P-selectin mediates the microvascular dysfunction associated with persistent cytomegalovirus infection in normocholesterolemic and hypercholesterolemic mice
- PMID: 21457388
- PMCID: PMC3148337
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1549-8719.2011.00106.x
P-selectin mediates the microvascular dysfunction associated with persistent cytomegalovirus infection in normocholesterolemic and hypercholesterolemic mice
Abstract
Objective: Cytomegalovirus has been implicated in cardiovascular disease, possibly through the induction of inflammatory processes. P-selectin and L-selectin are adhesion molecules that mediate early microvascular responses to inflammatory stimuli. This study examined the role of these selectins in the microvascular dysfunction that occurs during persistent CMV infection.
Methods: C57Bl/6, P- or L-selectin-deficient mice were mock-inoculated or infected with murine CMV, and five weeks later placed on normal diet or high cholesterol diet for six weeks. P-selectin expression was measured or intravital microscopy was performed to determine arteriolar vasodilation and venular blood cell recruitment.
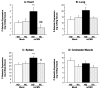
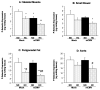
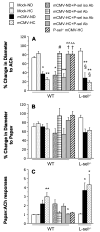
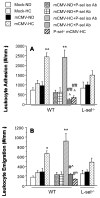
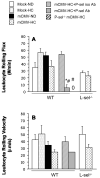
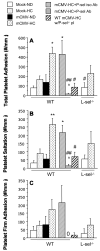
Results: P-selectin expression was significantly increased in the heart, lung, and spleen of mCMV-ND, but not mCMV-HC C57Bl/6. mCMV-ND and mCMV-HC exhibited impaired arteriolar function, which was reversed by treatment with an anti-P-selectin antibody, but not L-selectin deficiency. mCMV-HC also showed elevated leukocyte and platelet recruitment. P-selectin inhibition abrogated, whereas L-selectin deficiency partially reduced these responses.
Conclusions: We provide the first evidence for P-selectin upregulation by persistent mCMV infection and implicate this adhesion molecule in the associated arteriolar dysfunction. P-selectin, and to a lesser extent L-selectin, mediates the leukocyte and platelet recruitment induced by CMV infection combined with hypercholesterolemia.
© 2011 John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures
Similar articles
-
NAD(P)H oxidase and eNOS play differential roles in cytomegalovirus infection-induced microvascular dysfunction.Free Radic Biol Med. 2011 Dec 15;51(12):2300-8. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2011.09.039. Epub 2011 Oct 6. Free Radic Biol Med. 2011. PMID: 22033010 Free PMC article.
-
Platelets, acting in part via P-selectin, mediate cytomegalovirus-induced microvascular dysfunction.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2014 Dec 15;307(12):H1745-53. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00201.2014. Epub 2014 Oct 17. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2014. PMID: 25326535 Free PMC article.
-
Cytomegalovirus infection leads to microvascular dysfunction and exacerbates hypercholesterolemia-induced responses.Am J Pathol. 2010 Oct;177(4):2134-44. doi: 10.2353/ajpath.2010.100307. Epub 2010 Aug 27. Am J Pathol. 2010. PMID: 20802174 Free PMC article.
-
Insights into selectin function from knockout mice.Thromb Haemost. 1997 Jul;78(1):60-4. Thromb Haemost. 1997. PMID: 9198128 Review.
-
New discoveries with mice mutant in endothelial and platelet selectins.Thromb Haemost. 1999 Aug;82(2):850-7. Thromb Haemost. 1999. PMID: 10605793 Review.
Cited by
-
Increased risk of cardiovascular disease in premenopausal female ragpickers of Eastern India: involvement of inflammation, oxidative stress, and platelet hyperactivity.Mol Cell Biochem. 2016 Aug;419(1-2):193-203. doi: 10.1007/s11010-016-2773-3. Epub 2016 Jul 15. Mol Cell Biochem. 2016. PMID: 27421852
-
NAD(P)H oxidase and eNOS play differential roles in cytomegalovirus infection-induced microvascular dysfunction.Free Radic Biol Med. 2011 Dec 15;51(12):2300-8. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2011.09.039. Epub 2011 Oct 6. Free Radic Biol Med. 2011. PMID: 22033010 Free PMC article.
-
Current Understanding of Cytomegalovirus Reactivation in Critical Illness.J Infect Dis. 2020 Mar 5;221(Suppl 1):S94-S102. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiz638. J Infect Dis. 2020. PMID: 32134490 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Platelets, acting in part via P-selectin, mediate cytomegalovirus-induced microvascular dysfunction.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2014 Dec 15;307(12):H1745-53. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00201.2014. Epub 2014 Oct 17. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2014. PMID: 25326535 Free PMC article.
-
Microvascular dysfunction in pediatric patients with SARS-COV-2 pneumonia: report of three severe cases.Microvasc Res. 2022 May;141:104312. doi: 10.1016/j.mvr.2022.104312. Epub 2022 Jan 10. Microvasc Res. 2022. PMID: 35026289 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Blum A, Giladi M, Weinberg M, Kaplan G, Pasternack H, Laniado S, Miller H. High anti-cytomegalovirus (CMV) IgG antibody titer is associated with coronary artery disease and may predict post-coronary balloon angioplasty restenosis. Am J Cardiol. 1998;81:866–868. - PubMed
-
- Burger PC, Wagner DD. Platelet P-selectin facilitates atherosclerotic lesion development. Blood. 2003;101:2661–2666. - PubMed
-
- Burns LJ, Pooley JC, Walsh DJ, Vercellotti GM, Weber ML, Kovacs A. Intercellular adhesion molecule-1 expression in endothelial cells is activated by cytomegalovirus immediate early proteins. Transplantation. 1999;67:137–144. see comment. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

