Antifibrotic effects of magnesium lithospermate B on hepatic stellate cells and thioacetamide-induced cirrhotic rats
- PMID: 21499011
- PMCID: PMC3128912
- DOI: 10.3858/emm.2011.43.6.037
Antifibrotic effects of magnesium lithospermate B on hepatic stellate cells and thioacetamide-induced cirrhotic rats
Abstract
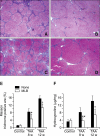
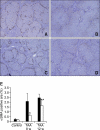
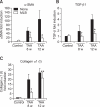
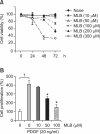
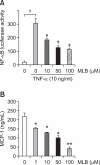
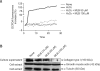
Magnesium lithospermate B (MLB) is one of the major active components of Salvia miltiorrhizae. The anti-oxidative effects of Salvia miltiorrhizae have been previously reported. The aim of this study was to investigate the effect of purified MLB on hepatic fibrosis in rats and on the fibrogenic responses in hepatic stellate cells (HSCs). Hepatic fibrosis was induced in rats by intraperitoneal thioacetamide (TAA) injections over a period of 8 or 12 weeks. MLB was orally administered daily by gavage tube. Serum AST and ALT levels in TAA+ MLB group were significantly lower than those in TAA only group at week 8. Hepatic fibrosis was significantly attenuated in TAA+MLB group than in TAA only group at week 8 or 12. Activation of HSCs was also decreased in TAA+MLB group as compared to TAA only group. Hepatic mRNA expression of α-smooth muscle actin (α-SMA), TGF-β1, and collagen α1(I) was significantly decreased in TAA+MLB group as compared to TAA only group. Incubation with HSCs and MLB (>or=100 μM) for up to 48 h showed no cytotoxicity. MLB suppressed PDGF-induced HSC proliferation. MLB inhibited NF-ΚB transcriptional activation and monocyte chemotactic protein 1 (MCP-1) production in HSCs. MLB strongly suppressed H(2)O(2)-induced reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation in HSCs, and MLB inhibited type I collagen secretion in HSCs. We concluded that MLB has potent antifibrotic effect in TAA-treated cirrhotic rats, and inhibits fibrogenic responses in HSCs. These data suggest that MLB has potential as a novel therapy for hepatic fibrosis.
Figures
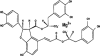
Similar articles
-
Ameliorative effect of grape seed proanthocyanidin extract on thioacetamide-induced mouse hepatic fibrosis.Toxicol Lett. 2012 Sep 18;213(3):353-60. doi: 10.1016/j.toxlet.2012.07.019. Epub 2012 Jul 31. Toxicol Lett. 2012. PMID: 22863721
-
Fibromodulin, an oxidative stress-sensitive proteoglycan, regulates the fibrogenic response to liver injury in mice.Gastroenterology. 2012 Mar;142(3):612-621.e5. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2011.11.029. Epub 2011 Dec 1. Gastroenterology. 2012. PMID: 22138190 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of armepavine against hepatic fibrosis induced by thioacetamide in rats.Phytother Res. 2012 Mar;26(3):344-53. doi: 10.1002/ptr.3539. Epub 2011 Jun 30. Phytother Res. 2012. PMID: 21717514
-
Molecular mechanisms in thioacetamide-induced acute and chronic liver injury models.Environ Toxicol Pharmacol. 2023 Apr;99:104093. doi: 10.1016/j.etap.2023.104093. Epub 2023 Mar 2. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36870405 Review.
-
Oxidative and nitrosative stress and fibrogenic response.Clin Liver Dis. 2008 Nov;12(4):769-90, viii. doi: 10.1016/j.cld.2008.07.005. Clin Liver Dis. 2008. PMID: 18984466 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Real time in vivo investigation of superoxide dynamics in zebrafish liver using a single-fiber fluorescent probe.Biomed Opt Express. 2013 Aug 21;4(9):1702-9. doi: 10.1364/BOE.4.001702. eCollection 2013. Biomed Opt Express. 2013. PMID: 24049691 Free PMC article.
-
Severity of Hepatocyte Damage and Prognosis in Cirrhotic Patients Correlate with Hepatocyte Magnesium Depletion.Nutrients. 2023 Jun 3;15(11):2626. doi: 10.3390/nu15112626. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 37299589 Free PMC article.
-
Alteration of micronutrient status in compensated and decompensated liver cirrhosis.Indian J Clin Biochem. 2014 Apr;29(2):232-7. doi: 10.1007/s12291-013-0349-5. Epub 2013 Jun 14. Indian J Clin Biochem. 2014. PMID: 24757308 Free PMC article.
-
Magnesium and Its Role in Primary Open Angle Glaucoma; A Novel Therapeutic?Front Ophthalmol (Lausanne). 2022 Jun 9;2:897128. doi: 10.3389/fopht.2022.897128. eCollection 2022. Front Ophthalmol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 38983515 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Protective Effect of Magnesium Lithospermate B on Hepatic Ischemia/Reperfusion via Inhibiting the Jak2/Stat3 Signaling Pathway.Front Pharmacol. 2019 May 31;10:620. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2019.00620. eCollection 2019. Front Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 31231218 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Czaja MJ. Cell signaling in oxidative stress-induced liver injury. Semin Liver Dis. 2007;27:378–389. - PubMed
-
- de Kok JB, Roelofs RW, Giesendorf BA, Pennings JL, Waas ET, Feuth T, Swinkels DW, Span PN. Normalization of gene expression measurements in tumor tissues: comparison of 13 endogenous control genes. Lab Invest. 2005;85:154–159. - PubMed
-
- Eng FJ, Friedman SL. Transcriptional regulation in hepatic stellate cells. Semin Liver Dis. 2001;21:385–395. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
