Effects of cell-type specific leptin receptor mutation on leptin transport across the BBB
- PMID: 21616110
- PMCID: PMC3137692
- DOI: 10.1016/j.peptides.2011.05.011
Effects of cell-type specific leptin receptor mutation on leptin transport across the BBB
Abstract
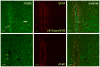
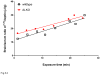
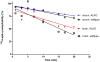
The functions of leptin receptors (LRs) are cell-type specific. At the blood-brain barrier, LRs mediate leptin transport that is essential for its CNS actions, and both endothelial and astrocytic LRs may be involved. To test this, we generated endothelia specific LR knockout (ELKO) and astrocyte specific LR knockout (ALKO) mice. ELKO mice were derived from a cross of Tie2-cre recombinase mice with LR-floxed mice, whereas ALKO mice were generated by a cross of GFAP-cre with LR-floxed mice, yielding mutant transmembrane LRs without signaling functions in endothelial cells and astrocytes, respectively. The ELKO mutation did not affect leptin half-life in blood or apparent influx rate to the brain and spinal cord, though there was an increase of brain parenchymal uptake of leptin after in situ brain perfusion. Similarly, the ALKO mutation did not affect blood-brain barrier permeation of leptin or its degradation in blood and brain. The results support our observation from cellular studies that membrane-bound truncated LRs are fully efficient in transporting leptin, and that basal levels of astrocytic LRs do not affect leptin transport across the endothelial monolayer. Nonetheless, the absence of leptin signaling at the BBB appears to enhance the availability of leptin to CNS parenchyma. The ELKO and ALKO mice provide new models to determine the dynamic regulation of leptin transport in metabolic and inflammatory disorders where cellular distribution of LRs is shifted.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Leukocyte infiltration into spinal cord of EAE mice is attenuated by removal of endothelial leptin signaling.Brain Behav Immun. 2014 Aug;40:61-73. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2014.02.003. Epub 2014 Feb 24. Brain Behav Immun. 2014. PMID: 24576482 Free PMC article.
-
Endothelial cell leptin receptor mutant mice have hyperleptinemia and reduced tissue uptake.J Cell Physiol. 2013 Jul;228(7):1610-6. doi: 10.1002/jcp.24325. J Cell Physiol. 2013. PMID: 23359322 Free PMC article.
-
Leptin action on nonneuronal cells in the CNS: potential clinical applications.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2012 Aug;1264(1):64-71. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2012.06472.x. Epub 2012 Apr 24. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2012. PMID: 22530983 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of Astrocytes in Leptin Signaling.J Mol Neurosci. 2015 Aug;56(4):829-839. doi: 10.1007/s12031-015-0518-5. Epub 2015 Feb 17. J Mol Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 25687329 Free PMC article.
-
Structural pathways for macromolecular and cellular transport across the blood-brain barrier during inflammatory conditions. Review.Histol Histopathol. 2004 Apr;19(2):535-64. doi: 10.14670/HH-19.535. Histol Histopathol. 2004. PMID: 15024715 Review.
Cited by
-
Leukocyte infiltration into spinal cord of EAE mice is attenuated by removal of endothelial leptin signaling.Brain Behav Immun. 2014 Aug;40:61-73. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2014.02.003. Epub 2014 Feb 24. Brain Behav Immun. 2014. PMID: 24576482 Free PMC article.
-
Endothelial cell leptin receptor mutant mice have hyperleptinemia and reduced tissue uptake.J Cell Physiol. 2013 Jul;228(7):1610-6. doi: 10.1002/jcp.24325. J Cell Physiol. 2013. PMID: 23359322 Free PMC article.
-
Pluronic modified leptin with increased systemic circulation, brain uptake and efficacy for treatment of obesity.J Control Release. 2014 Oct 10;191:34-46. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2014.05.044. Epub 2014 Jun 2. J Control Release. 2014. PMID: 24881856 Free PMC article.
-
Protective role of astrocytic leptin signaling against excitotoxicity.J Mol Neurosci. 2013 Mar;49(3):523-30. doi: 10.1007/s12031-012-9924-0. Epub 2012 Nov 23. J Mol Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23180096 Free PMC article.
-
Leptin action on nonneuronal cells in the CNS: potential clinical applications.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2012 Aug;1264(1):64-71. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2012.06472.x. Epub 2012 Apr 24. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2012. PMID: 22530983 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Banks WA, Coon AB, Robinson SM, Moinuddin A, Shultz JM, Nakaoke R, et al. Triglycerides induce leptin resistance at the blood-brain barrier. Diabetes. 2004;53:1253–60. - PubMed
-
- Banks WA, Farrell CL. Impaired transport of leptin across the blood-brain barrier in obesity is acquired and reversible. Am J Physiol. 2003;285:E10–E15. - PubMed
-
- Banks WA, Kastin AJ. Physiological consequences of the passage of peptides across the blood-brain barrier. Rev Neurosci. 1993;4:365–72. - PubMed
-
- Banks WA, Kastin AJ, Huang W, Jaspan JB, Maness LM. Leptin enters the brain by a saturable system independent of insulin. Peptides. 1996;17:305–11. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

