Branched-chain amino acids, mitochondrial biogenesis, and healthspan: an evolutionary perspective
- PMID: 21566257
- PMCID: PMC3156598
- DOI: 10.18632/aging.100322
Branched-chain amino acids, mitochondrial biogenesis, and healthspan: an evolutionary perspective
Abstract
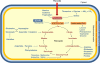
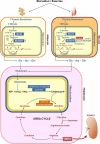
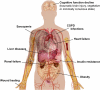
Malnutrition is common among older persons, with important consequences increasing frailty and morbidity and reducing health expectancy. On the contrary, calorie restriction (CR, a low-calorie dietary regimen with adequate nutrition) slows the progression of age-related diseases and extends the lifespan of many species. Identification of strategies mimicking key CR mechanisms - increased mitochondrial respiration and reduced production of oxygen radicals - is a hot topic in gerontology. Dietary supplementation with essential and/or branched chain amino acids (BCAAs) exerts a variety of beneficial effects in experimental animals and humans and has been recently demonstrated to support cardiac and skeletal muscle mitochondrial biogenesis, prevent oxidative damage, and enhance physical endurance in middle-aged mice, resulting in prolonged survival. Here we review recent studies addressing the possible role of BCAAs in energy metabolism and in the longevity of species ranging from unicellular organisms to mammals. We also summarize observations from human studies supporting the exciting hypothesis that dietary BCAA enriched mixture supplementation might be a health-promoting strategy in aged patients at risk.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors of this manuscript have no conflict of interests to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Leucine Supplementation Differently Modulates Branched-Chain Amino Acid Catabolism, Mitochondrial Function and Metabolic Profiles at the Different Stage of Insulin Resistance in Rats on High-Fat Diet.Nutrients. 2017 Jun 2;9(6):565. doi: 10.3390/nu9060565. Nutrients. 2017. PMID: 28574481 Free PMC article.
-
Restoration of metabolic health by decreased consumption of branched-chain amino acids.J Physiol. 2018 Feb 15;596(4):623-645. doi: 10.1113/JP275075. Epub 2017 Dec 27. J Physiol. 2018. PMID: 29266268 Free PMC article.
-
From mitochondria to healthy aging: The role of branched-chain amino acids treatment: MATeR a randomized study.Clin Nutr. 2020 Jul;39(7):2080-2091. doi: 10.1016/j.clnu.2019.10.013. Epub 2019 Oct 18. Clin Nutr. 2020. PMID: 31672329 Clinical Trial.
-
Essential amino acid formulations to prevent mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress.Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. 2021 Jan;24(1):88-95. doi: 10.1097/MCO.0000000000000704. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. 2021. PMID: 33060458 Review.
-
The Effects of BCAAs on Insulin Resistance in Athletes.J Nutr Sci Vitaminol (Tokyo). 2019;65(5):383-389. doi: 10.3177/jnsv.65.383. J Nutr Sci Vitaminol (Tokyo). 2019. PMID: 31666474 Review.
Cited by
-
Deficiency of Capicua disrupts bile acid homeostasis.Sci Rep. 2015 Feb 5;5:8272. doi: 10.1038/srep08272. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 25653040 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of metabolic pathways influenced by the G-protein coupled receptors GprB and GprD in Aspergillus nidulans.PLoS One. 2013 May 1;8(5):e62088. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0062088. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23658706 Free PMC article.
-
Circulating Metabolites as Potential Biomarkers for Neurological Disorders-Metabolites in Neurological Disorders.Metabolites. 2020 Sep 29;10(10):389. doi: 10.3390/metabo10100389. Metabolites. 2020. PMID: 33003305 Free PMC article.
-
Leucine Supplementation Differently Modulates Branched-Chain Amino Acid Catabolism, Mitochondrial Function and Metabolic Profiles at the Different Stage of Insulin Resistance in Rats on High-Fat Diet.Nutrients. 2017 Jun 2;9(6):565. doi: 10.3390/nu9060565. Nutrients. 2017. PMID: 28574481 Free PMC article.
-
Drosophila miR-277 controls branched-chain amino acid catabolism and affects lifespan.RNA Biol. 2013 Jun;10(6):1042-56. doi: 10.4161/rna.24810. Epub 2013 Apr 30. RNA Biol. 2013. PMID: 23669073 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Visvanathan R, Chapman IM. Undernutrition and anorexia in the older person. Gastroenterol Clin North Am. 2009;38:393–409. - PubMed
-
- Chapman IM. Nutritional disorders in the elderly. Med Clin North Am. 2006;90:887–907. - PubMed
-
- Ahmed N, Mandel R, Fain MJ. Frailty: An emerging geriatric syndrome. Am J Med. 2007;120:748–753. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

