Positive selecting cell type determines the phenotype of MHC class Ib-restricted CD8+ T cells
- PMID: 21788511
- PMCID: PMC3156174
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1105118108
Positive selecting cell type determines the phenotype of MHC class Ib-restricted CD8+ T cells
Abstract
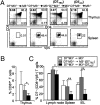
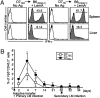
Several studies have demonstrated an apparent link between positive selection on hematopoietic cells (HCs) and an "innate" T-cell phenotype. Whereas conventional CD8(+) T cells are primarily selected on thymic epithelial cells (TECs) and certain innate T cells are exclusively selected on HCs, MHC class Ib-restricted CD8(+) T cells appear to be selected on both TECs and HCs. However, whether TEC- and HC-selected T cells represent distinct lineages or whether the same T-cell precursors have the capacity to be selected on either cell type is unknown. Using an M3-restricted T-cell receptor transgenic mouse model, we demonstrate that not only are MHC class Ib-restricted CD8(+) T cells capable of being selected on either cell type but that selecting cell type directly affects the phenotype of the resulting CD8(+) T cells. M3-restricted CD8(+) T cells selected on HCs acquire a more activated phenotype and possess more potent effector functions than those selected on TECs. Additionally, these two developmental pathways are active in the generation of the natural pool of M3-restricted CD8(+) T cells. Our results suggest that these two distinct populations may allow MHC class Ib-restricted CD8(+) T cells to occupy different immunological niches playing unique roles in immune responses to infection.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


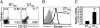

Similar articles
-
Positive selection of MHC class Ib-restricted CD8(+) T cells on hematopoietic cells.Nat Immunol. 2002 Aug;3(8):772-9. doi: 10.1038/ni814. Epub 2002 Jul 1. Nat Immunol. 2002. PMID: 12089507 Free PMC article.
-
Nonconventional CD8+ T cell responses to Listeria infection in mice lacking MHC class Ia and H2-M3.J Immunol. 2011 Jan 1;186(1):489-98. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1002639. Epub 2010 Nov 22. J Immunol. 2011. PMID: 21098224 Free PMC article.
-
Selective dependence of H2-M3-restricted CD8 responses on IL-15.J Immunol. 2012 Mar 15;188(6):2575-82. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1102393. Epub 2012 Feb 6. J Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22312130 Free PMC article.
-
Role of MHC class Ib molecule, H2-M3 in host immunity against tuberculosis.Vaccine. 2013 Aug 20;31(37):3818-25. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2013.04.005. Epub 2013 Apr 28. Vaccine. 2013. PMID: 23628242 Review.
-
MHC class I restricted T cell responses to Listeria monocytogenes, an intracellular bacterial pathogen.Immunol Res. 1999;19(2-3):211-23. doi: 10.1007/BF02786489. Immunol Res. 1999. PMID: 10493175 Review.
Cited by
-
SAP is required for the development of innate phenotype in H2-M3--restricted Cd8(+) T cells.J Immunol. 2012 Nov 15;189(10):4787-96. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1200579. Epub 2012 Oct 5. J Immunol. 2012. PMID: 23041566 Free PMC article.
-
Nonclassical MHC class Ib-restricted cytotoxic T cells monitor antigen processing in the endoplasmic reticulum.Nat Immunol. 2012 Apr 22;13(6):579-86. doi: 10.1038/ni.2282. Nat Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22522492 Free PMC article.
-
Human thymic MR1-restricted MAIT cells are innate pathogen-reactive effectors that adapt following thymic egress.Mucosal Immunol. 2013 Jan;6(1):35-44. doi: 10.1038/mi.2012.45. Epub 2012 Jun 13. Mucosal Immunol. 2013. PMID: 22692454 Free PMC article.
-
The promiscuous development of an unconventional Qa1b-restricted T cell population.Front Immunol. 2023 Oct 31;14:1250316. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1250316. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 38022509 Free PMC article.
-
Distinct behavior of myelomonocytic cells and CD8 T cells underlies the hepatic response to Listeria monocytogenes.Wellcome Open Res. 2018 Apr 24;3:48. doi: 10.12688/wellcomeopenres.12941.1. eCollection 2018. Wellcome Open Res. 2018. PMID: 29862325 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rodgers JR, Cook RG. MHC class Ib molecules bridge innate and acquired immunity. Nat Rev Immunol. 2005;5:459–471. - PubMed
-
- Bendelac A, Rivera MN, Park SH, Roark JH. Mouse CD1-specific NK1 T cells: Ddevelopment, specificity, and function. Annu Rev Immunol. 1997;15:535–562. - PubMed
-
- Chen YH, Chiu NM, Mandal M, Wang N, Wang CR. Impaired NK1+ T cell development and early IL-4 production in CD1-deficient mice. Immunity. 1997;6:459–467. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

