Identification of small-molecule inhibitors of the XendoU endoribonucleases family
- PMID: 21805647
- PMCID: PMC7162399
- DOI: 10.1002/cmdc.201100281
Identification of small-molecule inhibitors of the XendoU endoribonucleases family
Abstract
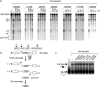
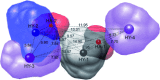
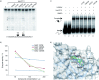
The XendoU family of enzymes includes several proteins displaying high sequence homology. The members characterized so far are endoribonucleases sharing similar biochemical properties and a common architecture in their active sites. Despite their similarities, these proteins are involved in distinct RNA-processing pathways in different organisms. The amphibian XendoU participates in the biosynthesis of small nucleolar RNAs, the human PP11 is supposed to play specialized roles in placental tissue, and NendoU has critical function in coronavirus replication. Notably, XendoU family members have been implicated in human pathologies such as cancer and respiratory diseases: PP11 is aberrantly expressed in various tumors, while NendoU activity has been associated with respiratory infections by pathogenic coronaviruses. The present study is aimed at identifying small molecules that may selectively interfere with these enzymatic activities. Combining structure-based virtual screening and experimental approaches, we identified four molecules that specifically inhibited the catalytic activity of XendoU and PP11 in the low micromolar range. Moreover, docking experiments strongly suggested that these compounds might also bind to the active site of NendoU, thus impairing the catalytic activity essential for the coronavirus life cycle. The identified compounds, while allowing deep investigation of the molecular functions of this enzyme family, may also represent leads for the development of new therapeutic tools.
Copyright © 2011 WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim.
Figures



Similar articles
-
The tumor marker human placental protein 11 is an endoribonuclease.J Biol Chem. 2008 Dec 12;283(50):34712-9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M805759200. Epub 2008 Oct 20. J Biol Chem. 2008. PMID: 18936097 Free PMC article.
-
Functional characterization of XendoU, the endoribonuclease involved in small nucleolar RNA biosynthesis.J Biol Chem. 2005 May 13;280(19):18996-9002. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M501160200. Epub 2005 Mar 7. J Biol Chem. 2005. PMID: 15755742
-
The structure of the endoribonuclease XendoU: From small nucleolar RNA processing to severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus replication.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006 Aug 15;103(33):12365-70. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0602426103. Epub 2006 Aug 8. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006. PMID: 16895992 Free PMC article.
-
A historical overview of protein kinases and their targeted small molecule inhibitors.Pharmacol Res. 2015 Oct;100:1-23. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2015.07.010. Epub 2015 Jul 21. Pharmacol Res. 2015. PMID: 26207888 Review.
-
Development of inhibitors as research tools for carbohydrate-processing enzymes.Biochem Soc Trans. 2012 Oct;40(5):913-28. doi: 10.1042/BST20120201. Biochem Soc Trans. 2012. PMID: 22988843 Review.
Cited by
-
Hsp90 inhibitors, part 2: combining ligand-based and structure-based approaches for virtual screening application.J Chem Inf Model. 2014 Mar 24;54(3):970-7. doi: 10.1021/ci400760a. Epub 2014 Mar 4. J Chem Inf Model. 2014. PMID: 24555544 Free PMC article.
-
ER morphology: sculpting with XendoU.Curr Biol. 2014 Dec 15;24(24):R1170-2. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2014.11.005. Curr Biol. 2014. PMID: 25514011 Free PMC article.
-
Ligand-based virtual screening and inductive learning for identification of SIRT1 inhibitors in natural products.Sci Rep. 2016 Jan 25;6:19312. doi: 10.1038/srep19312. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 26805727 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of Nucleotide Metabolism and Germline Proliferation in Response to Nucleotide Imbalance and Genotoxic Stresses by EndoU Nuclease.Cell Rep. 2020 Feb 11;30(6):1848-1861.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2020.01.050. Cell Rep. 2020. PMID: 32049015 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting the anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 family proteins: machine learning virtual screening and biological evaluation of new small molecules.Theranostics. 2022 Feb 28;12(5):2427-2444. doi: 10.7150/thno.64233. eCollection 2022. Theranostics. 2022. PMID: 35265218 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

