Role of mTOR in podocyte function and diabetic nephropathy in humans and mice
- PMID: 21606591
- PMCID: PMC3104746
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI44774
Role of mTOR in podocyte function and diabetic nephropathy in humans and mice
Abstract
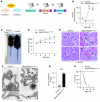
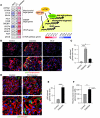
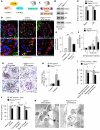
Chronic glomerular diseases, associated with renal failure and cardiovascular morbidity, represent a major health issue. However, they remain poorly understood. Here we have reported that tightly controlled mTOR activity was crucial to maintaining glomerular podocyte function, while dysregulation of mTOR facilitated glomerular diseases. Genetic deletion of mTOR complex 1 (mTORC1) in mouse podocytes induced proteinuria and progressive glomerulosclerosis. Furthermore, simultaneous deletion of both mTORC1 and mTORC2 from mouse podocytes aggravated the glomerular lesions, revealing the importance of both mTOR complexes for podocyte homeostasis. In contrast, increased mTOR activity accompanied human diabetic nephropathy, characterized by early glomerular hypertrophy and hyperfiltration. Curtailing mTORC1 signaling in mice by genetically reducing mTORC1 copy number in podocytes prevented glomerulosclerosis and significantly ameliorated the progression of glomerular disease in diabetic nephropathy. These results demonstrate the requirement for tightly balanced mTOR activity in podocyte homeostasis and suggest that mTOR inhibition can protect podocytes and prevent progressive diabetic nephropathy.
Figures
Comment in
-
The targeted podocyte.J Clin Invest. 2011 Jun;121(6):2142-5. doi: 10.1172/JCI57935. Epub 2011 May 23. J Clin Invest. 2011. PMID: 21606599 Free PMC article.
Similar articles
-
The targeted podocyte.J Clin Invest. 2011 Jun;121(6):2142-5. doi: 10.1172/JCI57935. Epub 2011 May 23. J Clin Invest. 2011. PMID: 21606599 Free PMC article.
-
mTORC1 activation in podocytes is a critical step in the development of diabetic nephropathy in mice.J Clin Invest. 2011 Jun;121(6):2181-96. doi: 10.1172/JCI44771. Epub 2011 May 23. J Clin Invest. 2011. PMID: 21606597 Free PMC article.
-
Translationally controlled tumour protein is associated with podocyte hypertrophy in a mouse model of type 1 diabetes.Diabetologia. 2012 Apr;55(4):1205-17. doi: 10.1007/s00125-012-2467-7. Epub 2012 Feb 4. Diabetologia. 2012. PMID: 22311416
-
The role of mechanistic target of rapamycin in maintenance of glomerular epithelial cells.Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2016 Jan;25(1):28-34. doi: 10.1097/MNH.0000000000000181. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2016. PMID: 26625863 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pathogenesis of the podocytopathy and proteinuria in diabetic glomerulopathy.Curr Diabetes Rev. 2008 Feb;4(1):39-45. doi: 10.2174/157339908783502370. Curr Diabetes Rev. 2008. PMID: 18220694 Review.
Cited by
-
Immune-mediated entities of (primary) focal segmental glomerulosclerosis.Cell Tissue Res. 2021 Aug;385(2):423-434. doi: 10.1007/s00441-021-03454-3. Epub 2021 Apr 27. Cell Tissue Res. 2021. PMID: 33907872 Free PMC article. Review.
-
KCa3.1 mediates dysfunction of tubular autophagy in diabetic kidneys via PI3k/Akt/mTOR signaling pathways.Sci Rep. 2016 Mar 31;6:23884. doi: 10.1038/srep23884. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27029904 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of insulin/IGF-1 receptor signaling protects from mitochondria-mediated kidney failure.EMBO Mol Med. 2015 Mar;7(3):275-87. doi: 10.15252/emmm.201404916. EMBO Mol Med. 2015. PMID: 25643582 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of mTOR in Diabetic Kidney Disease.Antioxidants (Basel). 2021 Feb 22;10(2):321. doi: 10.3390/antiox10020321. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33671526 Free PMC article.
-
Rictor/mTORC2 signaling mediates TGFβ1-induced fibroblast activation and kidney fibrosis.Kidney Int. 2015 Sep;88(3):515-27. doi: 10.1038/ki.2015.119. Epub 2015 May 13. Kidney Int. 2015. PMID: 25970154 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Estacio RO, Schrier RW. Diabetic nephropathy: pathogenesis, diagnosis, and prevention of progression. Adv Intern Med. 2001;46:359–408. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

