Integrating mechanisms of pulmonary fibrosis
- PMID: 21727191
- PMCID: PMC3136685
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20110551
Integrating mechanisms of pulmonary fibrosis
Abstract
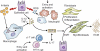
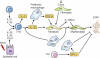
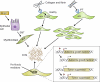
Pulmonary fibrosis is a highly heterogeneous and lethal pathological process with limited therapeutic options. Although research on the pathogenesis of pulmonary fibrosis has frequently focused on the mechanisms that regulate the proliferation, activation, and differentiation of collagen-secreting myofibroblasts, recent studies have identified new pathogenic mechanisms that are critically involved in the initiation and progression of fibrosis in a variety of settings. A more detailed and integrated understanding of the cellular and molecular mechanisms of pulmonary fibrosis could help pave the way for effective therapeutics for this devastating and complex disease.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Cellular players in lung fibrosis.Curr Pharm Des. 2012;18(27):4093-102. doi: 10.2174/138161212802430396. Curr Pharm Des. 2012. PMID: 22630084 Review.
-
Molecular mechanisms of pulmonary fibrosis and current treatment.Curr Mol Med. 2001 Nov;1(5):551-73. doi: 10.2174/1566524013363401. Curr Mol Med. 2001. PMID: 11899231 Review.
-
The role of TGF-beta in pulmonary fibrosis.Ciba Found Symp. 1991;157:194-207; discussion 207-11. doi: 10.1002/9780470514061.ch13. Ciba Found Symp. 1991. PMID: 1712697 Review.
-
The role of circulating mesenchymal progenitor cells, fibrocytes, in promoting pulmonary fibrosis.Trans Am Clin Climatol Assoc. 2009;120:49-59. Trans Am Clin Climatol Assoc. 2009. PMID: 19768162 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular mechanisms of and possible treatment strategies for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis.Curr Pharm Des. 2005;11(30):3943-71. doi: 10.2174/138161205774580561. Curr Pharm Des. 2005. PMID: 16305523 Review.
Cited by
-
Safety pharmacology of self-assembled-micelle inhibitory RNA-targeting amphiregulin (SAMiRNA-AREG), a novel siRNA nanoparticle platform.Toxicol Rep. 2021 Mar 31;8:839-845. doi: 10.1016/j.toxrep.2021.03.022. eCollection 2021. Toxicol Rep. 2021. PMID: 33912399 Free PMC article.
-
The Effect of Nintedanib on T-Cell Activation, Subsets and Functions.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2021 Mar 8;15:997-1011. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S288369. eCollection 2021. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2021. PMID: 33727792 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting the AXL Receptor in Combating Smoking-related Pulmonary Fibrosis.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2021 Jun;64(6):734-746. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2020-0303OC. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2021. PMID: 33730527 Free PMC article.
-
The impact of the myeloid response to radiation therapy.Clin Dev Immunol. 2013;2013:281958. doi: 10.1155/2013/281958. Epub 2013 Apr 7. Clin Dev Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23653658 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Delivery of RNAi Therapeutics to the Airways-From Bench to Bedside.Molecules. 2016 Sep 20;21(9):1249. doi: 10.3390/molecules21091249. Molecules. 2016. PMID: 27657028 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Asangani I.A., Rasheed S.A., Nikolova D.A., Leupold J.H., Colburn N.H., Post S., Allgayer H. 2008. MicroRNA-21 (miR-21) post-transcriptionally downregulates tumor suppressor Pdcd4 and stimulates invasion, intravasation and metastasis in colorectal cancer. Oncogene. 27:2128–2136 10.1038/sj.onc.1210856 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Atabai K., Jame S., Azhar N., Kuo A., Lam M., McKleroy W., Dehart G., Rahman S., Xia D.D., Melton A.C., et al. 2009. Mfge8 diminishes the severity of tissue fibrosis in mice by binding and targeting collagen for uptake by macrophages. J. Clin. Invest. 119:3713–3722 10.1172/JCI40053 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bauman K.A., Wettlaufer S.H., Okunishi K., Vannella K.M., Stoolman J.S., Huang S.K., Courey A.J., White E.S., Hogaboam C.M., Simon R.H., et al. 2010. The antifibrotic effects of plasminogen activation occur via prostaglandin E2 synthesis in humans and mice. J. Clin. Invest. 120:1950–1960 10.1172/JCI38369 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

