Heteromerization of the μ- and δ-opioid receptors produces ligand-biased antagonism and alters μ-receptor trafficking
- PMID: 21422164
- PMCID: PMC3097170
- DOI: 10.1124/jpet.111.179093
Heteromerization of the μ- and δ-opioid receptors produces ligand-biased antagonism and alters μ-receptor trafficking
Abstract
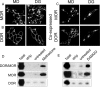
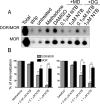
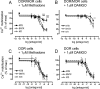
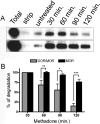
Heteromerization of opioid receptors has been shown to alter opioid receptor pharmacology. However, how receptor heteromerization affects the processes of endocytosis and postendocytic sorting has not been closely examined. This question is of particular relevance for heteromers of the μ-opioid receptor (MOR) and δ-opioid receptor (DOR), because the MOR is recycled primarily after endocytosis and the DOR is degraded in the lysosome. Here, we examined the endocytic and postendocytic fate of MORs, DORs, and DOR/MOR heteromers in human embryonic kidney 293 cells stably expressing each receptor alone or coexpressing both receptors. We found that the clinically relevant MOR agonist methadone promotes endocytosis of MOR but also the DOR/MOR heteromer. Furthermore, we show that DOR/MOR heteromers that are endocytosed in response to methadone are targeted for degradation, whereas MORs in the same cell are significantly more stable. It is noteworthy that we found that the DOR-selective antagonist naltriben mesylate could block both methadone- and [D-Ala2,NMe-Phe4,Gly-ol5]-enkephalin-induced endocytosis of the DOR/MOR heteromers but did not block signaling from this heteromer. Together, our results suggest that the MOR adopts novel trafficking properties in the context of the DOR/MOR heteromer. In addition, they suggest that the heteromer shows "biased antagonism," whereby DOR antagonist can inhibit trafficking but not signaling of the DOR/MOR heteromer.
Figures

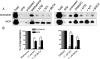
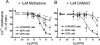
Similar articles
-
Anti-analgesic effect of the mu/delta opioid receptor heteromer revealed by ligand-biased antagonism.PLoS One. 2013;8(3):e58362. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0058362. Epub 2013 Mar 15. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23554887 Free PMC article.
-
Heteromerization of Endogenous Mu and Delta Opioid Receptors Induces Ligand-Selective Co-Targeting to Lysosomes.Molecules. 2020 Sep 30;25(19):4493. doi: 10.3390/molecules25194493. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 33007971 Free PMC article.
-
Two delta opioid receptor subtypes are functional in single ventral tegmental area neurons, and can interact with the mu opioid receptor.Neuropharmacology. 2017 Sep 1;123:420-432. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2017.06.019. Epub 2017 Jun 21. Neuropharmacology. 2017. PMID: 28645621 Free PMC article.
-
Opioid receptor heteromers in analgesia.Expert Rev Mol Med. 2012 Apr 10;14:e9. doi: 10.1017/erm.2012.5. Expert Rev Mol Med. 2012. PMID: 22490239 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Heteromers of μ-δ opioid receptors: new pharmacology and novel therapeutic possibilities.Br J Pharmacol. 2015 Jan;172(2):375-87. doi: 10.1111/bph.12663. Epub 2014 Jul 1. Br J Pharmacol. 2015. PMID: 24571499 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Targeting opioid receptor signaling in depression: do we need selective κ opioid receptor antagonists?Neuronal Signal. 2018 May 14;2(2):NS20170145. doi: 10.1042/NS20170145. eCollection 2018 Jun. Neuronal Signal. 2018. PMID: 32714584 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Arrestin recruitment and signaling by G protein-coupled receptor heteromers.Neuropharmacology. 2019 Jul 1;152:15-21. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2018.11.010. Epub 2018 Nov 9. Neuropharmacology. 2019. PMID: 30419245 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dynamic lateral organization of opioid receptors (kappa, muwt and muN40D ) in the plasma membrane at the nanoscale level.Traffic. 2018 May 28;19(9):690-709. doi: 10.1111/tra.12582. Online ahead of print. Traffic. 2018. PMID: 29808515 Free PMC article.
-
Disease-specific heteromerization of G-protein-coupled receptors that target drugs of abuse.Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. 2013;117:207-65. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-386931-9.00009-X. Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. 2013. PMID: 23663971 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tuned-Affinity Bivalent Ligands for the Characterization of Opioid Receptor Heteromers.ACS Med Chem Lett. 2012 Aug 9;3(8):640-644. doi: 10.1021/ml300083p. ACS Med Chem Lett. 2012. PMID: 23585918 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abdelhamid EE, Sultana M, Portoghese PS, Takemori AE. (1991) Selective blockage of δ-opioid receptors prevents the development of morphine tolerance and dependence in mice. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 258:299–303 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
