), and LAMP3 (Chr3; rs12493050, p = 0.005) in addition to the two most common PD susceptibility genes in the AJ population LRRK2 (Chr12q12; rs34637584, p = 1.56 × 10(-4)) and GBA (Chr1q21; rs2990245, p = 0.015).
Conclusions: We have demonstrated the utility of the AJ dataset in PD candidate gene and SNP discovery both by replication in dbGaP datasets with a larger sample size and by replicating association of previously identified PD susceptibility genes. Our GWAS study has identified candidate gene regions for PD that are implicated in neuronal signalling and the dopamine pathway.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Association analysis of STK39, MCCC1/LAMP3 and sporadic PD in the Chinese Han population.Neurosci Lett. 2014 Apr 30;566:206-9. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2014.03.007. Epub 2014 Mar 12. Neurosci Lett. 2014. PMID: 24631562
-
Imputation of sequence variants for identification of genetic risks for Parkinson's disease: a meta-analysis of genome-wide association studies.Lancet. 2011 Feb 19;377(9766):641-9. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(10)62345-8. Epub 2011 Feb 1. Lancet. 2011. PMID: 21292315 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic association study between STK39 and CCDC62/HIP1R and Parkinson's disease.PLoS One. 2013 Nov 27;8(11):e79211. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0079211. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24312176 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic variants in sporadic Parkinson's disease: East vs West.Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2012 Jan;18 Suppl 1:S63-5. doi: 10.1016/S1353-8020(11)70021-9. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2012. PMID: 22166457 Review.
-
Genetics of Parkinson's disease and essential tremor.Curr Opin Neurol. 2011 Aug;24(4):318-23. doi: 10.1097/WCO.0b013e3283484b87. Curr Opin Neurol. 2011. PMID: 21734494 Review.
Cited by
-
A customized high-resolution array-comparative genomic hybridization to explore copy number variations in Parkinson's disease.Neurogenetics. 2016 Oct;17(4):233-244. doi: 10.1007/s10048-016-0494-0. Epub 2016 Sep 17. Neurogenetics. 2016. PMID: 27637465 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic variants associated with breast cancer risk for Ashkenazi Jewish women with strong family histories but no identifiable BRCA1/2 mutation.Hum Genet. 2013 May;132(5):523-36. doi: 10.1007/s00439-013-1269-4. Epub 2013 Jan 25. Hum Genet. 2013. PMID: 23354978 Free PMC article.
-
Systematic Surveys of Iron Homeostasis Mechanisms Reveal Ferritin Superfamily and Nucleotide Surveillance Regulation to be Modified by PINK1 Absence.Cells. 2020 Oct 2;9(10):2229. doi: 10.3390/cells9102229. Cells. 2020. PMID: 33023155 Free PMC article.
-
Mitophagy and cGAS-STING crosstalk in neuroinflammation.Acta Pharm Sin B. 2024 Aug;14(8):3327-3361. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2024.05.012. Epub 2024 May 13. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2024. PMID: 39220869 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Association studies of sporadic Parkinson's disease in the genomic era.Curr Genomics. 2014 Feb;15(1):2-10. doi: 10.2174/1389202914666131210212745. Curr Genomics. 2014. PMID: 24653658 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Polymeropoulos MH, Lavedan C, Leroy E, Ide SE, Dehejia A, Dutra A, Pike B, Root H, Rubenstein J, Boyer R, Stenroos ES, Chandrasekharappa S, Athanassiadou A, Papapetropoulos T, Johnson WG, Lazzarini AM, Duvoisin RC, Di Iorio G, Golbe LI, Nussbaum RL. Mutation in the alpha-synuclein gene identified in families with Parkinson's disease. Science. 1997;276(5321):2045–2047. doi: 10.1126/science.276.5321.2045. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Valente EM, Abou-Sleiman PM, Caputo V, Muqit MM, Harvey K, Gispert S, Ali Z, Del Turco D, Bentivoglio AR, Healy DG, Albanese A, Nussbaum R, Gonzalez-Maldonado R, Deller T, Salvi S, Cortelli P, Gilks WP, Latchman DS, Harvey RJ, Dallapiccola B, Auburger G, Wood NW. Hereditary early-onset Parkinson's disease caused by mutations in PINK1. Science. 2004;304(5674):1158–1160. doi: 10.1126/science.1096284. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bonifati V, Rizzu P, van Baren MJ, Schaap O, Breedveld GJ, Krieger E, Dekker MC, Squitieri F, Ibanez P, Joosse M, van Dongen JW, Vanacore N, van Swieten JC, Brice A, Meco G, van Duijn CM, Oostra BA, Heutink P. Mutations in the DJ-1 gene associated with autosomal recessive early-onset parkinsonism. Science. 2003;299(5604):256–259. doi: 10.1126/science.1077209. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Paisan-Ruiz C, Jain S, Evans EW, Gilks WP, Simon J, van der Brug M, Lopez de Munain A, Aparicio S, Gil AM, Khan N, Johnson J, Martinez JR, Nicholl D, Carrera IM, Pena AS, de Silva R, Lees A, Marti-Masso JF, Perez-Tur J, Wood NW, Singleton AB. Cloning of the gene containing mutations that cause PARK8-linked Parkinson's disease. Neuron. 2004;44(4):595–600. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2004.10.023. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

