MDC1 directs chromosome-wide silencing of the sex chromosomes in male germ cells
- PMID: 21536735
- PMCID: PMC3084029
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.2030811
MDC1 directs chromosome-wide silencing of the sex chromosomes in male germ cells
Abstract
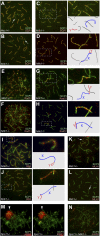
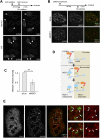
Chromosome-wide inactivation is an epigenetic signature of sex chromosomes. The mechanism by which the chromosome-wide domain is recognized and gene silencing is induced remains unclear. Here we identify an essential mechanism underlying the recognition of the chromosome-wide domain in the male germline. We show that mediator of DNA damage checkpoint 1 (MDC1), a binding partner of phosphorylated histone H2AX (γH2AX), defines the chromosome-wide domain, initiates meiotic sex chromosome inactivation (MSCI), and leads to XY body formation. Importantly, MSCI consists of two genetically separable steps. The first step is the MDC1-independent recognition of the unsynapsed axis by DNA damage response (DDR) factors such as ataxia telangiectasia and Rad3-related (ATR), TOPBP1, and γH2AX. The second step is the MDC1-dependent chromosome-wide spreading of DDR factors to the entire chromatin. Furthermore, we demonstrate that, in somatic cells, MDC1-dependent amplification of the γH2AX signal occurs following replicative stress and is associated with transcriptional silencing. We propose that a common DDR pathway underlies both MSCI and the response of somatic cells to replicative stress. These results establish that the DDR pathway centered on MDC1 triggers epigenetic silencing of sex chromosomes in germ cells.
Figures
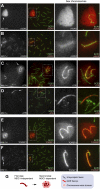
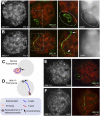
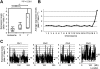
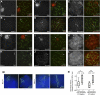
Comment in
-
The XY body: an attractive chromatin domain.Biol Reprod. 2020 Apr 24;102(5):985-987. doi: 10.1093/biolre/ioaa021. Biol Reprod. 2020. PMID: 32055839 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
The Initiation of Meiotic Sex Chromosome Inactivation Sequesters DNA Damage Signaling from Autosomes in Mouse Spermatogenesis.Curr Biol. 2020 Feb 3;30(3):408-420.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2019.11.064. Epub 2020 Jan 2. Curr Biol. 2020. PMID: 31902729 Free PMC article.
-
ATR acts stage specifically to regulate multiple aspects of mammalian meiotic silencing.Genes Dev. 2013 Jul 1;27(13):1484-94. doi: 10.1101/gad.219477.113. Genes Dev. 2013. PMID: 23824539 Free PMC article.
-
Sex chromosome inactivation in germ cells: emerging roles of DNA damage response pathways.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2012 Aug;69(15):2559-72. doi: 10.1007/s00018-012-0941-5. Epub 2012 Mar 2. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2012. PMID: 22382926 Free PMC article. Review.
-
UHRF1 is indispensable for meiotic sex chromosome inactivation and interacts with the DNA damage response pathway in mice†.Biol Reprod. 2022 Jul 25;107(1):168-182. doi: 10.1093/biolre/ioac054. Biol Reprod. 2022. PMID: 35284939
-
A Hypothesis: Linking Phase Separation to Meiotic Sex Chromosome Inactivation and Sex-Body Formation.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Aug 16;9:674203. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.674203. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34485277 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Histone H2A variants in nucleosomes and chromatin: more or less stable?Nucleic Acids Res. 2012 Nov;40(21):10719-41. doi: 10.1093/nar/gks865. Epub 2012 Sep 21. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012. PMID: 23002134 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Phospho-Regulation of Meiotic Prophase.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Apr 13;9:667073. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.667073. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 33928091 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Meiotic DNA double-strand breaks and chromosome asynapsis in mice are monitored by distinct HORMAD2-independent and -dependent mechanisms.Genes Dev. 2012 May 1;26(9):958-73. doi: 10.1101/gad.187559.112. Genes Dev. 2012. PMID: 22549958 Free PMC article.
-
Alterations in synaptonemal complex coding genes and human infertility.Int J Biol Sci. 2022 Feb 21;18(5):1933-1943. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.67843. eCollection 2022. Int J Biol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35342360 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Initiation of Meiotic Sex Chromosome Inactivation Sequesters DNA Damage Signaling from Autosomes in Mouse Spermatogenesis.Curr Biol. 2020 Feb 3;30(3):408-420.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2019.11.064. Epub 2020 Jan 2. Curr Biol. 2020. PMID: 31902729 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ahmed EA, van der Vaart A, Barten A, Kal HB, Chen J, Lou Z, Minter-Dykhouse K, Bartkova J, Bartek J, de Boer P, et al. 2007. Differences in DNA double strand breaks repair in male germ cell types: lessons learned from a differential expression of Mdc1 and 53BP1. DNA Repair (Amst) 6: 1243–1254 - PubMed
-
- Baker SM, Plug AW, Prolla TA, Bronner CE, Harris AC, Yao X, Christie DM, Monell C, Arnheim N, Bradley A, et al. 1996. Involvement of mouse Mlh1 in DNA mismatch repair and meiotic crossing over. Nat Genet 13: 336–342 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
