Splenectomy exacerbates lung injury after ischemic acute kidney injury in mice
- PMID: 21677145
- PMCID: PMC3191803
- DOI: 10.1152/ajprenal.00107.2011
Splenectomy exacerbates lung injury after ischemic acute kidney injury in mice
Abstract
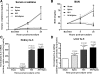
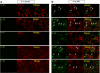
Patients with acute kidney injury (AKI) have increased serum proinflammatory cytokines and an increased occurrence of respiratory complications. The aim of the present study was to examine the effect of renal and extrarenal cytokine production on AKI-mediated lung injury in mice. C57Bl/6 mice underwent sham surgery, splenectomy, ischemic AKI, or ischemic AKI with splenectomy and kidney, spleen, and liver cytokine mRNA, serum cytokines, and lung injury were examined. The proinflammatory cytokines IL-6, CXCL1, IL-1β, and TNF-α were increased in the kidney, spleen, and liver within 6 h of ischemic AKI. Since splenic proinflammatory cytokines were increased, we hypothesized that splenectomy would protect against AKI-mediated lung injury. On the contrary, splenectomy with AKI resulted in increased serum IL-6 and worse lung injury as judged by increased lung capillary leak, higher lung myeloperoxidase activity, and higher lung CXCL1 vs. AKI alone. Splenectomy itself was not associated with increased serum IL-6 or lung injury vs. sham. To investigate the mechanism of the increased proinflammatory response, splenic production of the anti-inflammatory cytokine IL-10 was determined and was markedly upregulated. To confirm that splenic IL-10 downregulates the proinflammatory response of AKI, IL-10 was administered to splenectomized mice with AKI, which reduced serum IL-6 and improved lung injury. Our data demonstrate that AKI in the absence of a counter anti-inflammatory response by splenic IL-10 production results in an exuberant proinflammatory response and lung injury.
Figures

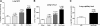
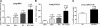
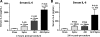
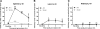

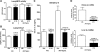
Similar articles
-
Circulating IL-6 mediates lung injury via CXCL1 production after acute kidney injury in mice.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2012 Sep 15;303(6):F864-72. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00025.2012. Epub 2012 Jul 11. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2012. PMID: 22791336 Free PMC article.
-
Circulating IL-6 upregulates IL-10 production in splenic CD4+ T cells and limits acute kidney injury-induced lung inflammation.Kidney Int. 2017 May;91(5):1057-1069. doi: 10.1016/j.kint.2016.12.014. Epub 2017 Feb 14. Kidney Int. 2017. PMID: 28214022
-
The inflammatory response in blood and in remote organs following acute kidney injury.APMIS. 2014 May;122(5):399-404. doi: 10.1111/apm.12157. Epub 2013 Sep 6. APMIS. 2014. PMID: 24033773
-
Acute Kidney Injury and Organ Dysfunction: What Is the Role of Uremic Toxins?Toxins (Basel). 2021 Aug 9;13(8):551. doi: 10.3390/toxins13080551. Toxins (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34437422 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Acute Kidney Injury in COVID-19: a Brief Review.Indian J Surg. 2021 Apr;83(2):398-402. doi: 10.1007/s12262-020-02697-8. Epub 2021 Apr 23. Indian J Surg. 2021. PMID: 33935396 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
IL-6-mediated hepatocyte production is the primary source of plasma and urine neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin during acute kidney injury.Kidney Int. 2020 May;97(5):966-979. doi: 10.1016/j.kint.2019.11.013. Epub 2019 Nov 28. Kidney Int. 2020. PMID: 32081304 Free PMC article.
-
Spleen-derived interleukin-10 downregulates the severity of high-fat diet-induced non-alcoholic fatty pancreas disease.PLoS One. 2012;7(12):e53154. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0053154. Epub 2012 Dec 28. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23285260 Free PMC article.
-
IL-6 mediates the hepatic acute phase response after prerenal azotemia in a clinically defined murine model.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2023 Sep 1;325(3):F328-F344. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00267.2022. Epub 2023 Jul 20. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2023. PMID: 37471421 Free PMC article.
-
A Decline in Intraoperative Renal Near-Infrared Spectroscopy Is Associated With Adverse Outcomes in Children Following Cardiac Surgery.Pediatr Crit Care Med. 2016 Apr;17(4):342-9. doi: 10.1097/PCC.0000000000000674. Pediatr Crit Care Med. 2016. PMID: 26914625 Free PMC article.
-
Xenobiotic metabolism: the effect of acute kidney injury on non-renal drug clearance and hepatic drug metabolism.Int J Mol Sci. 2014 Feb 13;15(2):2538-53. doi: 10.3390/ijms15022538. Int J Mol Sci. 2014. PMID: 24531139 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Aki K, Shimizu A, Masuda Y, Kuwahara N, Arai T, Ishikawa A, Fujita E, Mii A, Natori Y, Fukunaga Y, Fukuda Y. ANG II receptor blockade enhances anti-inflammatory macrophages in anti-glomerular basement membrane glomerulonephritis. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 298: F870–F882, 2010 - PubMed
-
- Bonventre JV, Zuk A. Ischemic acute renal failure: an inflammatory disease? Kidney Int 66: 480–485, 2004 - PubMed
-
- Chertow GM, Levy EM, Hammermeister KE, Grover F, Daley J. Independent association between acute renal failure and mortality following cardiac surgery. Am J Med 104: 343–348, 1998 - PubMed
-
- Daha MR, van Kooten C. Is the proximal tubular cell a proinflammatory cell? Nephrol Dial Transplant 15, Suppl 6: 41–43, 2000 - PubMed
-
- Faith M, Sukumaran A, Pulimood AB, Jacob M. How reliable an indicator of inflammation is myeloperoxidase activity? Clin Chim Acta 396: 23–25, 2008 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

