Prognostic role of FOXP3+ regulatory T cells infiltrating human carcinomas: the paradox of colorectal cancer
- PMID: 21644034
- PMCID: PMC11028605
- DOI: 10.1007/s00262-011-1046-y
Prognostic role of FOXP3+ regulatory T cells infiltrating human carcinomas: the paradox of colorectal cancer
Abstract
The accumulation of regulatory T cells (Tregs) at high density in various human carcinomas is generally associated with a poor prognosis, as expected from their capacity to inhibit antitumor immunity. Surprisingly, in patients bearing colorectal carcinoma (CRC), high regulatory T-cell infiltration is associated with a favorable prognosis, as shown by the analysis of seven clinical studies. To explain this paradox, we emphasize a putative role of the dense microbiological flora present in the large intestine with a trend toward translocation through the tumor. This microbiological hazard requires a T-cell-mediated inflammatory anti-microbial response that involves Th17 cells and can thereby promote cancer growth. This Th17-cell-dependent proinflammatory and tumor-enhancing response can be attenuated by Tregs, thus constituting a possible explanation for their favorable role in CRC prognosis. The link between a high density of FOXP3-positive cells in CRC immune infiltrates and favorable prognosis should lead us to consider tumor infiltrating Tregs as allies to be respected, rather than enemies to be destroyed during trials of CRC treatment.
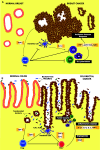
Figures
Similar articles
-
Two FOXP3(+)CD4(+) T cell subpopulations distinctly control the prognosis of colorectal cancers.Nat Med. 2016 Jun;22(6):679-84. doi: 10.1038/nm.4086. Epub 2016 Apr 25. Nat Med. 2016. PMID: 27111280
-
Tumor-infiltrating FOXP3+ T regulatory cells show strong prognostic significance in colorectal cancer.J Clin Oncol. 2009 Jan 10;27(2):186-92. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2008.18.7229. Epub 2008 Dec 8. J Clin Oncol. 2009. PMID: 19064967
-
OX40 expression enhances the prognostic significance of CD8 positive lymphocyte infiltration in colorectal cancer.Oncotarget. 2015 Nov 10;6(35):37588-99. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.5940. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 26439988 Free PMC article.
-
Tumor Infiltrating Regulatory T Cells in Sporadic and Colitis-Associated Colorectal Cancer: The Red Little Riding Hood and the Wolf.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Sep 14;21(18):6744. doi: 10.3390/ijms21186744. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32937953 Free PMC article. Review.
-
FOXP3+ Tregs: heterogeneous phenotypes and conflicting impacts on survival outcomes in patients with colorectal cancer.Immunol Res. 2015 Mar;61(3):338-47. doi: 10.1007/s12026-014-8616-y. Immunol Res. 2015. PMID: 25608795 Review.
Cited by
-
Crucial Contributions by T Lymphocytes (Effector, Regulatory, and Checkpoint Inhibitor) and Cytokines (TH1, TH2, and TH17) to a Pathological Complete Response Induced by Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy in Women with Breast Cancer.J Immunol Res. 2016;2016:4757405. doi: 10.1155/2016/4757405. Epub 2016 Sep 29. J Immunol Res. 2016. PMID: 27777963 Free PMC article.
-
Contrasting Prognostic Effects of Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocyte Density in Cardia and Non-cardia Gastric Adenocarcinomas.J Gastric Cancer. 2020 Jun;20(2):190-201. doi: 10.5230/jgc.2020.20.e21. Epub 2020 Jun 19. J Gastric Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32596002 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic Role of Immune Markers in Triple Negative Breast Carcinoma.Pathol Oncol Res. 2020 Oct;26(4):2733-2745. doi: 10.1007/s12253-020-00874-4. Epub 2020 Jul 17. Pathol Oncol Res. 2020. PMID: 32681436
-
Immune Cell Infiltration in the Microenvironment of Liver Oligometastasis from Colorectal Cancer: Intratumoural CD8/CD3 Ratio Is a Valuable Prognostic Index for Patients Undergoing Liver Metastasectomy.Cancers (Basel). 2019 Dec 2;11(12):1922. doi: 10.3390/cancers11121922. Cancers (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31810350 Free PMC article.
-
Deciphering the influence of urinary microbiota on FoxP3+ regulatory T cell infiltration and prognosis in Chinese patients with non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer.Hum Cell. 2022 Mar;35(2):511-521. doi: 10.1007/s13577-021-00659-0. Epub 2022 Jan 15. Hum Cell. 2022. PMID: 35032011
References
-
- Sakaguchi S, Sakaguchi N, Asano M, Itoh M, Toda M. Immunologic self-tolerance maintained by activated T cells expressing IL-2 receptor alpha-chains (CD25). Breakdown of a single mechanism of self-tolerance causes various autoimmune diseases. J Immunol. 1995;155:1151–1164. - PubMed
-
- Stephens LA, Mason D. CD25 is a marker for CD4+ thymocytes that prevent autoimmune diabetes in rats, but peripheral T cells with this function are found in both CD25+ and CD25− subpopulations. J Immunol. 2000;165:3105–3110. - PubMed
-
- Liyanage UK, Moore TT, Joo HG, Tanaka Y, Herrmann V, Doherty G, Drebin JA, Strasberg SM, Eberlein TJ, Goedegebuure PS, Linehan DC. Prevalence of regulatory T cells is increased in peripheral blood and tumor microenvironment of patients with pancreas or breast adenocarcinoma. J Immunol. 2002;169:2756–2761. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

