Angiotensin II evokes sensory long-term facilitation of the carotid body via NADPH oxidase
- PMID: 21636565
- PMCID: PMC3191792
- DOI: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00022.2011
Angiotensin II evokes sensory long-term facilitation of the carotid body via NADPH oxidase
Abstract
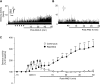
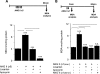
We previously reported that reactive oxygen species generated by NADPH oxidase 2 (Nox2) induces sensory plasticity of the carotid body, manifested as a progressive increase in baseline sensory activity or sensory long-term facilitation (sLTF). ANG II, a peptide generated within the carotid body, is a potent activator of Nox2. In the present study, we tested the hypothesis that ANG II evokes sLTF of the carotid body via Nox2 activation. Experiments were performed on carotid bodies ex vivo from adult rats and mice. Sensory activity was recorded from the carotid sinus nerve. Repetitive (5 times for 30 s each at 5-min intervals), but not continuous (for 150 s), application of 60 pM ANG II evoked robust sLTF of the carotid body. ACh, ATP, substance P, and KCl, when applied repetitively, stimulated the carotid body but did not evoke sLTF. Reactive oxygen species levels increased in response to repetitive applications of ANG II, and this effect was blocked by apocynin, an inhibitor of Nox2, as well as losartan, an angiotensin type 1 (AT(1)) receptor antagonist. Losartan, apocynin, and 4-(2-aminoethyl)benzenesulfonyl fluoride prevented ANG II-induced sLTF, which was absent in mice deficient in gp91(phox), the catalytic subunit of the Nox2 complex. These results demonstrate that repetitive application of ANG II induces sLTF of the carotid body via activation of Nox2 by AT(1) receptors.
Figures

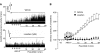
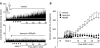
Similar articles
-
NADPH oxidase is required for the sensory plasticity of the carotid body by chronic intermittent hypoxia.J Neurosci. 2009 Apr 15;29(15):4903-10. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4768-08.2009. J Neurosci. 2009. PMID: 19369559 Free PMC article.
-
5-HT evokes sensory long-term facilitation of rodent carotid body via activation of NADPH oxidase.J Physiol. 2006 Oct 1;576(Pt 1):289-95. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2006.116020. Epub 2006 Aug 3. J Physiol. 2006. PMID: 16887872 Free PMC article.
-
Chronic intermittent hypoxia augments chemoreflex control of sympathetic activity: role of the angiotensin II type 1 receptor.Respir Physiol Neurobiol. 2010 Apr 15;171(1):36-45. doi: 10.1016/j.resp.2010.02.003. Epub 2010 Feb 12. Respir Physiol Neurobiol. 2010. PMID: 20153844 Free PMC article.
-
NOX2 is the primary source of angiotensin II-induced superoxide in the macula densa.Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2010 Mar;298(3):R707-12. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00762.2009. Epub 2010 Jan 6. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2010. PMID: 20053956 Free PMC article.
-
Sensory plasticity of the carotid body: role of reactive oxygen species and physiological significance.Respir Physiol Neurobiol. 2011 Sep 30;178(3):375-80. doi: 10.1016/j.resp.2011.05.012. Epub 2011 May 18. Respir Physiol Neurobiol. 2011. PMID: 21621009 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Angiotensin type 1a receptors in the median preoptic nucleus support intermittent hypoxia-induced hypertension.Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2019 May 1;316(5):R651-R665. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00393.2018. Epub 2019 Mar 20. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2019. PMID: 30892911 Free PMC article.
-
Role of oxidative stress-induced endothelin-converting enzyme activity in the alteration of carotid body function by chronic intermittent hypoxia.Exp Physiol. 2013 Nov;98(11):1620-30. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.2013.073700. Epub 2013 Aug 2. Exp Physiol. 2013. PMID: 23913764 Free PMC article.
-
The impact of inflammation on respiratory plasticity.Exp Neurol. 2017 Jan;287(Pt 2):243-253. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2016.07.022. Epub 2016 Jul 27. Exp Neurol. 2017. PMID: 27476100 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chronic Intermittent Hypoxia-Induced Diaphragm Muscle Weakness Is NADPH Oxidase-2 Dependent.Cells. 2023 Jul 12;12(14):1834. doi: 10.3390/cells12141834. Cells. 2023. PMID: 37508499 Free PMC article.
-
The role of the Nox4-derived ROS-mediated RhoA/Rho kinase pathway in rat hypertension induced by chronic intermittent hypoxia.Sleep Breath. 2017 Sep;21(3):667-677. doi: 10.1007/s11325-016-1449-2. Epub 2017 Jan 11. Sleep Breath. 2017. PMID: 28078487
References
-
- Cragg PA, Runold M, Kou YR, Prabhakar NR. Tachykinin antagonists in carotid body responses to hypoxia and substance P in the rat. Respir Physiol 95: 295–310, 1994 - PubMed
-
- Germano G, Sanguigni V, Pignatelli P, Caccese D, Lenti L, Ragazzo M, Lauro R, Violi F. Enhanced platelet release of superoxide anion in systemic hypertension: role of AT1 receptors. J Hypertens 22: 1151–1156, 2004 - PubMed
-
- Hanna IR, Taniyama Y, Szocs K, Rocic P, Griendling KK. NAD(P)H oxidase-derived reactive oxygen species as mediators of angiotensin II signaling. Antioxid Redox Signal 4: 899–914, 2002 - PubMed
-
- Lam SY, Leung PS. A locally generated angiotensin system in rat carotid body. Regul Pept 107: 97–103, 2002 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

