The 'invisible hand': regulation of RHO GTPases by RHOGDIs
- PMID: 21779026
- PMCID: PMC3260518
- DOI: 10.1038/nrm3153
The 'invisible hand': regulation of RHO GTPases by RHOGDIs
Abstract
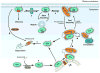
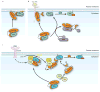
The 'invisible hand' is a term originally coined by Adam Smith in The Theory of Moral Sentiments to describe the forces of self-interest, competition and supply and demand that regulate the resources in society. This metaphor continues to be used by economists to describe the self-regulating nature of a market economy. The same metaphor can be used to describe the RHO-specific guanine nucleotide dissociation inhibitor (RHOGDI) family, which operates in the background, as an invisible hand, using similar forces to regulate the RHO GTPase cycle.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A Complete Survey of RhoGDI Targets Reveals Novel Interactions with Atypical Small GTPases.Biochemistry. 2021 May 18;60(19):1533-1551. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.1c00120. Epub 2021 Apr 29. Biochemistry. 2021. PMID: 33913706 Free PMC article.
-
Uncoupling of inhibitory and shuttling functions of rho GDP dissociation inhibitors.J Biol Chem. 2005 Feb 11;280(6):4674-83. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M409741200. Epub 2004 Oct 28. J Biol Chem. 2005. PMID: 15513926
-
RhoGDI SUMOylation at Lys-138 increases its binding activity to Rho GTPase and its inhibiting cancer cell motility.J Biol Chem. 2012 Apr 20;287(17):13752-60. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.337469. Epub 2012 Mar 5. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22393046 Free PMC article.
-
RhoGDI-3, a promising system to investigate the regulatory function of rhoGDIs: uncoupling of inhibitory and shuttling functions of rhoGDIs.Biochem Soc Trans. 2005 Aug;33(Pt 4):623-6. doi: 10.1042/BST0330623. Biochem Soc Trans. 2005. PMID: 16042558 Review.
-
RhoGDIs revisited: novel roles in Rho regulation.Traffic. 2005 Nov;6(11):957-66. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0854.2005.00335.x. Traffic. 2005. PMID: 16190977 Review.
Cited by
-
Rac-maninoff and Rho-vel: The symphony of Rho-GTPase signaling at excitatory synapses.Small GTPases. 2022 Jan;13(1):14-47. doi: 10.1080/21541248.2021.1885264. Epub 2021 May 6. Small GTPases. 2022. PMID: 33955328 Free PMC article.
-
A Complete Survey of RhoGDI Targets Reveals Novel Interactions with Atypical Small GTPases.Biochemistry. 2021 May 18;60(19):1533-1551. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.1c00120. Epub 2021 Apr 29. Biochemistry. 2021. PMID: 33913706 Free PMC article.
-
Atypical RhoUV GTPases in development and disease.Biochem Soc Trans. 2024 Feb 28;52(1):89-97. doi: 10.1042/BST20230212. Biochem Soc Trans. 2024. PMID: 38314621 Free PMC article. Review.
-
G-protein signaling leverages subunit-dependent membrane affinity to differentially control βγ translocation to intracellular membranes.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012 Dec 18;109(51):E3568-77. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1205345109. Epub 2012 Dec 3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012. PMID: 23213235 Free PMC article.
-
ArhGAP15, a Rac-specific GTPase-activating protein, plays a dual role in inhibiting small GTPase signaling.J Biol Chem. 2013 Jul 19;288(29):21117-21125. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.459719. Epub 2013 Jun 11. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23760270 Free PMC article.
References
-
- DerMardirossian C, Bokoch GM. GDIs: central regulatory molecules in Rho GTPase activation. Trends Cell Biol. 2005;15:356–63. - PubMed
-
- Fukumoto Y, et al. Molecular cloning and characterization of a novel type of regulatory protein (GDI) for the rho proteins, ras p21-like small GTP-binding proteins. Oncogene. 1990;5:1321–8. - PubMed
-
- Leonard D, et al. The identification and characterization of a GDP-dissociation inhibitor (GDI) for the CDC42Hs protein. J Biol Chem. 1992;267:22860–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

