The spatial and temporal organization of ubiquitin networks
- PMID: 21448225
- PMCID: PMC3654194
- DOI: 10.1038/nrm3099
The spatial and temporal organization of ubiquitin networks
Abstract
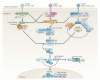
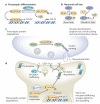
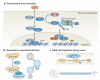
In the past decade, the diversity of signals generated by the ubiquitin system has emerged as a dominant regulator of biological processes and propagation of information in the eukaryotic cell. A wealth of information has been gained about the crucial role of spatial and temporal regulation of ubiquitin species of different lengths and linkages in the nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) pathway, endocytic trafficking, protein degradation and DNA repair. This spatiotemporal regulation is achieved through sophisticated mechanisms of compartmentalization and sequential series of ubiquitylation events and signal decoding, which control diverse biological processes not only in the cell but also during the development of tissues and entire organisms.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The role of ubiquitin in NF-kappaB regulatory pathways.Annu Rev Biochem. 2009;78:769-96. doi: 10.1146/annurev.biochem.78.070907.102750. Annu Rev Biochem. 2009. PMID: 19489733 Review.
-
Ubiquitin signalling in the NF-kappaB pathway.Nat Cell Biol. 2005 Aug;7(8):758-65. doi: 10.1038/ncb0805-758. Nat Cell Biol. 2005. PMID: 16056267 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Expanding role of ubiquitination in NF-κB signaling.Cell Res. 2011 Jan;21(1):6-21. doi: 10.1038/cr.2010.170. Epub 2010 Dec 7. Cell Res. 2011. PMID: 21135871 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Linear ubiquitination-mediated NF-κB regulation and its related disorders.J Biochem. 2013 Oct;154(4):313-23. doi: 10.1093/jb/mvt079. Epub 2013 Aug 21. J Biochem. 2013. PMID: 23969028 Review.
-
TRAF Family Member-associated NF-κB Activator (TANK) Inhibits Genotoxic Nuclear Factor κB Activation by Facilitating Deubiquitinase USP10-dependent Deubiquitination of TRAF6 Ligase.J Biol Chem. 2015 May 22;290(21):13372-85. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.643767. Epub 2015 Apr 10. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 25861989 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Neddylation and deneddylation in cardiac biology.Am J Cardiovasc Dis. 2014 Dec 29;4(4):140-58. eCollection 2014. Am J Cardiovasc Dis. 2014. PMID: 25628956 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Novel TDP2-ubiquitin interactions and their importance for the repair of topoisomerase II-mediated DNA damage.Nucleic Acids Res. 2016 Dec 1;44(21):10201-10215. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkw719. Epub 2016 Aug 19. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016. PMID: 27543075 Free PMC article.
-
A20 suppresses vascular inflammation by recruiting proinflammatory signaling molecules to intracellular aggresomes.FASEB J. 2015 May;29(5):1869-78. doi: 10.1096/fj.14-258533. Epub 2015 Feb 9. FASEB J. 2015. PMID: 25667218 Free PMC article.
-
The E3 ligase PIRH2 polyubiquitylates CHK2 and regulates its turnover.Cell Death Differ. 2013 Jun;20(6):812-22. doi: 10.1038/cdd.2013.7. Epub 2013 Mar 1. Cell Death Differ. 2013. PMID: 23449389 Free PMC article.
-
Nonenzymatic polymerization of ubiquitin: single-step synthesis and isolation of discrete ubiquitin oligomers.Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2012 Dec 21;51(52):13085-8. doi: 10.1002/anie.201207171. Epub 2012 Nov 19. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2012. PMID: 23161800 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Weissman AM. Themes and variations on ubiquitylation. Nature Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2001;2:169–178. - PubMed
-
- Hershko A, Ciechanover A. The ubiquitin system. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1998;67:425–479. - PubMed
-
- Varshavsky A. Regulated protein degradation. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2005;30:283–286. - PubMed
-
- Deshaies RJ, Joazeiro CA. RING domain E3 ubiquitin ligases. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2009;78:399–434. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

