Functionally biased modulation of A(3) adenosine receptor agonist efficacy and potency by imidazoquinolinamine allosteric enhancers
- PMID: 21718691
- PMCID: PMC3152598
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bcp.2011.06.017
Functionally biased modulation of A(3) adenosine receptor agonist efficacy and potency by imidazoquinolinamine allosteric enhancers
Abstract
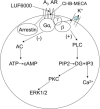
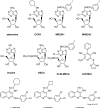
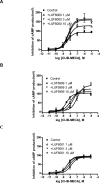
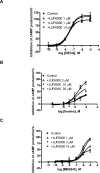
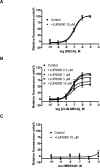
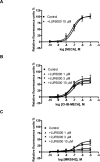
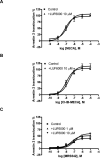
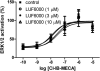
Allosteric modulators for the G(i)-coupled A(3) adenosine receptor (AR) are of considerable interest as therapeutic agents and as pharmacological tools to probe various signaling pathways. In this study, we initially characterized the effects of several imidazoquinolinamine allosteric modulators (LUF5999, LUF6000 and LUF6001) on the human A(3) AR stably expressed in CHO cells using a cyclic AMP functional assay. These modulators were found to affect efficacy and potency of the agonist Cl-IB-MECA differently. LUF5999 (2-cyclobutyl derivative) enhanced efficacy but decreased potency. LUF6000 (2-cyclohexyl derivative) enhanced efficacy without affecting potency. LUF6001 (2-H derivative) decreased both efficacy and potency. We further compared the agonist enhancing effects of LUF6000 in several other A(3) AR-mediated events. It was shown that although LUF6000 behaved somewhat differently in various signaling pathways, it was more effective in enhancing the effects of low-efficacy than of high-efficacy agonists. In an assay of cyclic AMP accumulation, LUF6000 enhanced the efficacy of all agonists examined, but in the membrane hyperpolarization assay, it only enhanced the efficacy of partial agonists. In calcium mobilization, LUF6000 did not affect the efficacy of the full agonist NECA but was able to switch the nucleoside antagonist MRS542 into a partial agonist. In translocation of β-arrestin2, the agonist-enhancing effect LUF6000 was not pronounced. In an assay of ERK1/2 phosphorylation LUF6000 did not show any effect on the efficacy of Cl-IB-MECA. The differential effects of LUF6000 on the efficacy and potency of the agonist Cl-IB-MECA in various signaling pathway were interpreted quantitatively using a mathematical model.
Published by Elsevier Inc.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Genetic and functional modulation by agonist MRS5698 and allosteric enhancer LUF6000 at the native A3 adenosine receptor in HL-60 cells.Purinergic Signal. 2024 Oct;20(5):559-570. doi: 10.1007/s11302-024-09992-z. Epub 2024 Feb 28. Purinergic Signal. 2024. PMID: 38416332 Free PMC article.
-
Flexible modulation of agonist efficacy at the human A3 adenosine receptor by the imidazoquinoline allosteric enhancer LUF6000.BMC Pharmacol. 2008 Dec 12;8:20. doi: 10.1186/1471-2210-8-20. BMC Pharmacol. 2008. PMID: 19077268 Free PMC article.
-
Species differences and mechanism of action of A3 adenosine receptor allosteric modulators.Purinergic Signal. 2018 Mar;14(1):59-71. doi: 10.1007/s11302-017-9592-1. Epub 2017 Nov 23. Purinergic Signal. 2018. PMID: 29170977 Free PMC article.
-
A3 Adenosine Receptors as Modulators of Inflammation: From Medicinal Chemistry to Therapy.Med Res Rev. 2018 Jul;38(4):1031-1072. doi: 10.1002/med.21456. Epub 2017 Jul 6. Med Res Rev. 2018. PMID: 28682469 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Partial agonists for A(3) adenosine receptors.Curr Top Med Chem. 2004;4(8):855-62. doi: 10.2174/1568026043450989. Curr Top Med Chem. 2004. PMID: 15078216 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
SPMs exert anti-inflammatory and pro-resolving effects through positive allosteric modulation of the prostaglandin EP4 receptor.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024 Oct 8;121(41):e2407130121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2407130121. Epub 2024 Oct 4. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024. PMID: 39365815 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging paradigms in GPCR allostery: implications for drug discovery.Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2013 Aug;12(8):630-44. doi: 10.1038/nrd4052. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2013. PMID: 23903222 Review.
-
New paradigms in GPCR drug discovery.Biochem Pharmacol. 2015 Dec 15;98(4):541-55. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2015.08.085. Epub 2015 Aug 8. Biochem Pharmacol. 2015. PMID: 26265138 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genetic and functional modulation by agonist MRS5698 and allosteric enhancer LUF6000 at the native A3 adenosine receptor in HL-60 cells.Purinergic Signal. 2024 Oct;20(5):559-570. doi: 10.1007/s11302-024-09992-z. Epub 2024 Feb 28. Purinergic Signal. 2024. PMID: 38416332 Free PMC article.
-
New paradigms in adenosine receptor pharmacology: allostery, oligomerization and biased agonism.Br J Pharmacol. 2018 Nov;175(21):4036-4046. doi: 10.1111/bph.14337. Epub 2018 Jun 21. Br J Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 29679502 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Yan L, Burbiel JC, Maass A, Müller CE. Adenosine receptor agonists: from basic medicinal chemistry to clinical development. Expert Opin Emerg Drugs. 2003;8:537–76. - PubMed
-
- Borea PA, Gessi S, Bar-Yehuda S, Fishman P. A3 adenosine receptor: pharmacology and role in disease. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2009:297–327. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

