Salinomycin inhibits Wnt signaling and selectively induces apoptosis in chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells
- PMID: 21788521
- PMCID: PMC3156152
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1110431108
Salinomycin inhibits Wnt signaling and selectively induces apoptosis in chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells
Abstract
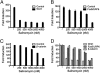
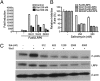
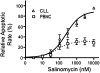
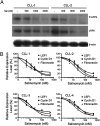
Salinomycin, an antibiotic potassium ionophore, has been reported recently to act as a selective breast cancer stem cell inhibitor, but the biochemical basis for its anticancer effects is not clear. The Wnt/β-catenin signal transduction pathway plays a central role in stem cell development, and its aberrant activation can cause cancer. In this study, we identified salinomycin as a potent inhibitor of the Wnt signaling cascade. In Wnt-transfected HEK293 cells, salinomycin blocked the phosphorylation of the Wnt coreceptor lipoprotein receptor related protein 6 (LRP6) and induced its degradation. Nigericin, another potassium ionophore with activity against cancer stem cells, exerted similar effects. In otherwise unmanipulated chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells with constitutive Wnt activation nanomolar concentrations of salinomycin down-regulated the expression of Wnt target genes such as LEF1, cyclin D1, and fibronectin, depressed LRP6 levels, and limited cell survival. Normal human peripheral blood lymphocytes resisted salinomycin toxicity. These results indicate that ionic changes induced by salinomycin and related drugs inhibit proximal Wnt signaling by interfering with LPR6 phosphorylation, and thus impair the survival of cells that depend on Wnt signaling at the plasma membrane.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
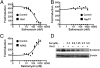
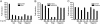
Similar articles
-
Salinomycin suppresses LRP6 expression and inhibits both Wnt/β-catenin and mTORC1 signaling in breast and prostate cancer cells.J Cell Biochem. 2014 Oct;115(10):1799-807. doi: 10.1002/jcb.24850. J Cell Biochem. 2014. PMID: 24905570 Free PMC article.
-
Ethacrynic acid exhibits selective toxicity to chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells by inhibition of the Wnt/beta-catenin pathway.PLoS One. 2009 Dec 14;4(12):e8294. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0008294. PLoS One. 2009. PMID: 20011538 Free PMC article.
-
Niclosamide suppresses cancer cell growth by inducing Wnt co-receptor LRP6 degradation and inhibiting the Wnt/β-catenin pathway.PLoS One. 2011;6(12):e29290. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0029290. Epub 2011 Dec 16. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 22195040 Free PMC article.
-
Wnt/β-catenin/LEF-1 signaling in chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL): a target for current and potential therapeutic options.Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2010 Nov;10(7):716-27. doi: 10.2174/156800910793605794. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2010. PMID: 20578984 Review.
-
Ionophores: Potential Use as Anticancer Drugs and Chemosensitizers.Cancers (Basel). 2018 Sep 27;10(10):360. doi: 10.3390/cancers10100360. Cancers (Basel). 2018. PMID: 30262730 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Trypanocidal activity of salinomycin is due to sodium influx followed by cell swelling.Parasit Vectors. 2013 Mar 21;6:78. doi: 10.1186/1756-3305-6-78. Parasit Vectors. 2013. PMID: 23517602 Free PMC article.
-
Understanding and Targeting the Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Pathway in Chronic Leukemia.Leuk Res Treatment. 2011;2011:329572. doi: 10.4061/2011/329572. Epub 2011 Dec 4. Leuk Res Treatment. 2011. PMID: 23213540 Free PMC article.
-
The evolving concept of cancer and metastasis stem cells.J Cell Biol. 2012 Aug 6;198(3):281-93. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201202014. J Cell Biol. 2012. PMID: 22869594 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Metadherin contributes to the pathogenesis of chronic lymphocytic leukemia partially through Wnt/β-catenin pathway.Med Oncol. 2015 Feb;32(2):479. doi: 10.1007/s12032-014-0479-5. Epub 2015 Jan 10. Med Oncol. 2015. PMID: 25575438
-
Identifying and targeting tumor-initiating cells in the treatment of breast cancer.Endocr Relat Cancer. 2015 Jun;22(3):R135-55. doi: 10.1530/ERC-14-0447. Epub 2015 Apr 15. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2015. PMID: 25876646 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Clevers H. Wnt/beta-catenin signaling in development and disease. Cell. 2006;127:469–480. - PubMed
-
- Moon RT, Kohn AD, De Ferrari GV, Kaykas A. WNT and beta-catenin signalling: Diseases and therapies. Nat Rev Genet. 2004;5:691–701. - PubMed
-
- Nusse R. Wnt signaling in disease and in development. Cell Res. 2005;15:28–32. - PubMed
-
- Willert K, Jones KA. Wnt signaling: is the party in the nucleus? Genes Dev. 2006;20:1394–1404. - PubMed
-
- Mao B, et al. LDL-receptor-related protein 6 is a receptor for Dickkopf proteins. Nature. 2001;411:321–325. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

