The RhoA-Rok-myosin II pathway is involved in extracellular matrix-mediated regulation of prolactin signaling in mammary epithelial cells
- PMID: 21678418
- PMCID: PMC3675639
- DOI: 10.1002/jcp.22886
The RhoA-Rok-myosin II pathway is involved in extracellular matrix-mediated regulation of prolactin signaling in mammary epithelial cells
Abstract
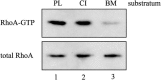
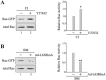
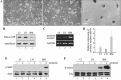
In mammary epithelial cells (MECs), prolactin-induced signaling and gene expression requires integrin-mediated cell adhesion to basement membrane (BM). In the absence of proper cell-BM interactions, for example, culturing cells on collagen-coated plastic dishes, signal propagation is substantially impaired. Here we demonstrate that the RhoA-Rok-myosin II pathway accounts for the ineffectiveness of prolactin signaling in MECs cultured on collagen I. Under these culture conditions, the RhoA pathway is activated, leading to downregulation of prolactin receptor expression and reduced prolactin signaling. Enforced activation of RhoA in MECs cultured on BM suppresses prolactin receptor levels, and prevents prolactin-induced Stat5 tyrosine phosphorylation and β-casein expression. Overexpression of dominant negative RhoA in MECs cultured on collagen I, or inhibiting Rok activity, increases prolactin receptor expression, and enhances prolactin signaling. In addition, inhibition of myosin II ATPase activity by blebbistatin also exerts a beneficial effect on prolactin receptor expression and prolactin signaling, suggesting that tension exerted by the collagen substratum, in collaboration with the RhoA-Rok-myosin II pathway, contributes to the failure of prolactin signaling. Furthermore, MECs cultured on laminin-coated plastic have similar morphology and response to prolactin as those cultured on collagen I. They display high levels of RhoA activity and are inefficient in prolactin signaling, stressing the importance of matrix stiffness in signal transduction. Our results reveal that RhoA has a central role in determining the fate decisions of MECs in response to cell-matrix interactions.
Copyright © 2011 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures

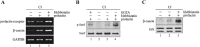
Similar articles
-
Extracellular matrix controls insulin signaling in mammary epithelial cells through the RhoA/Rok pathway.J Cell Physiol. 2009 Aug;220(2):476-84. doi: 10.1002/jcp.21793. J Cell Physiol. 2009. PMID: 19391109
-
In Drosophila, RhoGEF2 cooperates with activated Ras in tumorigenesis through a pathway involving Rho1-Rok-Myosin-II and JNK signalling.Dis Model Mech. 2013 May;6(3):661-78. doi: 10.1242/dmm.010066. Epub 2013 Jan 11. Dis Model Mech. 2013. PMID: 23324326 Free PMC article.
-
Zinc Finger Homeodomain Factor Zfhx3 Is Essential for Mammary Lactogenic Differentiation by Maintaining Prolactin Signaling Activity.J Biol Chem. 2016 Jun 10;291(24):12809-12820. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M116.719377. Epub 2016 Apr 20. J Biol Chem. 2016. PMID: 27129249 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular matrix signaling from the cellular membrane skeleton to the nuclear skeleton: a model of gene regulation.Recent Prog Horm Res. 1996;51:417-32. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1996. PMID: 8701089 Free PMC article. Review.
-
From mechanical force to RhoA activation.Biochemistry. 2012 Sep 25;51(38):7420-32. doi: 10.1021/bi300758e. Epub 2012 Sep 10. Biochemistry. 2012. PMID: 22931484 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
IL-4 and IL-13 Promote Proliferation of Mammary Epithelial Cells through STAT6 and IRS-1.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Nov 5;22(21):12008. doi: 10.3390/ijms222112008. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34769439 Free PMC article.
-
Epithelial polarization in 3D matrix requires DDR1 signaling to regulate actomyosin contractility.Life Sci Alliance. 2019 Feb 13;2(1):e201800276. doi: 10.26508/lsa.201800276. Print 2019 Feb. Life Sci Alliance. 2019. PMID: 30760555 Free PMC article.
-
Culture Models to Investigate Mechanisms of Milk Production and Blood-Milk Barrier in Mammary Epithelial Cells: a Review and a Protocol.J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 2023 May 1;28(1):8. doi: 10.1007/s10911-023-09536-y. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 2023. PMID: 37126158 Free PMC article. Review.
-
How integrins control breast biology.Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2013 Oct;25(5):633-41. doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2013.06.010. Epub 2013 Jul 22. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2013. PMID: 23886475 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prolactin signaling through focal adhesion complexes is amplified by stiff extracellular matrices in breast cancer cells.Oncotarget. 2016 Jul 26;7(30):48093-48106. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.10137. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27344177 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arthur WT, Petch LA, Burridge K. Integrin engagement suppresses RhoA activity via a c-Src-dependent mechanism. Curr Biol. 2000;10:719–722. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

