Increased levels of leukocyte-derived MMP-9 in patients with stable angina pectoris
- PMID: 21559401
- PMCID: PMC3084822
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0019340
Increased levels of leukocyte-derived MMP-9 in patients with stable angina pectoris
Abstract
Objective: There is a growing interest for matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) and their tissue inhibitors (TIMPs) in plasma as novel biomarkers in coronary artery disease (CAD). We aimed to identify the sources of MMP-8, MMP-9, TIMP-1 and TIMP-2 among peripheral blood cells and further explore whether gene expression or protein release was altered in patients with stable angina pectoris (SA).
Methods: In total, plasma MMP-9 was measured in 44 SA patients and 47 healthy controls. From 10 patients and 10 controls, peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) and neutrophils were isolated and stimulated ex vivo. MMPs, TIMPs and myeloperoxidase were measured in plasma and supernatants by ELISA. The corresponding gene expression was measured by real-time PCR.
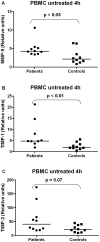
Results: Neutrophils were the dominant source of MMP-8 and MMP-9. Upon moderate stimulation with IL-8, the neutrophil release of MMP-9 was higher in the SA patients compared with controls (p<0.05). In PBMC, the TIMP-1 and MMP-9 mRNA expression was higher in SA patients compared with controls, p<0.01 and 0.05, respectively. There were no differences in plasma levels between patients and controls except for TIMP-2, which was lower in patients, p<0.01.
Conclusion: Measurements of MMPs and TIMPs in plasma may be of limited use. Despite similar plasma levels in SA patients and controls, the leukocyte-derived MMP-9 and TIMP-1 are significantly altered in patients. The findings indicate that the leukocytes are more prone to release and produce MMP-9 in symptomatic and angiographically verified CAD-a phenomenon that may have clinical implications in the course of disease.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Relation of matrix metalloproteinase-9/tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-1 ratio in peripheral circulating CD14+ monocytes to progression of coronary artery disease.Am J Cardiol. 2010 Feb 15;105(4):429-34. doi: 10.1016/j.amjcard.2009.10.013. Epub 2010 Jan 5. Am J Cardiol. 2010. PMID: 20152234
-
Plasma matrix metalloproteinase-9, tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-2, and CD40 ligand levels in patients with stable coronary artery disease.Am J Cardiol. 2005 Aug 1;96(3):339-45. doi: 10.1016/j.amjcard.2005.03.072. Am J Cardiol. 2005. PMID: 16054454
-
Expression of matrix metalloproteinase-2 and -9 and their inhibitors in peripheral blood cells of patients with chronic hepatitis C.Clin Chem. 2000 Feb;46(2):183-92. Clin Chem. 2000. PMID: 10657374
-
Imbalanced circulating matrix metalloproteinases in polycystic ovary syndrome.Mol Cell Biochem. 2011 Jul;353(1-2):251-7. doi: 10.1007/s11010-011-0793-6. Epub 2011 Mar 25. Mol Cell Biochem. 2011. PMID: 21437624
-
Serum MMPs 7-9 and their inhibitors during glucocorticoid and anti-TNF-α therapy in pediatric inflammatory bowel disease.Scand J Gastroenterol. 2012 Jul;47(7):785-94. doi: 10.3109/00365521.2012.677954. Epub 2012 Apr 23. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2012. PMID: 22519363
Cited by
-
Antimicrobial peptides and nitric oxide production by neutrophils from periodontitis subjects.Braz J Med Biol Res. 2012 Nov;45(11):1017-24. doi: 10.1590/s0100-879x2012007500123. Epub 2012 Aug 2. Braz J Med Biol Res. 2012. PMID: 22850872 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical usefulness of novel serum and imaging biomarkers in risk stratification of patients with stable angina.Dis Markers. 2014;2014:831364. doi: 10.1155/2014/831364. Epub 2014 Jun 19. Dis Markers. 2014. PMID: 25045198 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of early cartilage destruction in inflammatory arthritis by death receptor 3.Arthritis Rheumatol. 2014 Oct;66(10):2762-72. doi: 10.1002/art.38770. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2014. PMID: 25044706 Free PMC article.
-
Intricate relationship between SARS-CoV-2-induced shedding and cytokine storm generation: A signaling inflammatory pathway augmenting COVID-19.Health Sci Rev (Oxf). 2022 Mar;2:100011. doi: 10.1016/j.hsr.2021.100011. Epub 2022 Jan 6. Health Sci Rev (Oxf). 2022. PMID: 35013738 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inflammatory mediators in saliva associated with arterial stiffness and subclinical atherosclerosis.J Hypertens. 2013 Nov;31(11):2251-8; discussion 2258. doi: 10.1097/HJH.0b013e328363dccc. J Hypertens. 2013. PMID: 23868086 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Galis ZS, Khatri JJ. Matrix metalloproteinases in vascular remodeling and atherogenesis: The good, the bad, and the ugly. Circ Res. 2002;90(3):251–262. - PubMed
-
- Molloy KJ, Thompson MM, Jones JL, Schwalbe EC, Bell PRF, et al. Unstable carotid plaques exhibit raised matrix metalloproteinase-8 activity. Circulation. 2004;110(3):337–343. - PubMed
-
- Bäck M, Ketelhuth DFJ, Agewall S. Matrix metalloproteinases in atherothrombosis. Prog Cardiovasc Dis. 2010;52(5):410–428. - PubMed
-
- Zouridakis E, Avanzas P, Arroyo-Espliguero R, Fredericks S, Kaski JC. Markers of inflammation and rapid coronary artery disease progression in patients with stable angina pectoris. Circulation. 2004;110(13):1747–1753. - PubMed
-
- Jones GT, Kay IP, Chu JWS, Wilkins GT, Phillips LV, et al. Elevated plasma active matrix metalloproteinase-9 level is associated with coronary artery in-stent restenosis. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2006;26(7):e121–125. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous