In vivo PET imaging of histone deacetylases by 18F-suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid (18F-SAHA)
- PMID: 21721525
- PMCID: PMC3150598
- DOI: 10.1021/jm200620f
In vivo PET imaging of histone deacetylases by 18F-suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid (18F-SAHA)
Abstract
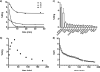
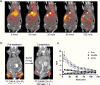
Histone deacetylases (HDACs) are a group of enzymes that modulate gene expression and cell state by deacetylation of both histone and non-histone proteins. A variety of HDAC inhibitors (HDACi) have already undergone clinical testing in cancer. Real-time in vivo imaging of HDACs and their inhibition would be invaluable; however, the development of appropriate imaging agents has remained a major challenge. Here, we describe the development and evaluation of (18)F-suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid ((18)F-SAHA 1a), a close analogue of the most clinically relevant HDAC inhibitor suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid (SAHA). We demonstrate that 1a has near identical biochemical activity profiles to that of SAHA and report findings from pharmacokinetic studies. Using a murine ovarian cancer model, we likewise show that HDAC inhibitor target binding efficacy can be quantitated within 24 h of administration. 1a thus represents the first (18)F-positron emission tomography (PET) HDAC imaging agent, which also exhibits low nanomolar potency and is pharmacologically analogous to a clinically relevant HDAC inhibitor.
Figures

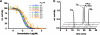
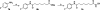

Similar articles
-
The synthesis and evaluation of N1-(4-(2-[18F]-fluoroethyl)phenyl)-N8-hydroxyoctanediamide ([18F]-FESAHA), a PET radiotracer designed for the delineation of histone deacetylase expression in cancer.Nucl Med Biol. 2011 Jul;38(5):683-96. doi: 10.1016/j.nucmedbio.2010.12.008. Epub 2011 Mar 3. Nucl Med Biol. 2011. PMID: 21718944 Free PMC article.
-
Defining the role of histone deacetylases in the inhibition of mammary carcinogenesis by dietary energy restriction (DER): effects of suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid (SAHA) and DER in a rat model.Cancer Prev Res (Phila). 2013 Apr;6(4):290-8. doi: 10.1158/1940-6207.CAPR-12-0449-T. Epub 2013 Jan 30. Cancer Prev Res (Phila). 2013. PMID: 23365133 Free PMC article.
-
Structural Requirements of Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors: SAHA Analogs Modified on the Hydroxamic Acid.Arch Pharm (Weinheim). 2016 May;349(5):373-82. doi: 10.1002/ardp.201500472. Epub 2016 Apr 9. Arch Pharm (Weinheim). 2016. PMID: 27062198 Free PMC article.
-
Zn(II)-dependent histone deacetylase inhibitors: suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid and trichostatin A.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2009 Apr;41(4):736-9. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2008.05.026. Epub 2008 Aug 3. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2009. PMID: 18725319 Review.
-
The Impact of Fluorination on the Design of Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors.Molecules. 2023 Feb 19;28(4):1973. doi: 10.3390/molecules28041973. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 36838960 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Development and Biological Evaluation of the First Highly Potent and Specific Benzamide-Based Radiotracer [18F]BA3 for Imaging of Histone Deacetylases 1 and 2 in Brain.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022 Mar 8;15(3):324. doi: 10.3390/ph15030324. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35337122 Free PMC article.
-
Convenient Entry to 18F-Labeled Amines through the Staudinger Reduction.European J Org Chem. 2019 Feb 28;2019(8):1722-1725. doi: 10.1002/ejoc.201801457. Epub 2019 Jan 22. European J Org Chem. 2019. PMID: 31007573 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in the Development of PET Ligands Targeting Histone Deacetylases for the Assessment of Neurodegenerative Diseases.Molecules. 2018 Jan 31;23(2):300. doi: 10.3390/molecules23020300. Molecules. 2018. PMID: 29385079 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Syntheses and discovery of a novel class of cinnamic hydroxamates as histone deacetylase inhibitors by multimodality molecular imaging in living subjects.Cancer Res. 2014 Dec 15;74(24):7475-86. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-14-0197. Epub 2014 Oct 15. Cancer Res. 2014. PMID: 25320008 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of [18F]-ATRi as PET tracer for in vivo imaging of ATR in mouse models of brain cancer.Nucl Med Biol. 2017 May;48:9-15. doi: 10.1016/j.nucmedbio.2017.01.002. Epub 2017 Jan 16. Nucl Med Biol. 2017. PMID: 28157626 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Minucci S, Pelicci PG. Histone deacetylase inhibitors and the promise of epigenetic (and more) treatments for cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer. 2006;6:38–51. - PubMed
-
- Choudhary C, Kumar C, Gnad F, Nielsen ML, Rehman M, Walther TC, Olsen JV, Mann M. Lysine acetylation targets protein complexes and co-regulates major cellular functions. Science. 2009;325:834–840. - PubMed
-
- Gregoretti I, Lee Y-M, Goodson HV. Molecular Evolution of the Histone Deacetylase Family: Functional Implications of Phylogenetic Analysis. J. Mol. Biol. 2004;338:17–31. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- U24 CA092782/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U24 CA092782-09/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 CA079443/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 CA086355/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 CA086355-09/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- T32CA079443/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P50CA086355/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 CA079443-11A1/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 CA079443-10/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U24CA092782/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 CA086355-10/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U24 CA092782-10/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Chemical Information

