The effect of TOMM40 poly-T length on gray matter volume and cognition in middle-aged persons with APOE ε3/ε3 genotype
- PMID: 21784354
- PMCID: PMC3143375
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jalz.2010.11.012
The effect of TOMM40 poly-T length on gray matter volume and cognition in middle-aged persons with APOE ε3/ε3 genotype
Abstract
Objective: Apolipoprotein E (APOE) genotypes are associated with variable risk of developing late-onset Alzheimer's disease (LOAD), with APOE epsilon 4 (APOE ε4) having higher risk. A variable poly-T length polymorphism at rs10524523, within intron 6 of the translocase of the outer mitochondrial membrane (TOMM40) gene, has been shown to influence age of onset in LOAD, with very long (VL) poly-T length associated with earlier disease onset, and short poly-T length associated with later onset. In this study, we tested the hypothesis that brain and cognitive changes suggestive of presymptomatic LOAD may be associated with this TOMM40 polymorphism.
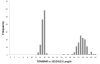
Methods: Among healthy APOE ε3 homozygous adults (N = 117; mean age, 55 years), we compared those who were homozygous for VL/VL (n = 35) TOMM40 poly-T lengths (who were presumably at higher risk) with those homozygous for short (S/S; n = 38) poly-T lengths, as well as those with heterozygous (S/VL; n = 44) poly-T length polymorphisms, on measures of learning and memory and on structural brain imaging.
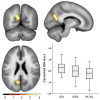
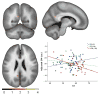
Results: The VL/VL group showed lower performance than the S/S TOMM40 group on primacy retrieval from a verbal list learning task, a finding which is also seen in early Alzheimer's disease. A dose-dependent increase in the VL TOMM40 polymorphism (from no VL alleles, to S/VL heterozygous, to VL/VL homozygous) was associated with decreasing gray matter volume in the ventral posterior cingulate and medial ventral precuneus, a region of the brain affected early in LOAD.
Conclusions: These findings among APOE ε3/ε3 late middle-aged adults suggest that a subgroup with VL TOMM40 poly-T lengths may be experiencing incipient LOAD-related cognitive and brain changes.
Published by Elsevier Inc.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The effect of TOMM40 on spatial navigation in amnestic mild cognitive impairment.Neurobiol Aging. 2015 Jun;36(6):2024-33. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2015.03.004. Epub 2015 Mar 16. Neurobiol Aging. 2015. PMID: 25862420
-
TOMM40 intron 6 poly-T length, age at onset, and neuropathology of AD in individuals with APOE ε3/ε3.Alzheimers Dement. 2013 Sep;9(5):554-61. doi: 10.1016/j.jalz.2012.06.009. Epub 2012 Nov 22. Alzheimers Dement. 2013. PMID: 23183136 Free PMC article.
-
The cis-regulatory effect of an Alzheimer's disease-associated poly-T locus on expression of TOMM40 and apolipoprotein E genes.Alzheimers Dement. 2014 Sep;10(5):541-51. doi: 10.1016/j.jalz.2013.08.280. Epub 2014 Jan 15. Alzheimers Dement. 2014. PMID: 24439168 Free PMC article.
-
The effects of the TOMM40 poly-T alleles on Alzheimer's disease phenotypes.Alzheimers Dement. 2018 May;14(5):692-698. doi: 10.1016/j.jalz.2018.01.015. Epub 2018 Mar 7. Alzheimers Dement. 2018. PMID: 29524426 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An inherited variable poly-T repeat genotype in TOMM40 in Alzheimer disease.Arch Neurol. 2010 May;67(5):536-41. doi: 10.1001/archneurol.2010.88. Arch Neurol. 2010. PMID: 20457951 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Genome-wide pathway analysis of memory impairment in the Alzheimer's Disease Neuroimaging Initiative (ADNI) cohort implicates gene candidates, canonical pathways, and networks.Brain Imaging Behav. 2012 Dec;6(4):634-48. doi: 10.1007/s11682-012-9196-x. Brain Imaging Behav. 2012. PMID: 22865056 Free PMC article.
-
Hippocampal thinning linked to longer TOMM40 poly-T variant lengths in the absence of the APOE ε4 variant.Alzheimers Dement. 2017 Jul;13(7):739-748. doi: 10.1016/j.jalz.2016.12.009. Epub 2017 Feb 7. Alzheimers Dement. 2017. PMID: 28183529 Free PMC article.
-
The Alu neurodegeneration hypothesis: A primate-specific mechanism for neuronal transcription noise, mitochondrial dysfunction, and manifestation of neurodegenerative disease.Alzheimers Dement. 2017 Jul;13(7):828-838. doi: 10.1016/j.jalz.2017.01.017. Epub 2017 Feb 24. Alzheimers Dement. 2017. PMID: 28242298 Free PMC article.
-
TOMM40-APOE haplotypes are associated with cognitive decline in non-demented Blacks.Alzheimers Dement. 2021 Aug;17(8):1287-1296. doi: 10.1002/alz.12295. Epub 2021 Feb 13. Alzheimers Dement. 2021. PMID: 33580752 Free PMC article.
-
An increase in mitochondrial TOM activates apoptosis to drive retinal neurodegeneration.Sci Rep. 2022 Dec 14;12(1):21634. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-23280-z. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 36517509 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Farrer LA, Cupples LA, Haines JL, et al. Effects of age, sex, and ethnicity on the association between apolipoprotein E genotype and Alzheimer disease. A meta-analysis. APOE and Alzheimer Disease Meta Analysis Consortium. Jama. 1997;278:1349–1356. - PubMed
-
- Strittmatter WJ, Roses AD. Apolipoprotein E and Alzheimer’s disease. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1996;19:53–77. - PubMed
-
- Sleegers K, Lambert JC, Bertram L, Cruts M, Amouyel P, Van Broeckhoven C. The pursuit of susceptibility genes for Alzheimer’s disease: progress and prospects. Trends Genet. 2010;26:84–93. - PubMed
-
- Saunders AM, Strittmatter WJ, Schmechel D, et al. Association of apolipoprotein E allele epsilon 4 with late-onset familial and sporadic Alzheimer’s disease. Neurology. 1993;43:1467–1472. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P50 AG033514-02/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG021155-04/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG027161-01A2/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG021155-03/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG027161-02/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG027161-03/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG033514-03/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- RC1 AG035635/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG027161-05/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG021155-05/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG033514-01/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 HD003352/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG021155-05S1/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG021155-02/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG027161/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG021155-01A2/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG021155-06A1/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR025011/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG021155/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- RC1AG035635-01/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG027161-04/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- UL1RR025011/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG033514/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

