CD4+ T cells from elite controllers resist HIV-1 infection by selective upregulation of p21
- PMID: 21403397
- PMCID: PMC3069774
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI44539
CD4+ T cells from elite controllers resist HIV-1 infection by selective upregulation of p21
Abstract
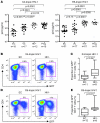
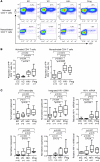
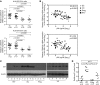
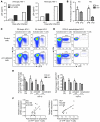
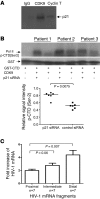
Elite controllers represent a unique group of HIV-1-infected persons with undetectable HIV-1 replication in the absence of antiretroviral therapy. However, the mechanisms contributing to effective viral immune defense in these patients remain unclear. Here, we show that compared with HIV-1 progressors and HIV-1-negative persons, CD4+ T cells from elite controllers are less susceptible to HIV-1 infection. This partial resistance to HIV-1 infection involved less effective reverse transcription and mRNA transcription from proviral DNA and was associated with strong and selective upregulation of the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p21 (also known as cip-1 and waf-1). Experimental blockade of p21 in CD4+ T cells from elite controllers resulted in a marked increase of viral reverse transcripts and mRNA production and led to higher enzymatic activities of cyclin-dependent kinase 9 (CDK9), which serves as a transcriptional coactivator of HIV-1 gene expression. This suggests that p21 acts as a barrier against HIV-1 infection in CD4+ T cells from elite controllers by inhibiting a cyclin-dependent kinase required for effective HIV-1 replication. These data demonstrate a mechanism of host resistance to HIV-1 in elite controllers and may open novel perspectives for clinical strategies to prevent or treat HIV-1 infection.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Increased expression of CDKN1A/p21 in HIV-1 controllers is correlated with upregulation of ZC3H12A/MCPIP1.Retrovirology. 2020 Jul 2;17(1):18. doi: 10.1186/s12977-020-00522-4. Retrovirology. 2020. PMID: 32615986 Free PMC article.
-
Infrequent recovery of HIV from but robust exogenous infection of activated CD4(+) T cells in HIV elite controllers.Clin Infect Dis. 2010 Jul 15;51(2):233-8. doi: 10.1086/653677. Clin Infect Dis. 2010. PMID: 20550452 Free PMC article.
-
Increased Levels of Macrophage Inflammatory Proteins Result in Resistance to R5-Tropic HIV-1 in a Subset of Elite Controllers.J Virol. 2015 May;89(10):5502-14. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00118-15. Epub 2015 Mar 4. J Virol. 2015. PMID: 25740989 Free PMC article.
-
Viral reservoirs in elite controllers of HIV-1 infection: Implications for HIV cure strategies.EBioMedicine. 2020 Dec;62:103118. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2020.103118. Epub 2020 Nov 10. EBioMedicine. 2020. PMID: 33181459 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Characteristics of plasmacytoid dendritic cell and CD4+ T cell in HIV elite controllers.Clin Dev Immunol. 2012;2012:869505. doi: 10.1155/2012/869505. Epub 2012 Nov 21. Clin Dev Immunol. 2012. PMID: 23243424 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
MiRNA-103 downmodulates CCR5 expression reducing human immunodeficiency virus type-1 entry and impacting latency establishment in CD4+ T cells.iScience. 2022 Sep 28;25(10):105234. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2022.105234. eCollection 2022 Oct 21. iScience. 2022. PMID: 36267915 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of protective killer inhibitory receptor/human leukocyte antigen genotypes on natural killer cell and T-cell function in HIV-1-infected controllers.AIDS. 2012 Sep 24;26(15):1869-78. doi: 10.1097/QAD.0b013e32835861b0. AIDS. 2012. PMID: 22874514 Free PMC article.
-
Thirty Years with HIV Infection-Nonprogression Is Still Puzzling: Lessons to Be Learned from Controllers and Long-Term Nonprogressors.AIDS Res Treat. 2012;2012:161584. doi: 10.1155/2012/161584. Epub 2012 May 27. AIDS Res Treat. 2012. PMID: 22693657 Free PMC article.
-
Both HLA-B*57 and plasma HIV RNA levels contribute to the HIV-specific CD8+ T cell response in HIV controllers.J Virol. 2014 Jan;88(1):176-87. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02098-13. Epub 2013 Oct 16. J Virol. 2014. PMID: 24131719 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of HIV early replication by the p53 and its downstream gene p21.Virol J. 2018 Mar 27;15(1):53. doi: 10.1186/s12985-018-0959-x. Virol J. 2018. PMID: 29587790 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Walker BD. Elite control of HIV Infection: implications for vaccines and treatment. Top HIV Med. 2007;15(4):134–136. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 DK082690/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI078799/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- DK082690/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- AI093203/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AI093203/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA135401/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- AI078799/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- CA135401/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AI093203-01A1/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI089339/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI060354/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI089339/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P50 CA119997/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

