Coexpression of angiopoietin-1 with VEGF increases the structural integrity of the blood-brain barrier and reduces atrophy volume
- PMID: 21772310
- PMCID: PMC3323197
- DOI: 10.1038/jcbfm.2011.97
Coexpression of angiopoietin-1 with VEGF increases the structural integrity of the blood-brain barrier and reduces atrophy volume
Abstract
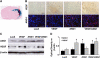
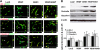
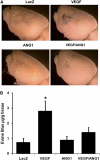
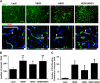
Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)-induced neovasculature is immature and leaky. We tested if coexpression of angiopoietin-1 (ANG1) with VEGF improves blood-brain barrier (BBB) integrity and VEGF neuroprotective and neurorestorative effects using a permanent distal middle cerebral artery occlusion (pMCAO) model. Adult CD-1 mice were injected with 2 × 10(9) virus genomes of adeno-associated viral vectors expressing VEGF (AAV-VEGF) or ANG1 (AAV-ANG1) individually or together in a 1:1 ratio into the ischemic penumbra 1 hour after pMCAO. AAV-LacZ was used as vector control. Samples were collected 3 weeks later. Compared with AAV-LacZ, coinjection of AAV-VEGF and AAV-ANG1 reduced atrophy volume (46%, P=0.004); injection of AAV-VEGF or AAV-ANG1 individually reduced atrophy volume slightly (36%, P=0.08 and 33%, P=0.09, respectively). Overexpression of VEGF reduced tight junction protein expression and increased Evans blue extravasation. Compared with VEGF expression alone, coexpression of ANG1 with VEGF resulted in upregulation of tight junction protein expression and reduction of Evans blue leakage (AAV-ANG1/AAV-VEGF: 1.4 ± 0.3 versus AAV-VEGF: 2.8 ± 0.7, P=0.001). Coinjection of AAV-VEGF and AAV-ANG1 induced a similar degree of angiogenesis as injection of AAV-VEGF alone (P=0.85). Thus, coexpression of ANG1 with VEGF improved BBB integrity and resulted in better neuroprotection compared with VEGF expression alone.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Adeno-associated virus vectors simultaneously encoding VEGF and angiopoietin-1 enhances neovascularization in ischemic rabbit hind-limbs.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2007 Apr;28(4):493-502. doi: 10.1111/j.1745-7254.2007.00527.x. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2007. PMID: 17376288
-
Angiopoietin 1 counteracts vascular endothelial growth factor-induced blood-brain barrier permeability and alleviates ischemic injury in the early stages of transient focal cerebral ischemia in rats.Neurol Res. 2010 Sep;32(7):748-55. doi: 10.1179/016164109X12445616596562. Epub 2009 Aug 5. Neurol Res. 2010. PMID: 19660197
-
Coexpression of VEGF and angiopoietin-1 promotes angiogenesis and cardiomyocyte proliferation reduces apoptosis in porcine myocardial infarction (MI) heart.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011 Feb 1;108(5):2064-9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1018925108. Epub 2011 Jan 18. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011. PMID: 21245320 Free PMC article.
-
Combination of VEGF(165)/Angiopoietin-1 gene and endothelial progenitor cells for therapeutic neovascularization.Eur J Pharmacol. 2007 Jul 30;568(1-3):222-30. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2007.04.047. Epub 2007 May 10. Eur J Pharmacol. 2007. PMID: 17553485
-
Complementary actions of VEGF and angiopoietin-1 on blood vessel growth and leakage.J Anat. 2002 Jun;200(6):575-80. doi: 10.1046/j.1469-7580.2002.00061.x. J Anat. 2002. PMID: 12162725 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Intravenous delivery of adeno-associated viral vector serotype 9 mediates effective gene expression in ischemic stroke lesion and brain angiogenic foci.Stroke. 2013 Jan;44(1):252-4. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.112.662965. Epub 2012 Dec 18. Stroke. 2013. PMID: 23250995 Free PMC article.
-
Glial regulation of the blood-brain barrier in health and disease.Semin Immunopathol. 2015 Nov;37(6):577-90. doi: 10.1007/s00281-015-0516-2. Epub 2015 Aug 6. Semin Immunopathol. 2015. PMID: 26245144 Review.
-
Know your tools--concordance of different methods for measuring brain volume change after ischemic stroke.Neuroradiology. 2015 Jul;57(7):685-95. doi: 10.1007/s00234-015-1522-8. Epub 2015 Apr 8. Neuroradiology. 2015. PMID: 25850861
-
The blood-brain barrier.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2015 Jan 5;7(1):a020412. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a020412. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2015. PMID: 25561720 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Injury and repair in the neurovascular unit.Neurol Res. 2012 May;34(4):325-30. doi: 10.1179/1743132812Y.0000000019. Neurol Res. 2012. PMID: 22643075 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Asahara T, Chen D, Takahashi T, Fujikawa K, Kearney M, Magner M, Yancopoulos GD, Isner JM. Tie2 receptor ligands, angiopoietin-1 and angiopoietin-2, modulate VEGF-induced postnatal neovascularization. Circ Res. 1998;83:233–240. - PubMed
-
- Baffert F, Le T, Thurston G, McDonald DM. Angiopoietin-1 decreases plasma leakage by reducing number and size of endothelial gaps in venules. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2006;290:H107–H118. - PubMed
-
- Beierle EA, Strande LF, Chen MK. VEGF upregulates Bcl-2 expression and is associated with decreased apoptosis in neuroblastoma cells. J Pediatr Surg. 2002;37:467–471. - PubMed
-
- Chan PH, Yang GY, Chen SF, Carlson E, Epstein CJ. Cold-induced brain edema and infarction are reduced in transgenic mice overexpressing CuZn-superoxide dismutase. Ann Neurol. 1991;29:482–486. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

