PEST motif serine and tyrosine phosphorylation controls vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 stability and downregulation
- PMID: 21402774
- PMCID: PMC3133358
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.01006-10
PEST motif serine and tyrosine phosphorylation controls vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 stability and downregulation
Abstract
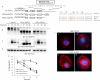
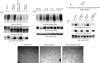
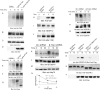
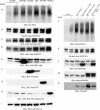
The internalization and degradation of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 (VEGFR-2), a potent angiogenic receptor tyrosine kinase, is a central mechanism for the regulation of the coordinated action of VEGF in angiogenesis. Here, we show that VEGFR-2 is ubiquitinated in response to VEGF, and Lys 48-linked polyubiquitination controls its degradation via the 26S proteosome. The degradation and ubiquitination of VEGFR-2 is controlled by its PEST domain, and the phosphorylation of Ser1188/Ser1191 is required for the ubiquitination of VEGFR-2. F-box-containing β-Trcp1 ubiquitin E3 ligase is recruited to S1188/S1191 VEGFR-2 and mediates the ubiquitination and degradation of VEGFR-2. The PEST domain also controls the activation of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) through phospho-Y1173. The activation of p38 stabilizes VEGFR-2, and its inactivation accelerates VEGFR-2 downregulation. The VEGFR-2-mediated activation of p38 is established through the protein kinase A (PKA)/MKK6 pathway. PKA is recruited to VEGFR-2 through AKAP1/AKAP149, and its phosphorylation requires Y1173 of VEGFR-2. The study has identified a unique mechanism in which VEGFR-2 stability and degradation is modulated. The PEST domain acts as a dual modulator of VEGFR-2; the phosphorylation of S1188/S1191 controls ubiquitination and degradation via β-Trcp1, where the phosphorylation of Y1173 through PKA/p38 MAPK controls the stability of VEGFR-2.
Figures





Similar articles
-
IQGAP1-dependent signaling pathway regulates endothelial cell proliferation and angiogenesis.PLoS One. 2008;3(12):e3848. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0003848. Epub 2008 Dec 3. PLoS One. 2008. PMID: 19050761 Free PMC article.
-
F-box only protein 31 (FBXO31) negatively regulates p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling by mediating lysine 48-linked ubiquitination and degradation of mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 6 (MKK6).J Biol Chem. 2014 Aug 1;289(31):21508-18. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.560342. Epub 2014 Jun 16. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 24936062 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of VEGF receptor-2 tyrosine phosphorylation sites involved in VEGF-mediated endothelial platelet-activating factor synthesis.Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 2010 Oct;88(10):968-76. doi: 10.1139/y10-064. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 2010. PMID: 20962896
-
VEGF-A-stimulated signalling in endothelial cells via a dual receptor tyrosine kinase system is dependent on co-ordinated trafficking and proteolysis.Biochem Soc Trans. 2009 Dec;37(Pt 6):1193-7. doi: 10.1042/BST0371193. Biochem Soc Trans. 2009. PMID: 19909245 Review.
-
Vascular endothelial growth factor receptors: molecular mechanisms of activation and therapeutic potentials.Exp Eye Res. 2006 Nov;83(5):1005-16. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2006.03.019. Epub 2006 May 19. Exp Eye Res. 2006. PMID: 16713597 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
An engineered channelrhodopsin optimized for axon terminal activation and circuit mapping.Commun Biol. 2021 Apr 12;4(1):461. doi: 10.1038/s42003-021-01977-7. Commun Biol. 2021. PMID: 33846537 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of PDCL3 as a novel chaperone protein involved in the generation of functional VEGF receptor 2.J Biol Chem. 2013 Aug 9;288(32):23171-81. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.473173. Epub 2013 Jun 21. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23792958 Free PMC article.
-
Spatial regulation of VEGF receptor endocytosis in angiogenesis.Nat Cell Biol. 2013 Mar;15(3):249-60. doi: 10.1038/ncb2679. Epub 2013 Jan 27. Nat Cell Biol. 2013. PMID: 23354168 Free PMC article.
-
Blebbishields, the emergency program for cancer stem cells: sphere formation and tumorigenesis after apoptosis.Cell Death Differ. 2013 Mar;20(3):382-95. doi: 10.1038/cdd.2012.140. Epub 2012 Nov 23. Cell Death Differ. 2013. PMID: 23175184 Free PMC article.
-
Bladder cancer: therapeutic challenges and role of 3D cell culture systems in the screening of novel cancer therapeutics.Cancer Cell Int. 2023 Oct 25;23(1):251. doi: 10.1186/s12935-023-03069-4. Cancer Cell Int. 2023. PMID: 37880676 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Adams R. H., Alitalo K. 2007. Molecular regulation of angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 8:464–478 - PubMed
-
- Bhattacharya R. 2005. Regulatory role of dynamin-2 in VEGFR-2/KDR-mediated endothelial signaling. FASEB J. 19:1692–1694 - PubMed
-
- Bruns A. F. 2010. Ligand-stimulated VEGFR2 signaling is regulated by co-ordinated trafficking and proteolysis. Traffic 11:161–174 - PubMed
-
- Cleaver O., Melton D. A. 2003. Endothelial signaling during development. Nat. Med. 9:661–668 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
