Interaction between ERAP1 and HLA-B27 in ankylosing spondylitis implicates peptide handling in the mechanism for HLA-B27 in disease susceptibility
- PMID: 21743469
- PMCID: PMC3640413
- DOI: 10.1038/ng.873
Interaction between ERAP1 and HLA-B27 in ankylosing spondylitis implicates peptide handling in the mechanism for HLA-B27 in disease susceptibility
Erratum in
- Nat Genet. 2011 Sep;43(9):919. Opperman, Udo [corrected to Oppermann, Udo]; Moutsianis, Loukas [corrected to Moutsianas, Loukas]
Abstract
Ankylosing spondylitis is a common form of inflammatory arthritis predominantly affecting the spine and pelvis that occurs in approximately 5 out of 1,000 adults of European descent. Here we report the identification of three variants in the RUNX3, LTBR-TNFRSF1A and IL12B regions convincingly associated with ankylosing spondylitis (P < 5 × 10(-8) in the combined discovery and replication datasets) and a further four loci at PTGER4, TBKBP1, ANTXR2 and CARD9 that show strong association across all our datasets (P < 5 × 10(-6) overall, with support in each of the three datasets studied). We also show that polymorphisms of ERAP1, which encodes an endoplasmic reticulum aminopeptidase involved in peptide trimming before HLA class I presentation, only affect ankylosing spondylitis risk in HLA-B27-positive individuals. These findings provide strong evidence that HLA-B27 operates in ankylosing spondylitis through a mechanism involving aberrant processing of antigenic peptides.
Figures
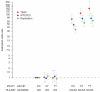
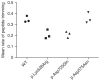
Comment in
-
Spondyloarthropathies: HLA-B27 and ERAP1 contribute to ankylosing spondylitis via aberrant peptide processing and presentation.Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2011 Aug 2;7(9):498. doi: 10.1038/nrrheum.2011.112. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2011. PMID: 21808290 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Association of ankylosing spondylitis with HLA-B27 and ERAP1: pathogenic role of antigenic peptide.Med Hypotheses. 2013 Jan;80(1):36-8. doi: 10.1016/j.mehy.2012.10.003. Epub 2012 Nov 1. Med Hypotheses. 2013. PMID: 23123136
-
ERAP1 in ankylosing spondylitis: genetics, biology and pathogenetic role.Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2013 Jul;25(4):419-25. doi: 10.1097/BOR.0b013e328362042f. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2013. PMID: 23656713 Review.
-
ERAP1/ERAP2 and RUNX3 polymorphisms are not associated with ankylosing spondylitis susceptibility in Chinese Han.Clin Exp Immunol. 2018 Jul;193(1):95-102. doi: 10.1111/cei.13121. Epub 2018 Mar 30. Clin Exp Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29480940 Free PMC article.
-
Combined effects of ankylosing spondylitis-associated ERAP1 polymorphisms outside the catalytic and peptide-binding sites on the processing of natural HLA-B27 ligands.J Biol Chem. 2014 Feb 14;289(7):3978-90. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.529610. Epub 2013 Dec 18. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 24352655 Free PMC article.
-
ERAP1 and ankylosing spondylitis.Curr Opin Immunol. 2013 Feb;25(1):97-102. doi: 10.1016/j.coi.2012.11.002. Curr Opin Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23452840 Review.
Cited by
-
Immune cell transcript modules reveal leukocyte heterogeneity in synovial biopsies of seronegative spondylarthropathy patients.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2014 Dec 19;15:446. doi: 10.1186/1471-2474-15-446. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2014. PMID: 25526985 Free PMC article.
-
IL-12 and IL-23 cytokines: from discovery to targeted therapies for immune-mediated inflammatory diseases.Nat Med. 2015 Jul;21(7):719-29. doi: 10.1038/nm.3895. Epub 2015 Jun 29. Nat Med. 2015. PMID: 26121196 Review.
-
Silencing or inhibition of endoplasmic reticulum aminopeptidase 1 (ERAP1) suppresses free heavy chain expression and Th17 responses in ankylosing spondylitis.Ann Rheum Dis. 2016 May;75(5):916-23. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2014-206996. Epub 2015 Jun 30. Ann Rheum Dis. 2016. PMID: 26130142 Free PMC article.
-
Large-scale integrative analysis of juvenile idiopathic arthritis for new insight into its pathogenesis.Arthritis Res Ther. 2024 Feb 10;26(1):47. doi: 10.1186/s13075-024-03280-2. Arthritis Res Ther. 2024. PMID: 38336809 Free PMC article.
-
Nonclassical MHC class Ib-restricted cytotoxic T cells monitor antigen processing in the endoplasmic reticulum.Nat Immunol. 2012 Apr 22;13(6):579-86. doi: 10.1038/ni.2282. Nat Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22522492 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Pedersen OB, et al. Ankylosing spondylitis in Danish and Norwegian twins: occurrence and the relative importance of genetic vs. environmental effectors in disease causation. Scand. J. Rheumatol. 2008;37:120–126. - PubMed
-
- Brown MA, et al. Susceptibility to ankylosing spondylitis in twins: the role of genes, HLA, and the environment. Arthritis Rheum. 1997;40:1823–1828. - PubMed
-
- Calin A, Marder A, Becks E, Burns T. Genetic differences between B27 positive patients with ankylosing spondylitis and B27 positive healthy controls. Arthritis Rheum. 1983;26:1460–1464. - PubMed
-
- van der Linden S, Valkenburg H, Cats A. The risk of developing ankylosing spondylitis in HLA-B27 positive individuals: a family and population study. Br. J. Rheumatol. 1983;22:18–19. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 083948/Z/07/Z/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- CAPMC/ CIHR/Canada
- G0800582/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- M01 RR000425/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- G0000934/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- ZIA AR041153-07/ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- 18797/ARC_/Arthritis Research UK/United Kingdom
- G19/2/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01-AR046208/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- 068545/Z/02/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- UL1RR024188/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- PDA/02/06/016/DH_/Department of Health/United Kingdom
- 19356/VAC_/Versus Arthritis/United Kingdom
- 076113/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- R01 AR046208/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- G0600705/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- 090532/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- 19536/ARC_/Arthritis Research UK/United Kingdom
- G0901310/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- 092809/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- ZIA AR041153/ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- MO1-RR00425/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

