Histone deacetylase inhibition alters dendritic cells to assume a tolerogenic phenotype and ameliorates arthritis in SKG mice
- PMID: 21592365
- PMCID: PMC3218887
- DOI: 10.1186/ar3339
Histone deacetylase inhibition alters dendritic cells to assume a tolerogenic phenotype and ameliorates arthritis in SKG mice
Abstract
Introduction: The purpose of this study was to elucidate the effects of histone deacetylase inhibition on the phenotype and function of dendritic cells and on arthritis in SKG mice.
Methods: Arthritis was induced in SKG mice by zymosan A injection. Trichostatin A, a histone deacetylase inhibitor, was administered and its effects on arthritis were evaluated by joint swelling and histological evaluation. Interleukin-17 production in lymph node cells was determined by an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Foxp3 expression in lymph node cells and the phenotypes of splenic dendritic cells were examined by fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS). Bone marrow-derived dendritic cells (BM-DC) were generated with granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor. The effects of trichostatin A on cell surface molecules, cytokine production, indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO) expression and T cell stimulatory capacity were examined by FACS, ELISA, quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction and Western blot, and the allo-mixed lymphocyte reaction, respectively.
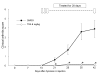
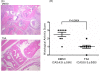
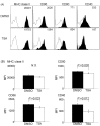
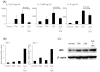
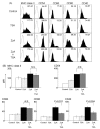
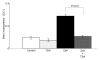
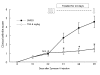
Results: Trichostatin A, when administered before the onset of arthritis, prevented SKG mice from getting arthritis. Trichostatin A treatment also showed therapeutic effects on arthritis in SKG mice, when it was administered after the onset of arthritis. Trichostatin A treatment reduced Th17 cells and induced regulatory T cells in lymph node, and also decreased co-stimulatory molecule expression on splenic dendritic cells in vivo. In vitro, trichostatin A markedly suppressed zymosan A-induced interleukin-12 and interleukin-6 production by BM-DC and up-regulated IDO expression at mRNA and protein levels. Trichostatin A-treated BM-DC also showed less T cell stimulatory capacity.
Conclusions: Histone deacetylase inhibition changes dendritic cells to a tolerogenic phenotype and ameliorates arthritis in SKG mice.
Figures

Comment in
-
Experimental arthritis: Inducing tolerogenic DCs in arthritis.Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2011 Jun 28;7(8):437. doi: 10.1038/nrrheum.2011.92. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2011. PMID: 21709701 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Vasoactive intestinal peptide-induced tolerogenic dendritic cells attenuated arthritis in experimental collagen-induced arthritic mice.Int J Rheum Dis. 2019 Jul;22(7):1255-1262. doi: 10.1111/1756-185X.13578. Epub 2019 May 6. Int J Rheum Dis. 2019. PMID: 31062502
-
Tolerogenic splenic IDO (+) dendritic cells from the mice treated with induced-Treg cells suppress collagen-induced arthritis.J Immunol Res. 2014;2014:831054. doi: 10.1155/2014/831054. Epub 2014 Oct 27. J Immunol Res. 2014. PMID: 25405209 Free PMC article.
-
Histone deacetylase inhibition modulates indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase-dependent DC functions and regulates experimental graft-versus-host disease in mice.J Clin Invest. 2008 Jul;118(7):2562-73. doi: 10.1172/JCI34712. J Clin Invest. 2008. PMID: 18568076 Free PMC article.
-
Allostimulatory activity of bone marrow-derived plasmacytoid dendritic cells is independent of indoleamine dioxygenase but regulated by inducible costimulator ligand expression.Hum Immunol. 2009 May;70(5):313-20. doi: 10.1016/j.humimm.2009.01.021. Epub 2009 Feb 3. Hum Immunol. 2009. PMID: 19208362 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of antitumor immunity with histone deacetylase inhibitors.Immunotherapy. 2017 Dec;9(16):1359-1372. doi: 10.2217/imt-2017-0134. Immunotherapy. 2017. PMID: 29185390 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Experimental arthritis: Inducing tolerogenic DCs in arthritis.Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2011 Jun 28;7(8):437. doi: 10.1038/nrrheum.2011.92. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2011. PMID: 21709701 No abstract available.
-
Trichostatin A Shows Transient Protection from Chronic Alcohol-Induced Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) Production in Human Monocyte-Derived Dendritic Cells.J Alcohol Drug Depend. 2018;6(4):316. doi: 10.4172/2329-6488.1000316. Epub 2018 Aug 31. J Alcohol Drug Depend. 2018. PMID: 30596124 Free PMC article.
-
Carboxylesterase-1 Assisted Targeting of HDAC Inhibitors to Mononuclear Myeloid Cells in Inflammatory Bowel Disease.J Crohns Colitis. 2022 May 10;16(4):668-681. doi: 10.1093/ecco-jcc/jjab176. J Crohns Colitis. 2022. PMID: 34633041 Free PMC article.
-
Tumor associated regulatory dendritic cells.Semin Cancer Biol. 2012 Aug;22(4):298-306. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2012.02.010. Epub 2012 Mar 6. Semin Cancer Biol. 2012. PMID: 22414911 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Glutaminase 1 plays a key role in the cell growth of fibroblast-like synoviocytes in rheumatoid arthritis.Arthritis Res Ther. 2017 Apr 11;19(1):76. doi: 10.1186/s13075-017-1283-3. Arthritis Res Ther. 2017. PMID: 28399896 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Santiago-Schwarz F, Anand P, Liu S, Carsons SE. Dendritic cells (DCs) in rheumatoid arthritis (RA): progenitor cells and soluble factors contained in RA synovial fluid yield a subset of myeloid DCs that preferentially activate Th1 inflammatory-type responses. J Immunol. 2001;167:1758–1768. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

