Induction of human neuronal cells by defined transcription factors
- PMID: 21617644
- PMCID: PMC3159048
- DOI: 10.1038/nature10202
Induction of human neuronal cells by defined transcription factors
Abstract
Somatic cell nuclear transfer, cell fusion, or expression of lineage-specific factors have been shown to induce cell-fate changes in diverse somatic cell types. We recently observed that forced expression of a combination of three transcription factors, Brn2 (also known as Pou3f2), Ascl1 and Myt1l, can efficiently convert mouse fibroblasts into functional induced neuronal (iN) cells. Here we show that the same three factors can generate functional neurons from human pluripotent stem cells as early as 6 days after transgene activation. When combined with the basic helix-loop-helix transcription factor NeuroD1, these factors could also convert fetal and postnatal human fibroblasts into iN cells showing typical neuronal morphologies and expressing multiple neuronal markers, even after downregulation of the exogenous transcription factors. Importantly, the vast majority of human iN cells were able to generate action potentials and many matured to receive synaptic contacts when co-cultured with primary mouse cortical neurons. Our data demonstrate that non-neural human somatic cells, as well as pluripotent stem cells, can be converted directly into neurons by lineage-determining transcription factors. These methods may facilitate robust generation of patient-specific human neurons for in vitro disease modelling or future applications in regenerative medicine.
Figures
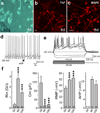
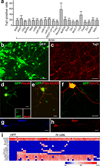
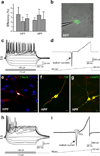
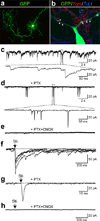
Comment in
-
Regenerative medicine: Bespoke cells for the human brain.Nature. 2011 Aug 10;476(7359):158-9. doi: 10.1038/476158a. Nature. 2011. PMID: 21833079 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Direct conversion of fibroblasts to functional neurons by defined factors.Nature. 2010 Feb 25;463(7284):1035-41. doi: 10.1038/nature08797. Epub 2010 Jan 27. Nature. 2010. PMID: 20107439 Free PMC article.
-
Regenerative medicine: Bespoke cells for the human brain.Nature. 2011 Aug 10;476(7359):158-9. doi: 10.1038/476158a. Nature. 2011. PMID: 21833079 No abstract available.
-
Generation of induced neuronal cells by the single reprogramming factor ASCL1.Stem Cell Reports. 2014 Aug 12;3(2):282-96. doi: 10.1016/j.stemcr.2014.05.020. Epub 2014 Jul 4. Stem Cell Reports. 2014. PMID: 25254342 Free PMC article.
-
Making neurons, made easy: The use of Neurogenin-2 in neuronal differentiation.Stem Cell Reports. 2022 Jan 11;17(1):14-34. doi: 10.1016/j.stemcr.2021.11.015. Epub 2021 Dec 30. Stem Cell Reports. 2022. PMID: 34971564 Free PMC article. Review.
-
bHLH transcription factors in neural development, disease, and reprogramming.Brain Res. 2019 Feb 15;1705:48-65. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2018.03.013. Epub 2018 Mar 12. Brain Res. 2019. PMID: 29544733 Review.
Cited by
-
Transfer to the clinic: refining forward programming of hPSCs to megakaryocytes for platelet production in bioreactors.Blood Adv. 2021 Apr 13;5(7):1977-1990. doi: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2020003236. Blood Adv. 2021. PMID: 33843988 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of synaptic functions in central nervous system by endocrine hormones and the maintenance of energy homoeostasis.Biosci Rep. 2012 Oct;32(5):423-32. doi: 10.1042/BSR20120026. Biosci Rep. 2012. PMID: 22582733 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neuronal transcription factors induce conversion of human glioma cells to neurons and inhibit tumorigenesis.PLoS One. 2012;7(7):e41506. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0041506. Epub 2012 Jul 31. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22859994 Free PMC article.
-
Modeling APOE ε4 familial Alzheimer's disease in directly converted 3D brain organoids.Front Aging Neurosci. 2024 Aug 9;16:1435445. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2024.1435445. eCollection 2024. Front Aging Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 39185458 Free PMC article.
-
Direct transcriptional reprogramming of adult cells to embryonic nephron progenitors.J Am Soc Nephrol. 2013 Sep;24(9):1424-34. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2012121143. Epub 2013 Jun 13. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2013. PMID: 23766537 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Blau HM, et al. Plasticity of the differentiated state. Science. 1985;230(4727):758–766. - PubMed
-
- Gurdon JB. From nuclear transfer to nuclear reprogramming: the reversal of cell differentiation. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2006;22:1–22. - PubMed
-
- Heins N, et al. Glial cells generate neurons: the role of the transcription factor Pax6. Nat Neurosci. 2002;5(4):308–315. - PubMed
-
- Shen CN, Slack JM, Tosh D. Molecular basis of transdifferentiation of pancreas to liver. Nat Cell Biol. 2000;2(12):879–887. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

