CD1d-independent activation of invariant natural killer T cells by staphylococcal enterotoxin B through major histocompatibility complex class II/T cell receptor interaction results in acute lung injury
- PMID: 21628519
- PMCID: PMC3147567
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.00177-11
CD1d-independent activation of invariant natural killer T cells by staphylococcal enterotoxin B through major histocompatibility complex class II/T cell receptor interaction results in acute lung injury
Abstract
There are two important mechanisms of activation of invariant natural killer T cells (iNKT cells) by microbes: direct activation of the invariant T-cell receptor (TCR) by microbial glycolipids presented by CD1d and indirect activation, mediated by the responses of antigen-presenting cells to microbes. In this study, we provide evidence for a novel CD1d-independent direct activation of iNKT cells involving a microbial protein superantigen presented in the context of major histocompatibility complex class II (MHC-II), which plays a critical role in pathogenesis, thereby redefining the role of iNKT cells. Intranasal exposure to staphylococcal enterotoxin B (SEB) in C57BL/6 wild-type mice caused acute lung injury (ALI) characterized by vascular leak, cytokine storm, and infiltration of mononuclear cells in the lungs. In contrast, the vascular leak and inflammation were decreased by ~50% in NKT cell-deficient Jα18(-/-) and CD1d(-/-) mice following SEB exposure, which was reversed following adoptive transfer of iNKT cells into CD1d(-/-) mice. In vitro, SEB could directly stimulate iNKT cells in a CD1d-independent manner via MHC-II/TCR interaction, specifically involving Vβ8. These studies not only demonstrate that iNKT cells can be activated directly by a bacterial protein superantigen independent of CD1d but also indicate that in addition to the conventional T cells, iNKT cells play a critical role in SEB-mediated ALI.
Figures
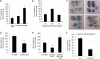
Similar articles
-
Type II Natural Killer T Cells Contribute to Protection Against Systemic Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Infection.Front Immunol. 2020 Nov 18;11:610010. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.610010. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 33312179 Free PMC article.
-
CD1d-independent activation of mouse and human iNKT cells by bacterial superantigens.Immunol Cell Biol. 2012 Aug;90(7):699-709. doi: 10.1038/icb.2011.90. Epub 2011 Nov 1. Immunol Cell Biol. 2012. PMID: 22041925
-
Turned on by danger: activation of CD1d-restricted invariant natural killer T cells.Immunology. 2012 Sep;137(1):20-7. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2012.03612.x. Immunology. 2012. PMID: 22734667 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Activated invariant natural killer T cells directly recognize leukemia cells in a CD1d-independent manner.Cancer Sci. 2020 Jul;111(7):2223-2233. doi: 10.1111/cas.14428. Epub 2020 Jun 19. Cancer Sci. 2020. PMID: 32324315 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Adaptor Proteins in the Biology of Natural Killer T (NKT) Cells.Front Immunol. 2019 Jun 25;10:1449. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.01449. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31293596 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Host defenses against bacterial lower respiratory tract infection.Curr Opin Immunol. 2012 Aug;24(4):424-30. doi: 10.1016/j.coi.2012.07.005. Epub 2012 Jul 25. Curr Opin Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22841348 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inhibition of miRNA-222-3p Relieves Staphylococcal Enterotoxin B-Induced Liver Inflammatory Injury by Upregulating Suppressors of Cytokine Signaling 1.Yonsei Med J. 2019 Nov;60(11):1093-1102. doi: 10.3349/ymj.2019.60.11.1093. Yonsei Med J. 2019. PMID: 31637892 Free PMC article.
-
Antibiotic Combined with Epitope-Specific Monoclonal Antibody Cocktail Protects Mice Against Bacteremia and Acute Pneumonia from Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Infection.J Inflamm Res. 2021 Aug 30;14:4267-4282. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S325286. eCollection 2021. J Inflamm Res. 2021. PMID: 34511967 Free PMC article.
-
Type II Natural Killer T Cells Contribute to Protection Against Systemic Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Infection.Front Immunol. 2020 Nov 18;11:610010. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.610010. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 33312179 Free PMC article.
-
Superantigenic Yersinia pseudotuberculosis induces the expression of granzymes and perforin by CD4+ T cells.Infect Immun. 2015 May;83(5):2053-64. doi: 10.1128/IAI.02339-14. Epub 2015 Mar 9. Infect Immun. 2015. PMID: 25754199 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Akbari O., et al. 2003. Essential role of NKT cells producing IL-4 and IL-13 in the development of allergen-induced airway hyperreactivity. Nat. Med. 9:582–588 - PubMed
-
- Baker M. D., Acharya K. R. 2004. Superantigens: structure-function relationships. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 293:529–537 - PubMed
-
- Balato A., Unutmaz D., Gaspari A. A. 2009. Natural killer T cells: an unconventional T-cell subset with diverse effector and regulatory functions. J. Invest. Dermatol. 129:1628–1642 - PubMed
-
- Berzins S. P., Smyth M. J., Godfrey D. I. 2005. Working with NKT cells—pitfalls and practicalities. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 17:448–454 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

