A framework for variation discovery and genotyping using next-generation DNA sequencing data
- PMID: 21478889
- PMCID: PMC3083463
- DOI: 10.1038/ng.806
A framework for variation discovery and genotyping using next-generation DNA sequencing data
Abstract
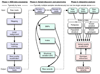
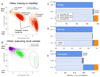
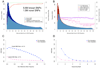
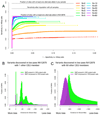
Recent advances in sequencing technology make it possible to comprehensively catalog genetic variation in population samples, creating a foundation for understanding human disease, ancestry and evolution. The amounts of raw data produced are prodigious, and many computational steps are required to translate this output into high-quality variant calls. We present a unified analytic framework to discover and genotype variation among multiple samples simultaneously that achieves sensitive and specific results across five sequencing technologies and three distinct, canonical experimental designs. Our process includes (i) initial read mapping; (ii) local realignment around indels; (iii) base quality score recalibration; (iv) SNP discovery and genotyping to find all potential variants; and (v) machine learning to separate true segregating variation from machine artifacts common to next-generation sequencing technologies. We here discuss the application of these tools, instantiated in the Genome Analysis Toolkit, to deep whole-genome, whole-exome capture and multi-sample low-pass (∼4×) 1000 Genomes Project datasets.
Figures


Similar articles
-
An efficient and scalable analysis framework for variant extraction and refinement from population-scale DNA sequence data.Genome Res. 2015 Jun;25(6):918-25. doi: 10.1101/gr.176552.114. Epub 2015 Apr 16. Genome Res. 2015. PMID: 25883319 Free PMC article.
-
A probabilistic method for the detection and genotyping of small indels from population-scale sequence data.Bioinformatics. 2011 Aug 1;27(15):2047-53. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btr344. Epub 2011 Jun 7. Bioinformatics. 2011. PMID: 21653520 Free PMC article.
-
A map of human genome variation from population-scale sequencing.Nature. 2010 Oct 28;467(7319):1061-73. doi: 10.1038/nature09534. Nature. 2010. PMID: 20981092 Free PMC article.
-
Model-based quality assessment and base-calling for second-generation sequencing data.Biometrics. 2010 Sep;66(3):665-74. doi: 10.1111/j.1541-0420.2009.01353.x. Biometrics. 2010. PMID: 19912177 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genome structural variation discovery and genotyping.Nat Rev Genet. 2011 May;12(5):363-76. doi: 10.1038/nrg2958. Epub 2011 Mar 1. Nat Rev Genet. 2011. PMID: 21358748 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Drosophila Toxicogenomics: genetic variation and sexual dimorphism in susceptibility to 4-Methylimidazole.Hum Genomics. 2024 Nov 4;18(1):119. doi: 10.1186/s40246-024-00689-3. Hum Genomics. 2024. PMID: 39497218 Free PMC article.
-
Whole-exome sequencing identifies novel LEPR mutations in individuals with severe early onset obesity.Obesity (Silver Spring). 2014 Feb;22(2):576-84. doi: 10.1002/oby.20492. Epub 2013 Oct 15. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2014. PMID: 23616257 Free PMC article.
-
Rapid genotype imputation from sequence with reference panels.Nat Genet. 2021 Jul;53(7):1104-1111. doi: 10.1038/s41588-021-00877-0. Epub 2021 Jun 3. Nat Genet. 2021. PMID: 34083788 Free PMC article.
-
De novo assembly of a haplotype-resolved human genome.Nat Biotechnol. 2015 Jun;33(6):617-22. doi: 10.1038/nbt.3200. Epub 2015 May 25. Nat Biotechnol. 2015. PMID: 26006006
-
Whole genome sequencing reveals high differentiation, low levels of genetic diversity and short runs of homozygosity among Swedish wels catfish.Heredity (Edinb). 2021 Jul;127(1):79-91. doi: 10.1038/s41437-021-00438-5. Epub 2021 May 7. Heredity (Edinb). 2021. PMID: 33963302 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lee W, et al. The mutation spectrum revealed by paired genome sequences from a lung cancer patient. Nature. 2010;465:473–477. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

