Calpain chronicle--an enzyme family under multidisciplinary characterization
- PMID: 21670566
- PMCID: PMC3153876
- DOI: 10.2183/pjab.87.287
Calpain chronicle--an enzyme family under multidisciplinary characterization
Abstract
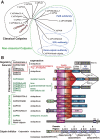
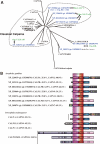
Calpain is an intracellular Ca2+-dependent cysteine protease (EC 3.4.22.17; Clan CA, family C02) discovered in 1964. It was also called CANP (Ca2+-activated neutral protease) as well as CASF, CDP, KAF, etc. until 1990. Calpains are found in almost all eukaryotes and a few bacteria, but not in archaebacteria. Calpains have a limited proteolytic activity, and function to transform or modulate their substrates' structures and activities; they are therefore called, "modulator proteases." In the human genome, 15 genes--CAPN1, CAPN2, etc.--encode a calpain-like protease domain. Their products are calpain homologs with divergent structures and various combinations of functional domains, including Ca2+-binding and microtubule-interaction domains. Genetic studies have linked calpain deficiencies to a variety of defects in many different organisms, including lethality, muscular dystrophies, gastropathy, and diabetes. This review of the study of calpains focuses especially on recent findings about their structure-function relationships. These discoveries have been greatly aided by the development of 3D structural studies and genetic models.
Figures



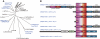






Similar articles
-
Impact of genetic insights into calpain biology.J Biochem. 2011 Jul;150(1):23-37. doi: 10.1093/jb/mvr070. Epub 2011 May 24. J Biochem. 2011. PMID: 21610046 Review.
-
Expanding members and roles of the calpain superfamily and their genetically modified animals.Exp Anim. 2010;59(5):549-66. doi: 10.1538/expanim.59.549. Exp Anim. 2010. PMID: 21030783 Review.
-
Calpains: an elaborate proteolytic system.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012 Jan;1824(1):224-36. doi: 10.1016/j.bbapap.2011.08.005. Epub 2011 Aug 16. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012. PMID: 21864727 Review.
-
Characterisation of capn1, capn2-like, capn3 and capn11 genes in Atlantic halibut (Hippoglossus hippoglossus L.): Transcriptional regulation across tissues and in skeletal muscle at distinct nutritional states.Gene. 2010 Mar 15;453(1-2):45-58. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2010.01.002. Epub 2010 Jan 20. Gene. 2010. PMID: 20093171
-
Both the conserved and the unique gene structure of stomach-specific calpains reveal processes of calpain gene evolution.J Mol Evol. 2001 Sep;53(3):191-203. doi: 10.1007/s002390010209. J Mol Evol. 2001. PMID: 11523006
Cited by
-
Expression of calpain-calpastatin system (CCS) member proteins in human lymphocytes of young and elderly individuals; pilot baseline data for the CALPACENT project.Immun Ageing. 2013 Jul 8;10(1):27. doi: 10.1186/1742-4933-10-27. Immun Ageing. 2013. PMID: 23835405 Free PMC article.
-
Massive expansion of the calpain gene family in unicellular eukaryotes.BMC Evol Biol. 2012 Sep 29;12:193. doi: 10.1186/1471-2148-12-193. BMC Evol Biol. 2012. PMID: 23020305 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular CIRP Induces Calpain Activation in Neurons via PLC-IP3-Dependent Calcium Pathway.Mol Neurobiol. 2023 Jun;60(6):3311-3328. doi: 10.1007/s12035-023-03273-3. Epub 2023 Feb 28. Mol Neurobiol. 2023. PMID: 36853429 Free PMC article.
-
GWAS identifies four novel eosinophilic esophagitis loci.Nat Commun. 2014 Nov 19;5:5593. doi: 10.1038/ncomms6593. Nat Commun. 2014. PMID: 25407941 Free PMC article.
-
Brain injury-induced proteolysis is reduced in a novel calpastatin-overexpressing transgenic mouse.J Neurochem. 2013 Jun;125(6):909-20. doi: 10.1111/jnc.12144. Epub 2013 Feb 3. J Neurochem. 2013. PMID: 23305291 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Guroff G. (1964) A neutral calcium-activated proteinase from the soluble fraction of rat brain. J. Biol. Chem. 239, 149–155 - PubMed
-
- Lazarovici P. (2000) Obituary: Dr. Gordon Guroff (1933–1999). J. Mol. Neurosci. 14, 1–2 - PubMed
-
- Huston R.B., Krebs E.G. (1968) Activation of skeletal muscle phosphorylase kinase by Ca2+. II. Identification of the kinase activating factor as a proteolytic enzyme. Biochemistry 7, 2116–2122 - PubMed
-
- Meyer W.L., Fischer E.H., Krebs E.G. (1964) Activation of skeletal muscle phosphorylase kinase by Ca2+. Biochemistry 3, 1033–1039 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

