Loss of PTB or negative regulation of Notch mRNA reveals distinct zones of Notch and actin protein accumulation in Drosophila embryo
- PMID: 21750738
- PMCID: PMC3130057
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0021876
Loss of PTB or negative regulation of Notch mRNA reveals distinct zones of Notch and actin protein accumulation in Drosophila embryo
Abstract
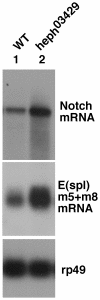
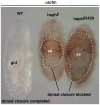
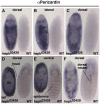
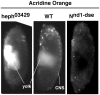
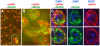
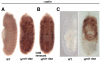
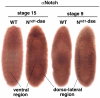
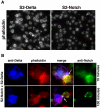
Polypyrimidine Tract Binding (PTB) protein is a regulator of mRNA processing and translation. Genetic screens and studies of wing and bristle development during the post-embryonic stages of Drosophila suggest that it is a negative regulator of the Notch pathway. How PTB regulates the Notch pathway is unknown. Our studies of Drosophila embryogenesis indicate that (1) the Notch mRNA is a potential target of PTB, (2) PTB and Notch functions in the dorso-lateral regions of the Drosophila embryo are linked to actin regulation but not their functions in the ventral region, and (3) the actin-related Notch activity in the dorso-lateral regions might require a Notch activity at or near the cell surface that is different from the nuclear Notch activity involved in cell fate specification in the ventral region. These data raise the possibility that the Drosophila embryo is divided into zones of different PTB and Notch activities based on whether or not they are linked to actin regulation. They also provide clues to the almost forgotten role of Notch in cell adhesion and reveal a role for the Notch pathway in cell fusions.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures





Similar articles
-
Hephaestus encodes a polypyrimidine tract binding protein that regulates Notch signalling during wing development in Drosophila melanogaster.Development. 2002 Dec;129(24):5553-66. doi: 10.1242/dev.00153. Development. 2002. PMID: 12421697
-
Drosophila polypyrimidine tract-binding protein (DmPTB) regulates dorso-ventral patterning genes in embryos.PLoS One. 2014 Jul 11;9(7):e98585. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0098585. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25014769 Free PMC article.
-
Notch and PKC are involved in formation of the lateral region of the dorso-ventral axis in Drosophila embryos.PLoS One. 2013 Jul 4;8(7):e67789. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0067789. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23861806 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic Regulation of Notch Signaling During Drosophila Development.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020;1218:59-75. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-34436-8_4. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020. PMID: 32060871 Review.
-
[Main components of gene network controlling development of dorsal appendages of egg chorion in Drosophila melanogaster].Ontogenez. 2012 May-Jun;43(3):163-74. Ontogenez. 2012. PMID: 22834131 Review. Russian.
Cited by
-
Fringe-positive Golgi outposts unite temporal Furin 2 convertase activity and spatial Delta signal to promote dendritic branch retraction.Cell Rep. 2022 Sep 20;40(12):111372. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2022.111372. Cell Rep. 2022. PMID: 36130510 Free PMC article.
-
Notch Intracellular Domain (NICD) Suppresses Long-Term Memory Formation in Adult Drosophila Flies.Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2015 Aug;35(6):763-8. doi: 10.1007/s10571-015-0183-9. Epub 2015 Mar 20. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2015. PMID: 25791355 Free PMC article.
-
High Throughput Sequencing Identifies Misregulated Genes in the Drosophila Polypyrimidine Tract-Binding Protein (hephaestus) Mutant Defective in Spermatogenesis.PLoS One. 2016 Mar 4;11(3):e0150768. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0150768. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 26942929 Free PMC article.
-
Notch-inducible hyperphosphorylated CREB and its ultradian oscillation in long-term memory formation.J Neurosci. 2013 Jul 31;33(31):12825-34. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0783-13.2013. J Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23904617 Free PMC article.
-
Bismuth Reduces Cisplatin-Induced Nephrotoxicity Via Enhancing Glutathione Conjugation and Vesicular Transport.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Jun 16;13:887876. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.887876. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35784696 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

