A therapeutic role for mesenchymal stem cells in acute lung injury independent of hypoxia-induced mitogenic factor
- PMID: 21477220
- PMCID: PMC3823300
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1582-4934.2011.01326.x
A therapeutic role for mesenchymal stem cells in acute lung injury independent of hypoxia-induced mitogenic factor
Abstract
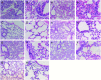
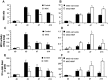
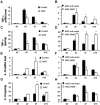
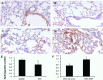
Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (BM-MSCs) have therapeutic potential in acute lung injury (ALI). Hypoxia-induced mitogenic factor (HIMF) is a lung-specific growth factor that participates in a variety of lung diseases. In this study, we evaluated the therapeutic role of BM-MSC transplantation in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)- induced ALI and assessed the importance of HIMF in MSC transplantation. MSCs were isolated and identified, and untransduced MSCs, MSCs transduced with null vector or MSCs transduced with a vector encoding HIMF were transplanted into mice with LPS-induced ALI. Histopathological changes, cytokine expression and indices of lung inflammation and lung injury were assessed in the various experimental groups. Lentiviral transduction did not influence the biological features of MSCs. In addition, transplantation of BM-MSCs alone had significant therapeutic effects on LPS-induced ALI, although BM-MSCs expressing HIMF failed to improve the histopathological changes observed with lung injury. Unexpectedly, tumour necrosis factor α levels in lung tissues, lung oedema and leucocyte infiltration into lungs were even higher after the transplantation of MSCs expressing HIMF, followed by a significant increase in lung hydroxyproline content and α-smooth muscle actin expression on day 14, as compared to treatment with untransduced MSCs. BM-MSC transplantation improved LPS-induced lung injury independent of HIMF.
© 2011 The Authors Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine © 2011 Foundation for Cellular and Molecular Medicine/Blackwell Publishing Ltd.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Chicken bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells improve lung and distal organ injury.Sci Rep. 2021 Sep 10;11(1):17937. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-97383-4. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34508136 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic effect of intravenous bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cell transplantation on early-stage LPS-induced acute lung injury in mice.Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2012 Mar;32(3):283-90. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2012. PMID: 22445968
-
Genetic Modification of Mesenchymal Stem Cells Overexpressing Angiotensin II Type 2 Receptor Increases Cell Migration to Injured Lung in LPS-Induced Acute Lung Injury Mice.Stem Cells Transl Med. 2018 Oct;7(10):721-730. doi: 10.1002/sctm.17-0279. Epub 2018 Aug 21. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2018. PMID: 30133167 Free PMC article.
-
Mesenchymal stem cells in acute lung injury: are they ready for translational medicine?J Cell Mol Med. 2013 Aug;17(8):927-35. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.12063. Epub 2013 Jul 3. J Cell Mol Med. 2013. PMID: 23834470 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Paracrine factors from mesenchymal stem cells: a proposed therapeutic tool for acute lung injury and acute respiratory distress syndrome.Int Wound J. 2014 Apr;11(2):114-21. doi: 10.1111/iwj.12202. Epub 2013 Dec 26. Int Wound J. 2014. PMID: 24373614 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Inhalational delivery of induced pluripotent stem cell secretome improves postpneumonectomy lung structure and function.J Appl Physiol (1985). 2020 Nov 1;129(5):1051-1061. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00205.2020. Epub 2020 Sep 10. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2020. PMID: 32909918 Free PMC article.
-
Adrenaline stimulates the proliferation and migration of mesenchymal stem cells towards the LPS-induced lung injury.J Cell Mol Med. 2014 Aug;18(8):1612-22. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.12283. Epub 2014 Mar 31. J Cell Mol Med. 2014. PMID: 24684532 Free PMC article.
-
Interaction between mesenchymal stem cells and endothelial cells restores endothelial permeability via paracrine hepatocyte growth factor in vitro.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2015 Mar 24;6(1):44. doi: 10.1186/s13287-015-0025-1. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2015. PMID: 25888925 Free PMC article.
-
Autologous serum improves bone formation in a primary stable silica-embedded nanohydroxyapatite bone substitute in combination with mesenchymal stem cells and rhBMP-2 in the sheep model.Int J Nanomedicine. 2014 Nov 19;9:5317-39. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S66867. eCollection 2014. Int J Nanomedicine. 2014. PMID: 25429218 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic Treatment with Abdominal Adipose Mesenchymal Cells Does Not Prevent Elastase-Induced Emphysema in Rats.Turk Thorac J. 2020 Jan;21(1):14-20. doi: 10.5152/TurkThoracJ.2019.180136. Epub 2020 Jan 1. Turk Thorac J. 2020. PMID: 32163359 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Brigham KL, Meyrick B. Endotoxin and lung injury. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1986;133:913–27. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

