The Role of p53 in Metabolic Regulation
- PMID: 21779507
- PMCID: PMC3135642
- DOI: 10.1177/1947601911409738
The Role of p53 in Metabolic Regulation
Abstract
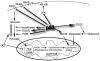
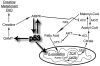
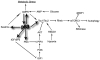
The metabolic changes that occur in a cancer cell have been studied for a few decades, but our appreciation of the complexity and importance of those changes is now being realized. The metabolic switch from oxidative phosphorylation to aerobic glycolysis provides intermediates for cell growth and division and is regulated by both oncogenes and tumor suppressor genes. The p53 tumor suppressor gene has long been shown to play key roles in responding to DNA damage, hypoxia, and oncogenic activation. However, now p53 has added the ability to mediate metabolic changes in cells through the regulation of energy metabolism and oxidative stress to its repertoire of activities. It is therefore the focus of this review to discuss the metabolic pathways regulated by p53 and their cooperation in controlling cancer cell metabolism.
Keywords: aerobic glycolysis; oxidative phosphorylation; oxidative stress; p53.
Conflict of interest statement
The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures
Similar articles
-
p53 and energy balance: meeting hypothalamic AgRP neurons.Cell Stress. 2018 Oct 18;2(11):329-331. doi: 10.15698/cst2018.11.165. Cell Stress. 2018. PMID: 31225457 Free PMC article.
-
The control of the metabolic switch in cancers by oncogenes and tumor suppressor genes.Science. 2010 Dec 3;330(6009):1340-4. doi: 10.1126/science.1193494. Science. 2010. PMID: 21127244 Review.
-
p53 and glucose metabolism: an orchestra to be directed in cancer therapy.Pharmacol Res. 2018 May;131:75-86. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2018.03.015. Epub 2018 Mar 23. Pharmacol Res. 2018. PMID: 29580896 Review.
-
Aerobic glycolysis suppresses p53 activity to provide selective protection from apoptosis upon loss of growth signals or inhibition of BCR-Abl.Cancer Res. 2010 Oct 15;70(20):8066-76. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-0608. Epub 2010 Sep 28. Cancer Res. 2010. PMID: 20876800 Free PMC article.
-
The regulation of energy generating metabolic pathways by p53.Cancer Biol Ther. 2006 Dec;5(12):1610-3. doi: 10.4161/cbt.5.12.3617. Epub 2006 Dec 26. Cancer Biol Ther. 2006. PMID: 17204863
Cited by
-
Effects of monosodium glutamate on testicular structural and functional alterations induced by quinine therapy in rat: An experimental study.Int J Reprod Biomed. 2021 Feb 21;19(2):167-180. doi: 10.18502/ijrm.v19i2.8475. eCollection 2021 Feb. Int J Reprod Biomed. 2021. PMID: 33718761 Free PMC article.
-
Mitochondrial stress-induced p53 attenuates HIF-1α activity by physical association and enhanced ubiquitination.Oncogene. 2017 Jan 19;36(3):397-409. doi: 10.1038/onc.2016.211. Epub 2016 Jun 27. Oncogene. 2017. PMID: 27345397 Free PMC article.
-
Mitochondrial Sirtuin 3: New emerging biological function and therapeutic target.Theranostics. 2020 Jul 9;10(18):8315-8342. doi: 10.7150/thno.45922. eCollection 2020. Theranostics. 2020. PMID: 32724473 Free PMC article. Review.
-
IR-Surviving NSCLC Cells Exhibit Different Patterns of Molecular and Cellular Reactions Relating to the Multifraction Irradiation Regimen and p53-Family Proteins Expression.Cancers (Basel). 2021 May 28;13(11):2669. doi: 10.3390/cancers13112669. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34071477 Free PMC article.
-
The role of the p53 tumor suppressor in metabolism and diabetes.J Endocrinol. 2016 Nov;231(2):R61-R75. doi: 10.1530/JOE-16-0324. Epub 2016 Sep 9. J Endocrinol. 2016. PMID: 27613337 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Warburg O. On respiratory impairment in cancer cells. Science. 1956;124(3215):269-70 - PubMed
-
- Vousden KH, Ryan KM. p53 and metabolism. Nat Rev Cancer. 2009;9(10):691-700 - PubMed
-
- Pfeiffer T, Schuster S, Bonhoeffer S. Cooperation and competition in the evolution of ATP-producing pathways. Science. 2001;292(5516):504-7 - PubMed
-
- Christofk HR, Vander Heiden MG, Harris MH, et al. The M2 splice isoform of pyruvate kinase is important for cancer metabolism and tumour growth. Nature. 2008;452(7184):230-3 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
