A high-resolution C. elegans essential gene network based on phenotypic profiling of a complex tissue
- PMID: 21529718
- PMCID: PMC3086541
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2011.03.037
A high-resolution C. elegans essential gene network based on phenotypic profiling of a complex tissue
Abstract
High-content screening for gene profiling has generally been limited to single cells. Here, we explore an alternative approach-profiling gene function by analyzing effects of gene knockdowns on the architecture of a complex tissue in a multicellular organism. We profile 554 essential C. elegans genes by imaging gonad architecture and scoring 94 phenotypic features. To generate a reference for evaluating methods for network construction, genes were manually partitioned into 102 phenotypic classes, predicting functions for uncharacterized genes across diverse cellular processes. Using this classification as a benchmark, we developed a robust computational method for constructing gene networks from high-content profiles based on a network context-dependent measure that ranks the significance of links between genes. Our analysis reveals that multi-parametric profiling in a complex tissue yields functional maps with a resolution similar to genetic interaction-based profiling in unicellular eukaryotes-pinpointing subunits of macromolecular complexes and components functioning in common cellular processes.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

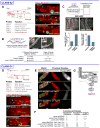

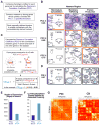
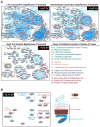
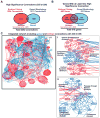
Comment in
-
Guilt by phenotypic association.Nat Methods. 2011 Jul;8(7):532-3. doi: 10.1038/nmeth0711-532a. Nat Methods. 2011. PMID: 21850732 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Automated profiling of gene function during embryonic development.Cell. 2024 Jun 6;187(12):3141-3160.e23. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2024.04.012. Epub 2024 May 16. Cell. 2024. PMID: 38759650
-
A regulatory network modeled from wild-type gene expression data guides functional predictions in Caenorhabditis elegans development.BMC Syst Biol. 2012 Jun 26;6:77. doi: 10.1186/1752-0509-6-77. BMC Syst Biol. 2012. PMID: 22734688 Free PMC article.
-
Expression and imaging of fluorescent proteins in the C. elegans gonad and early embryo.Methods Cell Biol. 2008;85:179-218. doi: 10.1016/S0091-679X(08)85009-1. Methods Cell Biol. 2008. PMID: 18155464
-
C. elegans network biology: a beginning.WormBook. 2006 Aug 21:1-20. doi: 10.1895/wormbook.1.118.1. WormBook. 2006. PMID: 18050437 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Toward a global picture of development: lessons from genome-scale analysis in Caenorhabditis elegans embryonic development.Dev Dyn. 2006 Aug;235(8):2009-17. doi: 10.1002/dvdy.20865. Dev Dyn. 2006. PMID: 16779860 Review.
Cited by
-
Introduction to germ cell development in Caenorhabditis elegans.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2013;757:1-16. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4614-4015-4_1. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2013. PMID: 22872472 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A nucleic acid binding protein map of germline regulation in Caenorhabditis elegans.Nat Commun. 2024 Aug 11;15(1):6884. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-51212-0. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 39128930 Free PMC article.
-
Loss of the Major Phosphatidylserine or Phosphatidylethanolamine Flippases Differentially Affect Phagocytosis.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020 Jul 21;8:648. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2020.00648. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020. PMID: 32793595 Free PMC article.
-
Sm protein down-regulation leads to defects in nuclear pore complex disassembly and distribution in C. elegans embryos.Dev Biol. 2012 May 15;365(2):445-57. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2012.02.036. Epub 2012 Mar 8. Dev Biol. 2012. PMID: 22426005 Free PMC article.
-
Ribonucleotide reductase inhibition improves the symptoms of a Caenorhabditis elegans model of Alzheimer's disease.G3 (Bethesda). 2024 May 7;14(5):jkae040. doi: 10.1093/g3journal/jkae040. G3 (Bethesda). 2024. PMID: 38412549 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bakal C, Aach J, Church G, Perrimon N. Quantitative morphological signatures define local signaling networks regulating cell morphology. Science. 2007;316:1753–1756. - PubMed
-
- Bochtler M, Ditzel L, Groll M, Hartmann C, Huber R. The proteasome. Annu Rev Biophys Biomol Struct. 1999;28:295–317. - PubMed
-
- Boone C, Bussey H, Andrews BJ. Exploring genetic interactions and networks with yeast. Nat Rev Genet. 2007;8:437–449. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

