Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 deficient mice are protected from angiotensin II-induced fibrosis
- PMID: 21501583
- PMCID: PMC3095665
- DOI: 10.1016/j.abb.2011.04.001
Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 deficient mice are protected from angiotensin II-induced fibrosis
Abstract
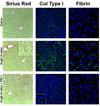
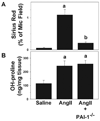
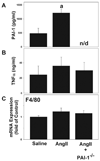
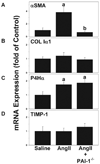
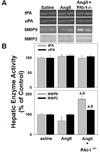
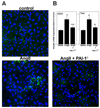
PAI-1 has been shown to be both profibrotic and antifibrotic in animal models of hepatic fibrosis. Although these models have similarities to human fibrotic liver disease, no rodent model completely recapitulates the clinical situation; indeed, transaminase values in most models of hepatic fibrosis are much higher than in chronic liver diseases in humans. Here, wild-type and PAI-1(-/-) mice were administered AngII (500 ng/kg/min) for 4 weeks. ECM accumulation was evaluated by Sirius red staining, hydroxyproline content, and fibrin and collagen immunostaining. Induction of pro-fibrotic genes was assessed by real-time RT-PCR. Despite the absence of any significant liver damage, AngII infusion increased the deposition of hepatic collagen and fibrin ECM, with a perisinusoidal pattern. PAI-1(-/-) mice were protected from these ECM changes, indicating a causal role of PAI-1 in this fibrosis model. Protection in the knockout strain correlated with a blunted increase in αSMA, and elevated activities of matrix metalloproteinases (MMP2, MMP9). These data suggest that PAI-1 plays a critical role in mediating fibrosis caused by AngII and lends weight-of-evidence to a pro-fibrotic role of this protein in liver. Furthermore, the current study proposes a new model of 'pure' hepatic fibrosis in mice with little inflammation or hepatocyte death.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Alcoholic liver disease and the potential role of plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 and fibrin metabolism.Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2012 Jan;237(1):1-9. doi: 10.1258/ebm.2011.011255. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2012. PMID: 22238286 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Critical role of plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 in cholestatic liver injury and fibrosis.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2006 Feb;316(2):592-600. doi: 10.1124/jpet.105.095042. Epub 2005 Oct 12. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2006. PMID: 16221737
-
PAI-1 deficiency reduces liver fibrosis after bile duct ligation in mice through activation of tPA.FEBS Lett. 2007 Jun 26;581(16):3098-104. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2007.05.049. Epub 2007 May 29. FEBS Lett. 2007. PMID: 17561000
-
Small leucine zipper protein negatively regulates liver fibrosis by suppressing the expression of plasminogen activator inhibitor-1.Exp Cell Res. 2024 Oct 1;442(2):114258. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2024.114258. Epub 2024 Sep 16. Exp Cell Res. 2024. PMID: 39293522
-
New role of plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 in alcohol-induced liver injury.J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2008 Mar;23 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):S54-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1746.2007.05285.x. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2008. PMID: 18336665 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Causal Effect of Plasminogen Activator Inhibitor Type 1 on Coronary Heart Disease.J Am Heart Assoc. 2017 May 26;6(6):e004918. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.116.004918. J Am Heart Assoc. 2017. PMID: 28550093 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The uPA/uPAR System Orchestrates the Inflammatory Response, Vascular Homeostasis, and Immune System in Fibrosis Progression.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jan 16;24(2):1796. doi: 10.3390/ijms24021796. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36675310 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Serpine1 Knockdown Enhances MMP Activity after Flexor Tendon Injury in Mice: Implications for Adhesions Therapy.Sci Rep. 2018 Apr 11;8(1):5810. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-24144-1. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29643421 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatic Stellate Cell-Specific Platelet-Derived Growth Factor Receptor-α Loss Reduces Fibrosis and Promotes Repair after Hepatocellular Injury.Am J Pathol. 2020 Oct;190(10):2080-2094. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2020.06.006. Epub 2020 Jun 29. Am J Pathol. 2020. PMID: 32615075 Free PMC article.
-
Alcoholic liver disease and the potential role of plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 and fibrin metabolism.Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2012 Jan;237(1):1-9. doi: 10.1258/ebm.2011.011255. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2012. PMID: 22238286 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Friedman SL. J. Hepatol. 2003;38 Suppl 1:S38–S53. S38–S53. - PubMed
-
- Mezzano SA, Ruiz-Ortega M, Egido J. Hypertension. 2001;38:635–638. - PubMed
-
- Jonsson JR, Clouston AD, Ando Y, Kelemen LI, Horn MJ, Adamson MD, Purdie DM, Powell EE. Gastroenterology. 2001;121:148–155. - PubMed
-
- Bataller R, Gabele E, Schoonhoven R, Morris T, Lehnert M, Yang L, Brenner DA, Rippe RA. Am. J. Physiol Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2003;285:G642–G651. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

