NMDA receptor regulates migration of newly generated neurons in the adult hippocampus via Disrupted-In-Schizophrenia 1 (DISC1)
- PMID: 21517847
- PMCID: PMC4142346
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2011.07282.x
NMDA receptor regulates migration of newly generated neurons in the adult hippocampus via Disrupted-In-Schizophrenia 1 (DISC1)
Abstract
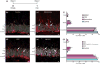
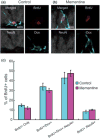
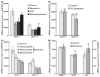
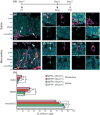
In the mammalian brain, new neurons are continuously generated throughout life in the dentate gyrus (DG) of the hippocampus. Previous studies have established that newborn neurons migrate a short distance to be integrated into a pre-existing neuronal circuit in the hippocampus. How the migration of newborn neurons is governed by extracellular signals, however, has not been fully understood. Here, we report that NMDA receptor (NMDA-R)-mediated signaling is essential for the proper migration and positioning of newborn neurons in the DG. An intraperitoneal injection of the NMDA-R antagonists, memantine, or 3-(2-carboxypiperazin-4-yl)propyl-1-phosphonic acid (CPP) into adult male mice caused the aberrant positioning of newborn neurons, resulting in the overextension of their migration in the DG. Interestingly, we revealed that the administration of NMDA-R antagonists leads to a decrease in the expression of Disrupted-In-Schizophrenia 1 (DISC1), a candidate susceptibility gene for major psychiatric disorders such as schizophrenia, which is also known as a critical regulator of neuronal migration in the DG. Furthermore, the overextended migration of newborn neurons induced by the NMDA-R antagonists was significantly rescued by exogenous expression of DISC1. Collectively, these results suggest that the NMDA-R signaling pathway governs the migration of newborn neurons via the regulation of DISC1 expression in the DG.
© 2011 The Authors. Journal of Neurochemistry © 2011 International Society for Neurochemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Roles of disrupted-in-schizophrenia 1-interacting protein girdin in postnatal development of the dentate gyrus.Neuron. 2009 Sep 24;63(6):774-87. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2009.08.015. Neuron. 2009. PMID: 19778507
-
DISC1 regulates new neuron development in the adult brain via modulation of AKT-mTOR signaling through KIAA1212.Neuron. 2009 Sep 24;63(6):761-73. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2009.08.008. Neuron. 2009. PMID: 19778506 Free PMC article.
-
The Alzheimer's disease drug memantine increases the number of radial glia-like progenitor cells in adult hippocampus.Glia. 2009 Aug 1;57(10):1082-90. doi: 10.1002/glia.20831. Glia. 2009. PMID: 19115386
-
NMDA receptor antagonist memantine promotes cell proliferation and production of mature granule neurons in the adult hippocampus.Neurosci Res. 2009 Apr;63(4):259-66. doi: 10.1016/j.neures.2008.12.006. Neurosci Res. 2009. PMID: 19367785
-
DISC1-related signaling pathways in adult neurogenesis of the hippocampus.Gene. 2013 Apr 15;518(2):223-30. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2013.01.015. Epub 2013 Jan 24. Gene. 2013. PMID: 23353011 Review.
Cited by
-
Nitric oxide synthase 1 adaptor protein, a protein implicated in schizophrenia, controls radial migration of cortical neurons.Biol Psychiatry. 2015 Jun 1;77(11):969-78. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2014.10.016. Epub 2014 Oct 30. Biol Psychiatry. 2015. PMID: 25542305 Free PMC article.
-
Measurement of NMDA Receptor Antagonist, CPP, in Mouse Plasma and Brain Tissue Following Systematic Administration Using Ion-Pair LCMS/MS.Anal Methods. 2014 Aug 21;6(16):6389-6396. doi: 10.1039/c4ay01168f. Anal Methods. 2014. PMID: 25663848 Free PMC article.
-
Gene Polymorphisms and Expression of NRG1, DAOA, and DISC1 Genes in a Chinese Han Population with an Ultra-High Risk for Psychosis.Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2023 Nov 21;19:2521-2533. doi: 10.2147/NDT.S434856. eCollection 2023. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2023. PMID: 38029052 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Strain and Species on the Septo-Temporal Distribution of Adult Neurogenesis in Rodents.Front Neurosci. 2017 Dec 19;11:719. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2017.00719. eCollection 2017. Front Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 29311796 Free PMC article.
-
Functional properties of extrasynaptic AMPA and NMDA receptors during postnatal hippocampal neurogenesis.J Physiol. 2014 Jan 1;592(1):125-40. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2013.267203. Epub 2013 Nov 11. J Physiol. 2014. PMID: 24218546 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adachi YU, Watanabe K, Satoh T, Vizi ES. Halothane potentiates the effect of methamphetamine and nomifensine on extracellular dopamine levels in rat striatum: a microdialysis study. Br J Anaesth. 2001;86:837–845. - PubMed
-
- Austin CP, Ky B, Ma L, Morris JA, Shughrue PJ. Expression of Disrupted-In-Schizophrenia-1, a schizophrenia-associated gene, is prominent in the mouse hippocampus throughout brain development. Neuroscience. 2004;124:3–10. - PubMed
-
- Brandon NJ, Handford EJ, Schurov I, et al. Disrupted in Schizophrenia 1 and Nudel form a neurodevelopmentally regulated protein complex: implications for schizophrenia and other major neurological disorders. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2004;25:42–55. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

