Analgesic tone conferred by constitutively active mu opioid receptors in mice lacking β-arrestin 2
- PMID: 21486473
- PMCID: PMC3090352
- DOI: 10.1186/1744-8069-7-24
Analgesic tone conferred by constitutively active mu opioid receptors in mice lacking β-arrestin 2
Abstract
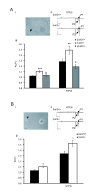
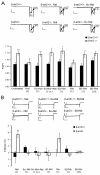
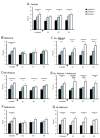
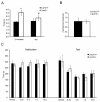
Hedonic reward, dependence and addiction are unwanted effects of opioid analgesics, linked to the phasic cycle of μ opioid receptor activation, tolerance and withdrawal. In vitro studies of recombinant G protein coupled receptors (GPCRs) over expressed in cell lines reveal an alternative tonic signaling mechanism that is independent of agonist. Such studies demonstrate that constitutive GPCR signaling can be inhibited by inverse agonists but not by neutral antagonists. However, ligand-independent activity has been difficult to examine in vivo, at the systems level, due to relatively low levels of constitutive activity of most GPCRs including μ receptors, often necessitating mutagenesis or pharmacological manipulation to enhance basal signaling. We previously demonstrated that the absence of β-arrestin 2 (β-arr2) augments the constitutive coupling of μ receptors to voltage-activated Ca²+ channels in primary afferent dorsal root ganglion neurons from β-arr2⁻/⁻ mice. We used this in vitro approach to characterize neutral competitive antagonists and inverse agonists of the constitutively active wild type μ receptors in neurons. We administered these agents to β-arr2⁻/⁻ mice to explore the role of constitutive μ receptor activity in nociception and hedonic tone. This study demonstrates that the induction of constitutive μ receptor activity in vivo in β-arr2⁻/⁻ mice prolongs tail withdrawal from noxious heat, a phenomenon that was reversed by inverse agonists, but not by antagonists that lack negative efficacy. By contrast, the aversive effects of inverse agonists were similar in β-arr2⁻/⁻ and β-arr2+/+ mice, suggesting that hedonic tone was unaffected.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Ligand-Free Signaling of G-Protein-Coupled Receptors: Relevance to μ Opioid Receptors in Analgesia and Addiction.Molecules. 2022 Sep 8;27(18):5826. doi: 10.3390/molecules27185826. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36144565 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evidence that behavioral phenotypes of morphine in β-arr2-/- mice are due to the unmasking of JNK signaling.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2012 Jul;37(8):1953-62. doi: 10.1038/npp.2012.42. Epub 2012 Apr 11. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2012. PMID: 22491351 Free PMC article.
-
Beta-arrestin2 and c-Src regulate the constitutive activity and recycling of mu opioid receptors in dorsal root ganglion neurons.J Neurosci. 2007 May 9;27(19):5092-104. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1157-07.2007. J Neurosci. 2007. PMID: 17494695 Free PMC article.
-
Differential mechanisms of morphine antinociceptive tolerance revealed in (beta)arrestin-2 knock-out mice.J Neurosci. 2002 Dec 1;22(23):10494-500. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.22-23-10494.2002. J Neurosci. 2002. PMID: 12451149 Free PMC article.
-
Interaction and regulatory functions of μ- and δ-opioid receptors in nociceptive afferent neurons.Neurosci Bull. 2012 Apr;28(2):121-30. doi: 10.1007/s12264-012-1206-x. Neurosci Bull. 2012. PMID: 22466123 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Ligand-Free Signaling of G-Protein-Coupled Receptors: Relevance to μ Opioid Receptors in Analgesia and Addiction.Molecules. 2022 Sep 8;27(18):5826. doi: 10.3390/molecules27185826. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36144565 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evidence that behavioral phenotypes of morphine in β-arr2-/- mice are due to the unmasking of JNK signaling.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2012 Jul;37(8):1953-62. doi: 10.1038/npp.2012.42. Epub 2012 Apr 11. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2012. PMID: 22491351 Free PMC article.
-
Endogenous analgesia, dependence, and latent pain sensitization.Curr Top Behav Neurosci. 2014;20:283-325. doi: 10.1007/7854_2014_351. Curr Top Behav Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 25227929 Free PMC article.
-
Postsurgical Latent Pain Sensitization Is Driven by Descending Serotonergic Facilitation and Masked by µ-Opioid Receptor Constitutive Activity in the Rostral Ventromedial Medulla.J Neurosci. 2022 Jul 27;42(30):5870-5881. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2038-21.2022. Epub 2022 Jun 14. J Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35701159 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of μ-opioid receptors: desensitization, phosphorylation, internalization, and tolerance.Pharmacol Rev. 2013 Jan 15;65(1):223-54. doi: 10.1124/pr.112.005942. Print 2013 Jan. Pharmacol Rev. 2013. PMID: 23321159 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Sadee W, Wang Z. Agonist induced constitutive receptor activation as a novel regulatory mechanism. Mu receptor regulation. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1995;373:85–90. - PubMed
-
- Bilsky EJ, Giuvelis D, Osborn MD, Dersch CM, Xu H, Rothman RB. In vitro and in vivo assessment of mu opioid receptor constitutive activity. Methods Enzymol. 2010;484:413–43. full_text. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

