Complement dependency of cardiomyocyte release of mediators during sepsis
- PMID: 21478262
- PMCID: PMC3114524
- DOI: 10.1096/fj.11-183236
Complement dependency of cardiomyocyte release of mediators during sepsis
Abstract
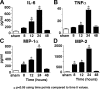
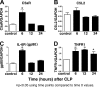
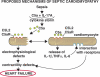
We have recently shown that antibody-induced blockade of C5a, C5a receptors, or IL-17A greatly reduced the harmful outcomes of sepsis. In the current study, normal cardiomyocytes from young (300 g) male Sprague-Dawley rats responded in vitro to C5a (ED(50)=55 nM) with release of IL-6 and TNFα, peaking between 2 to 8 h. Neutralizing antibodies to mouse C5a or IL-17A (ED(50)=40 μg for each, based on improved survival) reduced spontaneous in vitro release of cardiosuppressive cytokines and chemokines in cardiomyocytes obtained from mice with polymicrobial sepsis. A non-neutralizing C5a antibody had no such effects. Cardiomyocytes from septic mice (C57Bl/6) showed increased mRNA for TNFR1, IL-6 (gp80), and C5aR at 6 h after sepsis. Cardiomyocytes from septic C5aR(-/-) or C5L2(-/-) mice did not show spontaneous in vitro release of cytokines and chemokines. These data suggest that cardiomyocytes from septic mice release suppressive cytokines in a C5a-, C5aR-, and IL-17A-dependent manner, followed by mediator reactivity with receptors on cardiomyocytes, resulting in defective contractility and relaxation. These data may be relevant to a strategy for the treatment of heart dysfunction developing during sepsis.
Figures
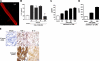
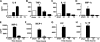
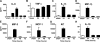
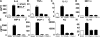

Similar articles
-
Functional roles for C5a receptors in sepsis.Nat Med. 2008 May;14(5):551-7. doi: 10.1038/nm1753. Epub 2008 May 4. Nat Med. 2008. PMID: 18454156 Free PMC article.
-
An essential role for complement C5a in the pathogenesis of septic cardiac dysfunction.J Exp Med. 2006 Jan 23;203(1):53-61. doi: 10.1084/jem.20051207. Epub 2005 Dec 27. J Exp Med. 2006. PMID: 16380509 Free PMC article.
-
The interaction between C5a and both C5aR and C5L2 receptors is required for production of G-CSF during acute inflammation.Eur J Immunol. 2013 Jul;43(7):1907-13. doi: 10.1002/eji.201243075. Epub 2013 May 13. Eur J Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23575697 Free PMC article.
-
C5L2: a controversial receptor of complement anaphylatoxin, C5a.FASEB J. 2013 Mar;27(3):855-64. doi: 10.1096/fj.12-220509. Epub 2012 Dec 13. FASEB J. 2013. PMID: 23239822 Review.
-
The harmful role of c5a on innate immunity in sepsis.J Innate Immun. 2010;2(5):439-45. doi: 10.1159/000317194. Epub 2010 Jun 26. J Innate Immun. 2010. PMID: 20588003 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
New insights for C5a and C5a receptors in sepsis.Front Immunol. 2012 Dec 10;3:368. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2012.00368. eCollection 2012. Front Immunol. 2012. PMID: 23233853 Free PMC article.
-
Complement and sepsis-induced heart dysfunction.Mol Immunol. 2017 Apr;84:57-64. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2016.11.012. Epub 2016 Dec 5. Mol Immunol. 2017. PMID: 27931779 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Controversial C5a Receptor C5aR2: Its Role in Health and Disease.J Immunol Res. 2017;2017:8193932. doi: 10.1155/2017/8193932. Epub 2017 Jun 15. J Immunol Res. 2017. PMID: 28706957 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inhibition of complement C5 protects against organ failure and reduces mortality in a baboon model of Escherichia coli sepsis.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017 Aug 1;114(31):E6390-E6399. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1706818114. Epub 2017 Jul 18. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017. PMID: 28720697 Free PMC article.
-
Rho kinase regulates induction of T-cell immune dysfunction in abdominal sepsis.Infect Immun. 2013 Jul;81(7):2499-506. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00126-13. Epub 2013 Apr 29. Infect Immun. 2013. PMID: 23630965 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rabuel C., Mebazaa A. (2006) Septic shock: a heart story since the 1960s. Intensive Care Med. 32, 799–807 - PubMed
-
- Parrillo J. E., Burch C., Shelhamer J. H., Parker M. M., Natanson C., Schuette W. (1985) A circulating myocardial depressant substance in humans with septic shock. Septic shock patients with a reduced ejection fraction have a circulating factor that depresses in vitro myocardial cell performance. J. Clin. Invest. 76, 1539–1553 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

