Phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase gamma plays a central role in blood-brain barrier dysfunction in acute experimental stroke
- PMID: 21546487
- PMCID: PMC3129812
- DOI: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.110.601369
Phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase gamma plays a central role in blood-brain barrier dysfunction in acute experimental stroke
Abstract
Background and purpose: Phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K)-γ is linked to inflammation and oxidative stress. This study was conducted to investigate the role of the PI3Kγ in the blood-brain barrier dysfunction and brain damage induced by focal cerebral ischemia/reperfusion.
Methods: Wild-type and PI3Kγ knockout mice were subjected to middle cerebral artery occlusion (60 minutes) followed by reperfusion. Evans blue leakage, brain edema, infarct volumes, and neurological deficits were examined. Oxidative stress, neutrophil infiltration, and matrix metallopeptidase-9 were assessed. Activation of nuclear factor-κB and expression of proinflammatory and pro-oxidative genes were studied.
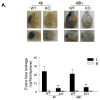
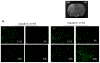
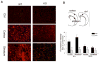
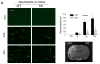
Results: PI3Kγ deficiency significantly reduced blood-brain barrier permeability and brain edema formation, which were time-dependently correlated with preventing the degradation of the tight junction protein, claudin-5, and the basal lamina protein, collagen IV, and the phosphorylation of myosin light chain in brain microvessels. PI3Kγ deficiency suppressed ischemia/reperfusion-induced nuclear factor-κB p65 (Ser536) phosphorylation and the expression of the pro-oxidant enzyme NADPH oxidase (Nox1, Nox2, and Nox4) and proinflammatory adhesion molecules (E- and P-selectin, intercellular adhesion molecule-1) at different time points. These molecular changes were associated with significant inhibition of oxidative stress (superoxide production and malondialdehyde content), neutrophil infiltration, and matrix metallopeptidase-9 expression/activity in PI3Kγ knockout mice. Eventually, PI3Kγ deficiency significantly reduced infarct volumes and neurological scores at 24 hours after ischemia/reperfusion.
Conclusions: Our results provide the first direct demonstration that PI3Kγ plays a significant role in ischemia/reperfusion-induced blood-brain barrier disruption and brain damage. Future studies need to explore PI3Kγ as a potential target for stroke therapy.
Figures














Similar articles
-
Phosphoinositide 3-Kinase γ Restrains Neurotoxic Effects of Microglia After Focal Brain Ischemia.Mol Neurobiol. 2016 Oct;53(8):5468-79. doi: 10.1007/s12035-015-9472-z. Epub 2015 Oct 9. Mol Neurobiol. 2016. PMID: 26452362
-
NADPH oxidase plays a central role in blood-brain barrier damage in experimental stroke.Stroke. 2007 Nov;38(11):3000-6. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.107.489765. Epub 2007 Oct 4. Stroke. 2007. PMID: 17916764
-
Carcinoembryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule 1 inhibits MMP-9-mediated blood-brain-barrier breakdown in a mouse model for ischemic stroke.Circ Res. 2013 Sep 27;113(8):1013-22. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.113.301207. Epub 2013 Jun 18. Circ Res. 2013. PMID: 23780386
-
The role of PI3Kγ in the immune system: new insights and translational implications.Nat Rev Immunol. 2022 Nov;22(11):687-700. doi: 10.1038/s41577-022-00701-8. Epub 2022 Mar 23. Nat Rev Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35322259 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase gamma (PI3Kγ): Discovery and development of its selective inhibitors.Med Res Rev. 2021 May;41(3):1599-1621. doi: 10.1002/med.21770. Epub 2020 Dec 10. Med Res Rev. 2021. PMID: 33300614 Review.
Cited by
-
High glucose, glucose fluctuation and carbonyl stress enhance brain microvascular endothelial barrier dysfunction: Implications for diabetic cerebral microvasculature.Redox Biol. 2015 Aug;5:80-90. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2015.03.005. Epub 2015 Apr 2. Redox Biol. 2015. PMID: 25867911 Free PMC article.
-
Pigment Epithelium-Derived Factor Improves Paracellular Blood-Brain Barrier Integrity in the Normal and Ischemic Mouse Brain.Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2020 Jul;40(5):751-764. doi: 10.1007/s10571-019-00770-9. Epub 2019 Dec 20. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2020. PMID: 31858356
-
Simvastatin attenuates stroke-induced splenic atrophy and lung susceptibility to spontaneous bacterial infection in mice.Stroke. 2013 Apr;44(4):1135-43. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.111.000633. Epub 2013 Feb 7. Stroke. 2013. PMID: 23391769 Free PMC article.
-
QiShenYiQi Inhibits Tissue Plasminogen Activator-Induced Brain Edema and Hemorrhage after Ischemic Stroke in Mice.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Jan 12;12:759027. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.759027. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35095486 Free PMC article.
-
NADPH oxidases as therapeutic targets in ischemic stroke.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2012 Jul;69(14):2345-63. doi: 10.1007/s00018-012-1011-8. Epub 2012 May 23. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2012. PMID: 22618244 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

