MicroRNAs 130a/b are regulated by BCR-ABL and downregulate expression of CCN3 in CML
- PMID: 21638198
- PMCID: PMC3145871
- DOI: 10.1007/s12079-011-0139-x
MicroRNAs 130a/b are regulated by BCR-ABL and downregulate expression of CCN3 in CML
Abstract
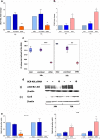
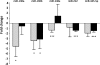
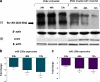
Chronic Myeloid Leukaemia (CML) is a myeloproliferative disorder characterized by the expression of the oncoprotein, Bcr-Abl kinase. CCN3 normally functions as a negative growth regulator, but it is downregulated in CML, the mechanism of which is not known. MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are small non-coding RNAs, which negatively regulate protein translation by binding to the complimentary sequences of the 3' UTR of messenger RNAs. Deregulated miRNA expression has emerged as a hallmark of cancer. In CML, BCR-ABL upregulates oncogenic miRNAs and downregulates tumour suppressor miRNAs favouring leukaemic transformation. We report here that the downregulation of CCN3 in CML is mediated by BCR-ABL dependent miRNAs. Using the CML cell line K562, we profiled miRNAs, which are BCR-ABL dependent by transfecting K562 cells with anti-BCR-ABL siRNA. MiRNA expression levels were quantified using the Taqman Low Density miRNA array platform. From the miRNA target prediction databases we identified miRNAs that could potentially bind to CCN3 mRNA and reduce expression. Of these, miR-130a, miR-130b, miR-148a, miR-212 and miR-425-5p were significantly reduced on BCR-ABL knockdown, with both miR-130a and miR-130b decreasing the most within 24 h of siRNA treatment. Transfection of mature sequences of miR-130a and miR-130b individually into BCR-ABL negative HL60 cells resulted in a decrease of both CCN3 mRNA and protein. The reduction in CCN3 was greatest with overexpression of miR-130a whereas miR-130b overexpression resulted only in marginal repression of CCN3. This study shows that miRNAs modulate CCN3 expression. Deregulated miRNA expression initiated by BCR-ABL may be one mechanism of downregulating CCN3 whereby leukaemic cells evade negative growth regulation.
Figures
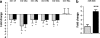
Similar articles
-
ApoptomiRs expression modulated by BCR-ABL is linked to CML progression and imatinib resistance.Blood Cells Mol Dis. 2014 Jun-Aug;53(1-2):47-55. doi: 10.1016/j.bcmd.2014.02.008. Epub 2014 Mar 11. Blood Cells Mol Dis. 2014. PMID: 24629639
-
A novel mechanism for BCR-ABL action: stimulated secretion of CCN3 is involved in growth and differentiation regulation.Blood. 2006 Sep 1;108(5):1716-23. doi: 10.1182/blood-2006-04-016113. Epub 2006 May 2. Blood. 2006. PMID: 16670264
-
Restoration of miR-424 suppresses BCR-ABL activity and sensitizes CML cells to imatinib treatment.Cancer Lett. 2015 May 1;360(2):245-56. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2015.02.031. Epub 2015 Feb 16. Cancer Lett. 2015. PMID: 25697481
-
CCN3: a key growth regulator in Chronic Myeloid Leukaemia.J Cell Commun Signal. 2009 Jun;3(2):115-24. doi: 10.1007/s12079-009-0058-2. Epub 2009 Jul 22. J Cell Commun Signal. 2009. PMID: 19623482 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of the MIR155 host gene in physiological and pathological processes.Gene. 2013 Dec 10;532(1):1-12. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2012.12.009. Epub 2012 Dec 14. Gene. 2013. PMID: 23246696 Review.
Cited by
-
CCN2 (Cellular Communication Network factor 2) in the bone marrow microenvironment, normal and malignant hematopoiesis.J Cell Commun Signal. 2021 Mar;15(1):25-56. doi: 10.1007/s12079-020-00602-2. Epub 2021 Jan 11. J Cell Commun Signal. 2021. PMID: 33428075 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cellular and Molecular Networks in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia: The Leukemic Stem, Progenitor and Stromal Cell Interplay.Curr Drug Targets. 2017;18(4):377-388. doi: 10.2174/1389450117666160615074120. Curr Drug Targets. 2017. PMID: 27307150 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identifying factors associated with the direction and significance of microRNA tumor-normal expression differences in colorectal cancer.BMC Cancer. 2017 Oct 30;17(1):707. doi: 10.1186/s12885-017-3690-x. BMC Cancer. 2017. PMID: 29084506 Free PMC article.
-
The oncogenic role of microRNA-130a/301a/454 in human colorectal cancer via targeting Smad4 expression.PLoS One. 2013;8(2):e55532. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0055532. Epub 2013 Feb 5. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23393589 Free PMC article.
-
A cellular regulator of the niche: telocyte.Tissue Barriers. 2023 Oct 2;11(4):2131955. doi: 10.1080/21688370.2022.2131955. Epub 2022 Oct 11. Tissue Barriers. 2023. PMID: 36218299 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bhatia R, Holtz M, Niu N, Gray R, Snyder DS, Sawyers CL, Arber DA, Slovak ML, Forman SJ. Persistence of malignant hematopoietic progenitors in chronic myelogenous leukemia patients in complete cytogenetic remission following imatinib mesylate treatment. Blood. 2003;101:4701–4707. doi: 10.1182/blood-2002-09-2780. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Deininger MW, Goldman JM, Melo JV. The molecular biology of chronic myeloid leukemia. Blood. 2000;10:3343–3356. - PubMed
-
- Duisters RF, Tijsen AJ, Schroen B, Leenders JJ, Lentink V, Made I, Herias V, Leeuwen RE, Schellings MW, Barenbrug P, Maessen JG, Heymans S, Pinto YM, Creemers EE. miR-133 and miR-30 regulate connective tissue growth factor: implications for a role of microRNAs in myocardial matrix remodeling. Circ Res. 2009;104:170–178. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.108.182535. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

