Investigating endogenous peptides and peptidases using peptidomics
- PMID: 21786763
- PMCID: PMC3418817
- DOI: 10.1021/bi200417k
Investigating endogenous peptides and peptidases using peptidomics
Abstract
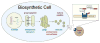
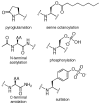
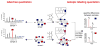
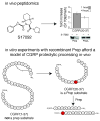
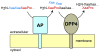
Rather than simply being protein degradation products, peptides have proven to be important bioactive molecules. Bioactive peptides act as hormones, neurotransmitters, and antimicrobial agents in vivo. The dysregulation of bioactive peptide signaling is also known to be involved in disease, and targeting peptide hormone pathways has been a successful strategy in the development of novel therapeutics. The importance of bioactive peptides in biology has spurred research to elucidate the function and regulation of these molecules. Classical methods for peptide analysis have relied on targeted immunoassays, but certain scientific questions necessitated a broader and more detailed view of the peptidome--all the peptides in a cell, tissue, or organism. In this review we discuss how peptidomics has emerged to fill this need through the application of advanced liquid chromatography--tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) methods that provide unique insights into peptide activity and regulation.
Figures
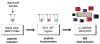


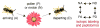

Similar articles
-
Peptidomics approach to elucidate the proteolytic regulation of bioactive peptides.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012 May 29;109(22):8523-7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1203195109. Epub 2012 May 14. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012. PMID: 22586115 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of the proteolysis of bioactive peptides using a peptidomics approach.Nat Protoc. 2013 Sep;8(9):1730-42. doi: 10.1038/nprot.2013.104. Epub 2013 Aug 15. Nat Protoc. 2013. PMID: 23949379 Free PMC article.
-
Peptidomics methods for the identification of peptidase-substrate interactions.Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2013 Feb;17(1):83-9. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpa.2012.10.038. Epub 2013 Jan 15. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2013. PMID: 23332665 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Quantitative Peptidomics with Isotopic and Isobaric Tags.Methods Mol Biol. 2018;1719:141-159. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-7537-2_9. Methods Mol Biol. 2018. PMID: 29476509
-
The Peptidome Comes of Age: Mass Spectrometry-Based Characterization of the Circulating Cancer Peptidome.Enzymes. 2017;42:27-64. doi: 10.1016/bs.enz.2017.08.003. Epub 2017 Oct 10. Enzymes. 2017. PMID: 29054270 Review.
Cited by
-
Liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry methods for measuring dipeptide abundance in non-small-cell lung cancer.Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom. 2013 Sep 30;27(18):2091-2098. doi: 10.1002/rcm.6656. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom. 2013. PMID: 23943330 Free PMC article.
-
Selective, bead-based global peptide capture using a bifunctional cross-linker.Anal Chem. 2013 Nov 19;85(22):10675-9. doi: 10.1021/ac401825m. Epub 2013 Oct 28. Anal Chem. 2013. PMID: 24117407 Free PMC article.
-
Biomarkers in Alzheimer's disease analysis by mass spectrometry-based proteomics.Int J Mol Sci. 2014 May 6;15(5):7865-82. doi: 10.3390/ijms15057865. Int J Mol Sci. 2014. PMID: 24806343 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Revealing Natural Intracellular Peptides in Gills of Seahorse Hippocampus reidi.Biomolecules. 2023 Feb 24;13(3):433. doi: 10.3390/biom13030433. Biomolecules. 2023. PMID: 36979368 Free PMC article.
-
An Optimized Informatics Pipeline for Mass Spectrometry-Based Peptidomics.J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 2015 Dec;26(12):2002-8. doi: 10.1007/s13361-015-1169-z. Epub 2015 May 27. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 2015. PMID: 26015166 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Berg JM, Tymoczko JL, Stryer L. Biochemistry. 6. W.H. Freeman; New York: 2007.
-
- Gardner DG, Shoback DM, Greenspan FS. Greenspan’s basic & clinical endocrinology. 8. McGraw-Hill Medical; New York: 2007.
-
- Kastin AJ. Handbook of biologically active peptides. Academic Press; Amsterdam; Boston: 2006.
-
- Brady MJ, Saltiel AR. Insulin and Glucagon. John Wiley & Sons, Ltd; 2001.
-
- Aronoff SL, Berkowitz K, Shreiner B, Want L. Glucose metabolism and regulation: Beyond insulin and glucagon. Diabetes Spectrum. 2004;17:183–190.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

