Impaired fetal adrenal function in intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy
- PMID: 21525808
- PMCID: PMC3539589
- DOI: 10.12659/msm.881766
Impaired fetal adrenal function in intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy
Abstract
Background: Intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy (ICP) is a pregnancy-associated liver disease of unknown etiology. The aim of this study was to investigate the change in maternal and fetal adrenal function in clinical and experimental ICP.
Material/methods: The maternal and fetal serum levels of cortisol and dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate (DHEAS) were determined in 14 women with ICP and in pregnant rats with estrogen-induced intrahepatic cholestasis.
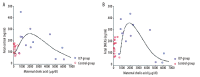
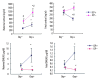
Results: In women with ICP, the fetal serum cortisol and DHEAS levels were significantly higher than those in women with normal pregnancy, after correcting the impact of gestational age at delivery. The relationship between fetal cortisol and maternal cholic acid levels was bidirectional; the fetal cortisol tended to increase in mild ICP, while it decreased in severe ICP. In pregnant rats with estrogen-induced cholestasis, the fetal cortisol level was significantly lower in the group with oxytocin injection, compared with the group without oxytocin injection (191.92±18.86 vs. 272.71±31.83 ng/ml, P<0.05). In contrast, the fetal cortisol concentration was increased after oxytocin injection in normal control rats.
Conclusions: The data indicate that fetal stress-responsive system is stimulated in mild ICP, but it is suppressed in severe ICP, which might contribute to the occurrence of unpredictable sudden fetal death. Further studies are warranted to explore the role of impaired fetal adrenal function in the pathogenesis of ICP and the clinical implications.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Effect of intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy on the functions of hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenocortical axis and adrenal cortex in normal neonates].Zhongguo Dang Dai Er Ke Za Zhi. 2010 Jan;12(1):5-8. Zhongguo Dang Dai Er Ke Za Zhi. 2010. PMID: 20113624 Chinese.
-
The concentrations of bile acids and erythropoietin in pregnant women with intrahepatic cholestasis and the state of the fetus and newborn.Med Wieku Rozwoj. 2013 Jul-Sep;17(3):232-45. Med Wieku Rozwoj. 2013. PMID: 24296447
-
[Clinical practice guidelines of the Team of Experts of the Polish Gynecological Society: management of the intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy].Ginekol Pol. 2012 Sep;83(9):713-7. Ginekol Pol. 2012. PMID: 23342903 Polish.
-
Intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy: changes in maternal-fetal bile acid balance and improvement by ursodeoxycholic acid.Ann Hepatol. 2002 Jan-Mar;1(1):20-8. Ann Hepatol. 2002. PMID: 15114292 Review.
-
Society for Maternal-Fetal Medicine Consult Series #53: Intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy: Replaces Consult #13, April 2011.Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2021 Feb;224(2):B2-B9. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2020.11.002. Epub 2020 Nov 13. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2021. PMID: 33197417 Review.
Cited by
-
Relations of neuropeptide Y and heme oxygenase-1 expressions with fetal brain injury in rats with intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy.Acta Cir Bras. 2019 May 6;34(4):e201900401. doi: 10.1590/s0102-865020190040000001. Acta Cir Bras. 2019. PMID: 31066785 Free PMC article.
-
A Comprehensive Evaluation of Steroid Metabolism in Women with Intrahepatic Cholestasis of Pregnancy.PLoS One. 2016 Aug 5;11(8):e0159203. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0159203. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27494119 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hepburn IS, Schade RR. Pregnancy-associated liver disorders. Dig Dis Sci. 2008;53:2334–58. - PubMed
-
- Joshi D, James A, Quaglia A, et al. Liver disease in pregnancy. Lancet. 2010;375:594–605. - PubMed
-
- Pathak B, Sheibani L, Lee RH. Cholestasis of pregnancy. Obstet Gynecol Clin North Am. 2010;37:269–82. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

