A hitchhiker's guide to mechanobiology
- PMID: 21763607
- PMCID: PMC3155761
- DOI: 10.1016/j.devcel.2011.06.015
A hitchhiker's guide to mechanobiology
Abstract
More than a century ago, it was proposed that mechanical forces could drive tissue formation. However, only recently with the advent of enabling biophysical and molecular technologies are we beginning to understand how individual cells transduce mechanical force into biochemical signals. In turn, this knowledge of mechanotransduction at the cellular level is beginning to clarify the role of mechanics in patterning processes during embryonic development. In this perspective, we will discuss current mechanotransduction paradigms, along with the technologies that have shaped the field of mechanobiology.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
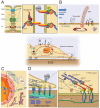
Similar articles
-
On growth and force: mechanical forces in development.Development. 2020 Feb 17;147(4):dev187302. doi: 10.1242/dev.187302. Development. 2020. PMID: 32066591
-
Mechanobiology of neural development.Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2020 Oct;66:104-111. doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2020.05.012. Epub 2020 Jul 17. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2020. PMID: 32687993 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Appreciating force and shape—the rise of mechanotransduction in cell biology.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2014 Dec;15(12):825-33. doi: 10.1038/nrm3903. Epub 2014 Oct 30. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2014. PMID: 25355507 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular Force Measurement with Tension Sensors.Annu Rev Biophys. 2021 May 6;50:595-616. doi: 10.1146/annurev-biophys-101920-064756. Epub 2021 Mar 12. Annu Rev Biophys. 2021. PMID: 33710908 Review.
-
A toolbox to explore the mechanics of living embryonic tissues.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2016 Jul;55:119-30. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2016.03.011. Epub 2016 Apr 6. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2016. PMID: 27061360 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Mechanical Tensions Regulate Gene Expression in the Xenopus laevis Axial Tissues.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jan 10;25(2):870. doi: 10.3390/ijms25020870. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38255964 Free PMC article.
-
Engineering physical microenvironments to study innate immune cell biophysics.APL Bioeng. 2022 Sep 20;6(3):031504. doi: 10.1063/5.0098578. eCollection 2022 Sep. APL Bioeng. 2022. PMID: 36156981 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Click-functionalized hydrogel design for mechanobiology investigations.Mol Syst Des Eng. 2021 Sep;6(9):670-707. doi: 10.1039/d1me00049g. Epub 2021 Jul 19. Mol Syst Des Eng. 2021. PMID: 36338897 Free PMC article.
-
Cytoskeleton Dynamics in Peripheral T Cell Lymphomas: An Intricate Network Sustaining Lymphomagenesis.Front Oncol. 2021 Apr 13;11:643620. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.643620. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33928032 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Engineering microscale topographies to control the cell-substrate interface.Biomaterials. 2012 Jul;33(21):5230-46. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2012.03.079. Epub 2012 Apr 21. Biomaterials. 2012. PMID: 22521491 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Alenghat FJ, Fabry B, Tsai KY, Goldmann WH, Ingber DE. Analysis of cell mechanics in single vinculin-deficient cells using a magnetic tweezer. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2000;277:93–99. - PubMed
-
- Altman D, Sweeney HL, Spudich JA. The mechanism of myosin VI translocation and its load-induced anchoring. Cell. 2004;116:737–749. - PubMed
-
- Arrenberg AB, Stainier DY, Baier H, Huisken J. Optogenetic control of cardiac function. Science. 2010;330:971–974. - PubMed
-
- Balaban NQ, Schwarz US, Riveline D, Goichberg P, Tzur G, Sabanay I, Mahalu D, Safran S, Bershadsky A, Addadi L, Geiger B. Force and focal adhesion assembly: a close relationship studied using elastic micropatterned substrates. Nat. Cell Biol. 2001;3:466–472. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

