IGF-I stimulates cooperative interaction between the IGF-I receptor and CSK homologous kinase that regulates SHPS-1 phosphorylation in vascular smooth muscle cells
- PMID: 21799000
- PMCID: PMC3165910
- DOI: 10.1210/me.2011-0035
IGF-I stimulates cooperative interaction between the IGF-I receptor and CSK homologous kinase that regulates SHPS-1 phosphorylation in vascular smooth muscle cells
Abstract
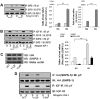
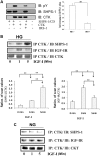
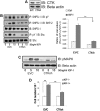
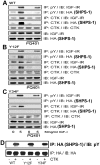
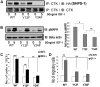
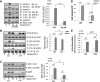
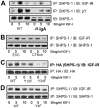
IGF-I plays an important role in smooth muscle cell proliferation and migration. In vascular smooth muscle cells cultured in 25 mm glucose, IGF-I stimulated a significant increase in Src homology 2 domain containing protein tyrosine phosphatase substrate-1 (SHPS-1) phosphorylation compared with 5 mm glucose and this increase was required for smooth muscle cell proliferation. A proteome-wide screen revealed that carboxyl-terminal SRC kinase homologous kinase (CTK) bound directly to phosphotyrosines in the SHPS-1 cytoplasmic domain. Because the kinase(s) that phosphorylates these tyrosines in response to IGF-I is unknown, we determined the roles of IGF-I receptor (IGF-IR) and CTK in mediating SHPS-1 phosphorylation. After IGF-I stimulation, CTK was recruited to IGF-IR and subsequently to phospho-SHPS-1. Expression of an IGF-IR mutant that eliminated CTK binding reduced CTK transfer to SHPS-1, SHPS-1 phosphorylation, and cell proliferation. IGF-IR phosphorylated SHPS-1, which provided a binding site for CTK. CTK recruitment to SHPS-1 resulted in a further enhancement of SHPS-1 phosphorylation. CTK knockdown also impaired IGF-I-stimulated SHPS-1 phosphorylation and downstream signaling. Analysis of specific tyrosines showed that mutation of tyrosines 428/452 in SHPS-1 to phenylalanine reduced SHPS-1 phosphorylation but allowed CTK binding. In contrast, the mutation of tyrosines 469/495 inhibited IGF-IR-mediated the phosphorylation of SHPS-1 and CTK binding, suggesting that IGF-IR phosphorylated Y469/495, allowing CTK binding, and that CTK subsequently phosphorylated Y428/452. Based on the above findings, we conclude that after IGF-I stimulation, CTK is recruited to IGF-IR and its recruitment facilitates CTK's subsequent association with phospho-SHPS-1. This results in the enhanced CTK transfer to SHPS-1, and the two kinases then fully phosphorylate SHPS-1, which is necessary for IGF-I stimulated cellular proliferation.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Insulin-like growth factor-I-stimulated insulin receptor substrate-1 negatively regulates Src homology 2 domain-containing protein-tyrosine phosphatase substrate-1 function in vascular smooth muscle cells.J Biol Chem. 2010 May 21;285(21):15682-95. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.092270. Epub 2010 Mar 5. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20207740 Free PMC article.
-
Role of SHPS-1 in the regulation of insulin-like growth factor I-stimulated Shc and mitogen-activated protein kinase activation in vascular smooth muscle cells.Mol Biol Cell. 2005 Jul;16(7):3353-64. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e04-10-0918. Epub 2005 May 11. Mol Biol Cell. 2005. PMID: 15888547 Free PMC article.
-
The association between integrin-associated protein and SHPS-1 regulates insulin-like growth factor-I receptor signaling in vascular smooth muscle cells.Mol Biol Cell. 2003 Sep;14(9):3519-28. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e03-04-0239. Epub 2003 May 29. Mol Biol Cell. 2003. PMID: 12972543 Free PMC article.
-
Interaction between insulin-like growth factor-I receptor and alphaVbeta3 integrin linked signaling pathways: cellular responses to changes in multiple signaling inputs.Mol Endocrinol. 2005 Jan;19(1):1-11. doi: 10.1210/me.2004-0376. Epub 2004 Nov 4. Mol Endocrinol. 2005. PMID: 15528274 Review.
-
Role of the integrin alphaVbeta3 in mediating increased smooth muscle cell responsiveness to IGF-I in response to hyperglycemic stress.Growth Horm IGF Res. 2007 Aug;17(4):265-70. doi: 10.1016/j.ghir.2007.01.004. Epub 2007 Apr 6. Growth Horm IGF Res. 2007. PMID: 17412627 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Acromegaly, inflammation and cardiovascular disease: a review.Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 2020 Dec;21(4):547-568. doi: 10.1007/s11154-020-09560-x. Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 2020. PMID: 32458292 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mutual connected IL-6, EGFR and LIN28/Let7-related mechanisms modulate PD-L1 and IGF upregulation in HNSCC using immunotherapy.Front Oncol. 2023 Apr 12;13:1140133. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1140133. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37124491 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inhibition of Aberrant IGF-I Signaling in Diabetic Male Rat Retina Prevents and Reverses Changes of Diabetic Retinopathy.J Diabetes Res. 2019 Mar 27;2019:6456032. doi: 10.1155/2019/6456032. eCollection 2019. J Diabetes Res. 2019. PMID: 31049357 Free PMC article.
-
Insulin-like growth factor (IGF) binding protein 2 functions coordinately with receptor protein tyrosine phosphatase β and the IGF-I receptor to regulate IGF-I-stimulated signaling.Mol Cell Biol. 2012 Oct;32(20):4116-30. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01011-12. Epub 2012 Aug 6. Mol Cell Biol. 2012. PMID: 22869525 Free PMC article.
-
Hyperglycemia induces vascular smooth muscle cell dedifferentiation by suppressing insulin receptor substrate-1-mediated p53/KLF4 complex stabilization.J Biol Chem. 2019 Feb 15;294(7):2407-2421. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.005398. Epub 2018 Dec 21. J Biol Chem. 2019. PMID: 30578299 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arnqvist HJ, Bornfeldt KE, Chen Y, Lindström T. 1995. The insulin-like growth factor system in vascular smooth muscle: interaction with insulin and growth factors. Metabolism 44:58–66 - PubMed
-
- Joslin E, Kahn CR. 2005. Joslin's diabetes mellitus. 14th ed. Boston: Lippincott Williams, Wilkins
-
- Radhakrishnan Y, Busby WH, Jr, Shen X, Maile LA, Clemmons DR. 2010. Insulin-like growth factor-I-stimulated insulin receptor substrate-1 negatively regulates Src homology 2 domain-containing protein-tyrosine phosphatase substrate-1 function in vascular smooth muscle cells. J Biol Chem 285:15682–15695 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

