Adolescent HIV/AIDS: Issues and challenges
- PMID: 21808429
- PMCID: PMC3140141
- DOI: 10.4103/0253-7184.68993
Adolescent HIV/AIDS: Issues and challenges
Abstract
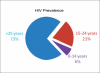
Adolescence (10-19 years) is a phase of physical growth and development accompanied by sexual maturation, often leading to intimate relationships. Adolescent HIV/AIDS is a separate epidemic and needs to be handled and managed separately from adult HIV. The adolescents can be subdivided into student, slum and street youth; street adolescents being most vulnerable to HIV/AIDS. Among various risk factors and situations for adolescents contracting HIV virus are adolescent sex workers, child trafficking, child labor, migrant population, childhood sexual abuse, coercive sex with an older person and biologic (immature reproductive tract) as well as psychological vulnerability. The most common mode of transmission is heterosexual, yet increasing number of perinatally infected children are entering adolescence. This is due to "bimodal progression" (rapid and slow progressors) among the vertically infected children. Clinically, the HIV infected adolescents present as physically stunted individuals, with delayed puberty and adrenarche. Mental illness and substance abuse are important co-morbidities. The disclosure and declaration of HIV status to self and family is challenging and guilt in sexually infected adolescents and tendency to blame parents if vertically affected need special consideration and proper counseling. Serodiscordance of the twins and difference in disease progression of seroconcordant twins are added causes of emotional trauma. Treatment related issues revolve around the when and what of initiation of ART; the choice of antiretrovirals and their dosages; issues related to long term ADRs; sense of disinhibition following ART commencement; adherence and resistance.
Keywords: Adolescent; human immunodeficiency syndrome / acquired immunodeficiency syndrome; issues.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Human immunodeficiency virus and migrant labor in South Africa.Int J Health Serv. 1991;21(1):157-73. doi: 10.2190/11UE-L88J-46HN-HR0K. Int J Health Serv. 1991. PMID: 2004869
-
Human immunodeficiency virus-infected adolescents: a descriptive study of older children in New York City, Los Angeles County, Massachusetts and Washington, DC.Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2000 Jun;19(6):551-5. doi: 10.1097/00006454-200006000-00012. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2000. PMID: 10877172
-
Women and AIDS in Zimbabwe: the making of an epidemic.Int J Health Serv. 1991;21(1):143-56. doi: 10.2190/N0NJ-FKXB-CT25-PA09. Int J Health Serv. 1991. PMID: 2004868
-
Adolescents living with HIV in India - the clock is ticking.Indian J Pediatr. 2012 Dec;79(12):1642-7. doi: 10.1007/s12098-012-0902-x. Epub 2012 Nov 13. Indian J Pediatr. 2012. PMID: 23150229 Review.
-
HIV in adolescents.Clin Perinatol. 1994 Mar;21(1):75-84. Clin Perinatol. 1994. PMID: 8013187 Review.
Cited by
-
Adolescent pre-exposure prophylaxis for HIV prevention: current perspectives.Adolesc Health Med Ther. 2017 Nov 29;8:137-148. doi: 10.2147/AHMT.S112757. eCollection 2017. Adolesc Health Med Ther. 2017. PMID: 29238237 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prevalence of Mollicutes among men who have sex with men and transgender women aged 15 to 19 years in Salvador, North-eastern Brazil.BMC Infect Dis. 2023 Apr 18;23(1):244. doi: 10.1186/s12879-023-08213-z. BMC Infect Dis. 2023. PMID: 37072756 Free PMC article.
-
Psychosocial and mental health challenges facing perinatally HIV-infected adolescents along the Kenyan coast: a qualitative inquiry using the socioecological model.Front Public Health. 2024 Jul 23;12:1379262. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2024.1379262. eCollection 2024. Front Public Health. 2024. PMID: 39109160 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence and Correlates of HIV Disclosure Among Children and Adolescents in Low- and Middle-Income Countries: A Systematic Review.J Dev Behav Pediatr. 2016 Jul-Aug;37(6):496-505. doi: 10.1097/DBP.0000000000000303. J Dev Behav Pediatr. 2016. PMID: 27262128 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Knowledge of HIV/AIDS transmission among the adolescent girls in slum areas.Indian J Sex Transm Dis AIDS. 2011 Jul;32(2):139-41. doi: 10.4103/0253-7184.85435. Indian J Sex Transm Dis AIDS. 2011. PMID: 22021985 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- HIV/AIDS Epidemic in India. Available from: http://www.aidsfree-india.org/youth-adolescence/hiv-aids-youth-adolescen... [last cited on 2010 Jun 6]
-
- Bell M. HIV treatment series: Care of the HIV-positive adolescentdevelopmental stages and provider sensitivity play a special role. The Body- the complete HIV/AIDS resource- July/August. 2006. Available from: http://www.thebody.com/content/art1141.html [last cited on 2010 Jun 6] - PubMed
-
- AIDS epidemic update 2009. [last updated on 2009 Nov]. Available from: http://www.data.unaids.org/pub/Report/2009/JC1700_Epi_Update_2009_en.pdf [last cited on 2010 Jun 30]
-
- Mimi (Meheret) Melles. [last updated on 2009 Apr]. Available from: http://www.advocatesforyouth.org/index.php?option=com_contentandtask=vie... [last cited on 2010 Jun 30]
-
- Adolescent HIV infection and disease. Available from: http://www.nichd.nih.gov/about/org/crmc/pama/prog_hivadol/index.cfm [last cited on 2010 Jun 8th]
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials