Phosphorylation of Estrogen Receptor α at serine 118 directs recruitment of promoter complexes and gene-specific transcription
- PMID: 21505052
- PMCID: PMC3100622
- DOI: 10.1210/en.2010-1281
Phosphorylation of Estrogen Receptor α at serine 118 directs recruitment of promoter complexes and gene-specific transcription
Abstract
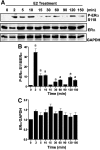
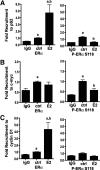
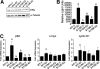
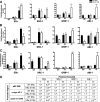
Phosphorylation of estrogen receptor α (ERα) is important for receptor function, although the role of specific ERα phosphorylation sites in ERα-mediated transcription remains to be fully evaluated. Transcriptional activation by ERα involves dynamic, coordinate interactions with coregulators at promoter enhancer elements to effect gene expression. To determine whether ERα phosphorylation affects recruitment of unique protein complexes at gene-specific promoters, changes in ERα Ser118 phosphorylation were assessed for effects on receptor and coregulator recruitment and transcription of ERα-regulated genes. Chromatin immunoprecipitation assays to measure promoter association found a 17β-estradiol (E2)-dependent recruitment of ERα at 150 min to ERα-regulated promoters, whereas ERα phosphorylated at Ser118 was dissociated from promoters after E2 treatment. Mutation of Ser118 to alanine (S118A) altered unliganded and ligand-induced association of ERα and p160 coregulators with ERα target promoters when compared with wild-type (WT)-ERα transfection. S118A and WT-ERα exhibited a similar level of recruitment to the estrogen response element-driven pS2 promoter and induced pS2 mRNA after E2 treatment. Although WT-ERα was recruited to c-myc and cyclin D1 promoters after E2 treatment and induced mRNA expression, S118A exhibited reduced interaction with c-myc and cyclin D1 promoters, and E2 did not induce c-myc and cyclin D1 mRNA. In addition, S118A resulted in increased recruitment of steroid receptor coactivator-1, glucocorticoid receptor interacting protein-1, and activated in breast cancer-1 to pS2, c-myc, and cyclin D1 irrespective of the presence of E2. Together, these data indicate that site specific phosphorylation of ERα directs gene-specific recruitment of ERα and transcriptional coregulators to ERα target gene promoters.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Protein kinase A exhibits selective modulation of estradiol-dependent transcription in breast cancer cells that is associated with decreased ligand binding, altered estrogen receptor alpha promoter interaction, and changes in receptor phosphorylation.Mol Endocrinol. 2007 Feb;21(2):439-56. doi: 10.1210/me.2006-0059. Epub 2006 Oct 26. Mol Endocrinol. 2007. PMID: 17068199
-
Estrogen receptor (ER) beta modulates ERalpha-mediated transcriptional activation by altering the recruitment of c-Fos and c-Jun to estrogen-responsive promoters.Mol Endocrinol. 2006 Mar;20(3):534-43. doi: 10.1210/me.2005-0140. Epub 2005 Nov 17. Mol Endocrinol. 2006. PMID: 16293641
-
Cyclin D1 antagonizes BRCA1 repression of estrogen receptor alpha activity.Cancer Res. 2005 Aug 1;65(15):6557-67. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-0486. Cancer Res. 2005. PMID: 16061635
-
Estrogen receptor alpha phosphorylation and its functional impact in human breast cancer.Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2015 Dec 15;418 Pt 3:264-72. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2015.01.016. Epub 2015 Jan 15. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2015. PMID: 25597633 Review.
-
Dynamic transcriptional events mediated by estrogen receptor alpha.Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2019 Jan 1;24(2):245-276. doi: 10.2741/4716. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2019. PMID: 30468654 Review.
Cited by
-
Pin1 modulates ERα levels in breast cancer through inhibition of phosphorylation-dependent ubiquitination and degradation.Oncogene. 2014 Mar 13;33(11):1438-47. doi: 10.1038/onc.2013.78. Epub 2013 Apr 1. Oncogene. 2014. PMID: 23542176 Free PMC article.
-
Benzothiophenone Derivatives Targeting Mutant Forms of Estrogen Receptor-α in Hormone-Resistant Breast Cancers.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Feb 15;19(2):579. doi: 10.3390/ijms19020579. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29462880 Free PMC article.
-
Distribution and posttranslational modification of synaptic ERα in the adult female rat hippocampus.Endocrinology. 2013 Feb;154(2):819-30. doi: 10.1210/en.2012-1870. Epub 2012 Nov 26. Endocrinology. 2013. PMID: 23183182 Free PMC article.
-
Maternal Dietary Exposure to Low-Dose Bisphenol A Affects Metabolic and Signaling Pathways in the Brain of Rat Fetuses.Nutrients. 2020 May 17;12(5):1448. doi: 10.3390/nu12051448. Nutrients. 2020. PMID: 32429515 Free PMC article.
-
Acetylation at lysine 183 of progesterone receptor by p300 accelerates DNA binding kinetics and transactivation of direct target genes.J Biol Chem. 2014 Jan 24;289(4):2180-94. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.517896. Epub 2013 Dec 3. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 24302725 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tsai MJ, O'Malley BW. 1994. Molecular mechanisms of action of steroid/thyroid receptor superfamily members. Annu Rev Biochem 63:451–486 - PubMed
-
- Björnström L, Sjöberg M. 2005. Mechanisms of estrogen receptor signaling: convergence of genomic and nongenomic actions on target genes. Mol Endocrinol 19:833–842 - PubMed
-
- Gronemeyer H. 1991. Transcription activation by estrogen and progesterone receptors. Annu Rev Genet 25:89–123 - PubMed
-
- Duan R, Porter W, Safe S. 1998. Estrogen-induced c-fos protooncogene expression in MCF-7 human breast cancer cells - role of estrogen receptor SP1 complex formation. Endocrinology 139:1981–1990 - PubMed
-
- Kelley KM, Rowan BG, Ratnam M. 2003. Modulation of the folate receptor α gene by the estrogen receptor: mechanism and implications in tumor targeting. Cancer Res 63:2820–2828 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

