The n3-polyunsaturated fatty acid docosahexaenoic acid induces immunogenic cell death in human cancer cell lines via pre-apoptotic calreticulin exposure
- PMID: 21779875
- PMCID: PMC11028828
- DOI: 10.1007/s00262-011-1074-7
The n3-polyunsaturated fatty acid docosahexaenoic acid induces immunogenic cell death in human cancer cell lines via pre-apoptotic calreticulin exposure
Abstract
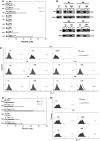
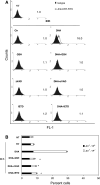
Some anticancer chemotherapeutics, such as anthracyclines and oxaliplatin, elicit immunogenic apoptosis, meaning that dying cancer cells are engulfed by dendritic cells and tumor antigens are efficiently presented to CD8+ T cells, which control residual tumor cells. Immunogenic apoptosis is characterized by pre-apoptotic cell surface exposure of calreticulin (CRT), which usually resides into the endoplasmic reticulum. We investigated the ability of the n3-polyunsaturated fatty acid docosahexaenoic acid (22:6n3, DHA) to induce pre-apoptotic CRT exposure on the surface of the human PaCa-44 pancreatic and EJ bladder cancer cell lines. Cells were treated with 150 μM DHA for different time periods, and, by immunoblot and immunofluorescence, we showed that DHA induced CRT exposure, before the apoptosis-associated phosphatidylserine exposure. As for the known immunogenic compounds, CRT exposure was inhibited by the antioxidant GSH, the pan-caspase zVAD-FMK, and caspase-8 IETD-FMK inhibitor. We provide the first evidence that DHA induces CRT exposure, representing thus a novel potential anticancer immunogenic chemotherapeutic agent.
Conflict of interest statement
We do not have any financial/commercial conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Immunogenic tumor cell death for optimal anticancer therapy: the calreticulin exposure pathway.Clin Cancer Res. 2010 Jun 15;16(12):3100-4. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-09-2891. Epub 2010 Apr 26. Clin Cancer Res. 2010. PMID: 20421432
-
The histone deacetylase inhibitor vorinostat induces calreticulin exposure in childhood brain tumour cells in vitro.Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2010 Aug;66(3):611-6. doi: 10.1007/s00280-010-1302-4. Epub 2010 Mar 10. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2010. PMID: 20221600
-
Mechanisms of pre-apoptotic calreticulin exposure in immunogenic cell death.EMBO J. 2009 Mar 4;28(5):578-90. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2009.1. Epub 2009 Jan 22. EMBO J. 2009. PMID: 19165151 Free PMC article.
-
Ecto-calreticulin in immunogenic chemotherapy.Immunol Rev. 2007 Dec;220:22-34. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065X.2007.00567.x. Immunol Rev. 2007. PMID: 17979837 Review.
-
Molecular determinants of immunogenic cell death: surface exposure of calreticulin makes the difference.J Mol Med (Berl). 2007 Oct;85(10):1069-76. doi: 10.1007/s00109-007-0214-1. Epub 2007 May 22. J Mol Med (Berl). 2007. PMID: 17891368 Review.
Cited by
-
Omega-3 fatty acids inhibit tumor growth in a rat model of bladder cancer.Biomed Res Int. 2013;2013:368178. doi: 10.1155/2013/368178. Epub 2013 Jun 20. Biomed Res Int. 2013. PMID: 23865049 Free PMC article.
-
Trial watch: Chemotherapy with immunogenic cell death inducers.Oncoimmunology. 2013 Mar 1;2(3):e23510. doi: 10.4161/onci.23510. Oncoimmunology. 2013. PMID: 23687621 Free PMC article.
-
Consensus guidelines for the detection of immunogenic cell death.Oncoimmunology. 2014 Dec 13;3(9):e955691. doi: 10.4161/21624011.2014.955691. eCollection 2014 Oct. Oncoimmunology. 2014. PMID: 25941621 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immunogenic Cell Death Role in Urothelial Cancer Therapy.Curr Oncol. 2022 Sep 18;29(9):6700-6713. doi: 10.3390/curroncol29090526. Curr Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36135095 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced release and binding of calreticulin from human ovarian cancer cells.Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2022 Jul;71(7):1655-1669. doi: 10.1007/s00262-021-03072-6. Epub 2021 Nov 20. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2022. PMID: 34800147 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

